Customizing the AutoCAD environment is a great way to increase not only your productivity, but those in your office or on your extended team. By default, when you customize the AutoCAD environment, you are editing the files and settings that are local to your workstation. While you could customize each AutoCAD installation one at a time, that would be a very daunting task and make it difficult to rollout future changes to any shared custom files. Read on to understand the basics of sharing custom AutoCAD files with others in your office or those that might work in remote locations.
Where Are My Custom AutoCAD Files?
Before you can share your custom files with others, you will need to know where the files are currently located on your workstation. By default, custom files for use with the AutoCAD environment are stored in locations that are defined locally on a per install or user basis. Most custom files are stored in locations that are specific to the user that is currently logged into the operating system. While storing custom files locally on a per user basis makes sense as the default behavior, the default behavior makes it difficult to ensure everyone within a group is using the same custom files.
There are two primary locations in which the AutoCAD program stores custom files that can be edited by the user; the Roaming and Local folders. These two folders are located under the AppData folder of the user’s profile, which by default is hidden.
- Roaming Folder – Files in this folder are commonly machine independent and allowed to roam with the user’s profile based on how the user’s account has been configured. The default location of the Roaming folder is C:Users<user name>AppDataRoaming. The folder location can be accessed by entering %AppData% in the Address Bar of Windows Explorer or File Explorer (see Figure 1).
- Local Folder – Files in this folder might be machine specific or too large to consider when roaming is enabled for the user’s account. The default location of the Local folder is C:Users<user name>AppDataLocal. The folder location can be accessed by entering %LocalAppData% in the Address Bar of Windows Explorer or File Explorer.
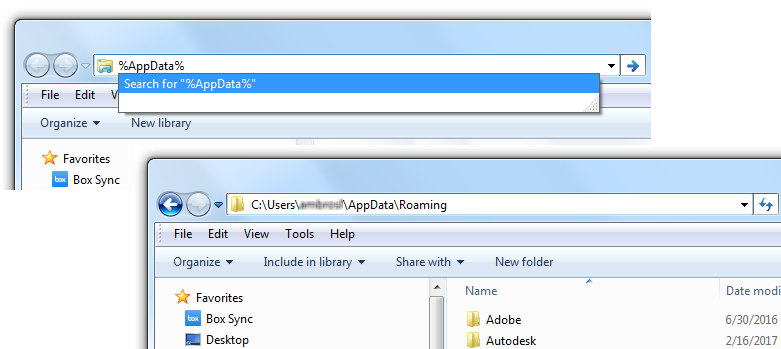 Figure 1. Navigating to the Roaming folder
Figure 1. Navigating to the Roaming folder
Tip: The AppData folder is hidden by default in Windows and can’t be directly navigated to by default, but can be made visible so it can be navigated to using Windows Explorer or File Explorer. To show the AppData folder, in Windows Explorer or File Explorer, click Tools > Folder Options. In the Folder Options dialog box, View tab, click Show Hidden Files, Folders, and Drives. Then click OK to save the setting change.
The Roaming and Local folders both contain a folder named Autodesk along with folders associated with other applications installed on the workstation. The Autodesk folder contains a number of folders that are related to the AutoCAD product and other Autodesk products (see Figure 2).
 Figure 2. Folder structure of the Autodesk and AutoCAD folders
Figure 2. Folder structure of the Autodesk and AutoCAD folders
The most commonly edited custom files for the AutoCAD 2018 program are located in these three locations:
- %AppData%AutodeskAutoCAD 2018R22.0enuSupport
- %AppData%AutodeskAutoCAD 2018R22.0enuPlotters
- %LocalAppData%AutodeskAutoCAD 2018R22.0enuTemplate
Tip: In the AutoCAD product, it is possible to find most custom files as long as you know the name of the file that you are trying to locate. The FINDFILE AutoLISP function can be used to scan the folders in the AutoCAD Support File Search Path for a specific file, and if the function locates the file it returns the full path to the file. For example, entering (findfile “acad.pgp”) returns the string value “C:Users<user name>appdataroamingautodeskautocad 2018r22.0enusupportacad.pgp” which indicates that the acad.pgp file is under the Roaming folder of the user’s profile. Replace acad.pgp in the previous example with the file you are interested in locating, such as acad.dwt or acad.cuix.
Check out the entire basic AutoCAD customization series, and tune in next time for part 2 on sharing your custom AutoCAD files. For more from Lee, follow him on Twitter.


