The integration of 2D and 3D workflows using AutoCAD and Inventor enhances productivity, quality, and competitiveness by enabling a seamless design process, improving collaboration, and automating tasks.

The integration of 2D and 3D workflows is crucial for enhancing productivity, product quality, and market competitiveness in manufacturing. AutoCAD and Inventor, offer powerful capabilities that, when used together, allow for seamless design processes. This article explores the top workflows that leverage both 2D and 3D environments, demonstrating how these tools can significantly improve your design and manufacturing operations.
2D and 3D workflows
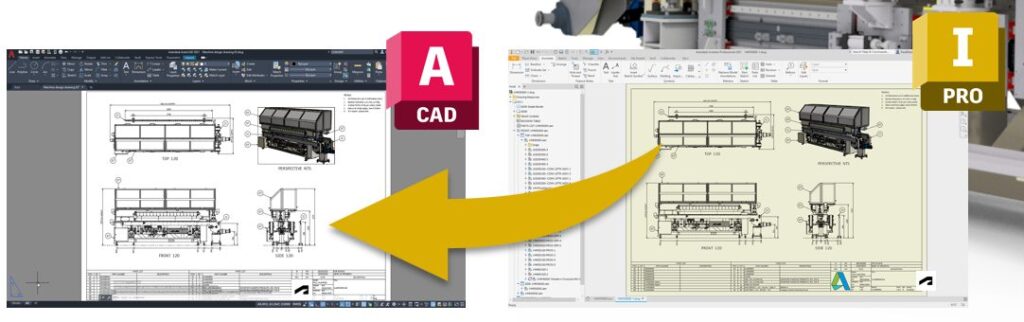
Manufacturing documentation
Creating 2D drawings as DWG in Inventor ensures flexibility and collaboration between teams as the manufacturing drawings can also be edited or reviewed in AutoCAD. Users can add detailed annotations, dimensions, and manufacturing notes in Inventor or AutoCAD. This method facilitates better collaboration with team members, suppliers, and manufacturers, as DWG files are widely accepted in the industry. It also ensures consistency and adherence to industry standards. This ultimately helps to save time, reduce errors, and increase efficiency throughout the design and manufacturing process.
Mechanical design with 2D layouts and 3D models
The process of mechanical design using 2D layouts in AutoCAD and 3D models in Inventor begins with conceptual sketches in AutoCAD. From there, detailed 3D models are created in Inventor, using its parametric tools for precision and validation. The DWG file maintains associativity with the 3D models for consistent updates. This integrated approach ensures accuracy, provides flexibility, streamlines the process, and improves collaboration.
Electromechanical collaboration
Collaboration between mechanical and electrical engineering teams is often challenging. AutoCAD and Inventor offer a comprehensive electromechanical workflow that facilitates efficient collaboration between these teams.
While AutoCAD is widely used for creating electrical schematics, Inventor excels in 3D mechanical design. The integration between these tools allows for the synchronization of data between electrical schematics and 3D mechanical designs.
Electrical engineers can create detailed schematics in AutoCAD using intelligent tools that automate tasks such as wire numbering and component breakdowns. These schematics can then be linked to 3D models in Inventor. This allows mechanical engineers to design around the electrical components, ensuring proper fit and function.
Factory planning and layout
For decades, AutoCAD has been the tool of choice for creating facility layouts due to its ease of defining zones and arranging equipment in 2D. However, integrating these layouts into Inventor offers additional benefits. This workflow allows for the creation of detailed 2D layouts in AutoCAD, which can then be brought into Inventor for further refinement and analysis. The 3D model can be used to ensure that all equipment fits within the space, that there are no interferences, and that the layout is optimized for efficiency.
With the Product Design and Manufacturing Collection, users gain access to tools that enhance factory planning. This includes the ability to analyze material flow, energy consumption, and interference checks. Layouts created in AutoCAD can be synchronized with Inventor to create automatic 3D representations.
Enhance Your Engineering Workflows
Precise, powerful, and ready for innovation with Autodesk Inventor.
Moving from 2D to 3D
Creating 3D models from existing 2D drawings
Since its introduction into the market over 40 years ago, AutoCAD has been the industry standard tool for generating a wide array of technical documentation, from mechanical manufacturing details to facility plans. Over the years, many companies amass extensive libraries of 2D drawings containing invaluable data. The integration between AutoCAD and Inventor allows for the reuse of existing 2D data to build a detailed 3D model in Inventor. Using this existing data when transitioning to 3D or converting 2D outlines into 3D models is critical for efficiency and accuracy. Inventor allows users to import 2D drawings from AutoCAD seamlessly. This can be done by copying and pasting directly from AutoCAD or by linking DWG files as references in Inventor. This integration ensures that any updates to the 2D drawings are automatically reflected in the 3D model, maintaining consistency and saving time.
3D capabilities
Moving from 2D to 3D design can bring numerous advantages to your workflows. One of the primary benefits is automation. With 3D modeling, parameters and formulas drive your design intent, allowing you to build intelligence into your models. This means that when changes are necessary, the model behaves as expected. Further, all associated 2D manufacturing drawings remain up to date. This reduces errors and ensures consistency across your design documents.

Specialized toolsets
Another significant advantage is the specialized toolsets available in Autodesk Inventor, which can greatly speed up product design. Models can be used for advanced analysis, such as finite element analysis (FEA) and CAM toolpath strategies, enhancing the design’s performance, functionality, and manufacturability. Complex geometries such as bends in sheet metal can be automatically generated with accurate bend allowances, providing a flat pattern ready for production. Similarly, weld frames and tube and pipe routes can be created effortlessly using predefined libraries and intelligent features that automate much of the design work. This helps users to focus on the overall design rather than the intricate details of modeling each component.
Model-based definition
Model-Based Definition (MBD) is another powerful feature in Inventor that enhances the transition to 3D. MBD allows you to apply dimensions, annotations, and tolerances directly onto your 3D models. Thus eliminating the need for traditional 2D drawings. These 3D annotations can be shared with collaborators using shared views, ensuring everyone is on the same page. The tolerance advisor in Inventor provides a visual display of the faces of your design that have been fully or partially defined. This ultimately makes it easy to add or change annotations as needed. Even if you still need 2D drawings, the annotations remain associative with the 3D model. Thsi ensures updates are reflected across all views.
iLogic integration
Additionally, Inventor’s integration with iLogic technology allows you to automate repetitive design tasks by establishing engineering rules and creating forms that drive your designs. This automation is further enhanced by the Autodesk Forge platform, which enables web-based configuration of new products. Overall, moving to 3D not only streamlines your design process but also reduces the time and effort required to create manufacturing documentation. It also improves accuracy, and provides numerous downstream benefits, including CAM toolpath strategies, tolerance analysis, and enhanced collaboration.
Benefits of 2D and 3D workflows
Ultimately, the integration of 2D and 3D workflows using AutoCAD and Inventor significantly enhances design and manufacturing processes. By leveraging these tools together, users can easily transition from 2D drawings to detailed 3D models. This ensures dynamic updates and consistency and facilitates collaboration between different engineering disciplines. The advanced capabilities offered by Inventor streamline the design process, improve accuracy, and provide numerous downstream benefits. The result – improved productivity, better product quality, and enhanced market competitiveness.
Enhance Your Engineering Workflows
Precise, powerful, and ready for innovation with Autodesk Inventor.