LAND-SURVEYING SOFTWARE
Autodesk makes surveying software for land surveyors, civil engineers, project managers, and construction professionals.
Autodesk makes surveying software for land surveyors, civil engineers, project managers, and construction professionals.
Land-surveying software assists in the process of evaluating a 3D landscape to determine the angles and distances between a series of points. Measuring the positioning of these points is typically used to establish maps and boundaries for buildings and other subterranean civic projects.
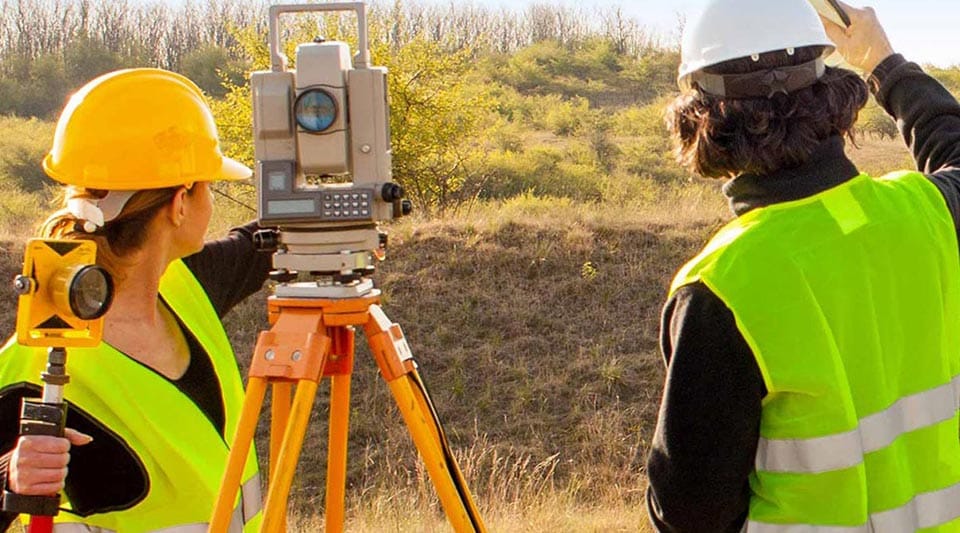
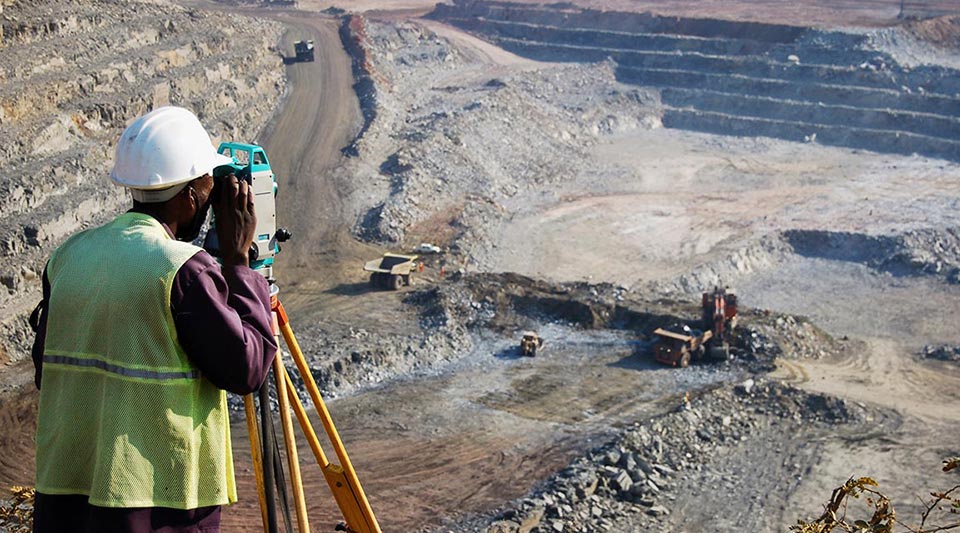
Land surveyors use a variety of tools, such as total stations (which use beams of light and built-in electronic distance measurement to collect data and triangulate positions), GPS devices, theodolites, drones, retroreflectors, 3D laser scanners (US Site) and other technological devices. Surveying also utilises knowledge and practices from many different fields, including trigonometry, geometry, engineering and physics. Today, the data and measurements collected by surveyors in the field can be fed into surveying software to generate precise calculations, visualisations and more.
While there are many different land-surveying techniques, there are three fundamental ones that are used the most often. These three techniques can be used alone or in combination with each other.
One of the more commonly used surveying methods, this assumes that the Earth is a flat surface and disregards its curve.
Used for surveying large areas, this method takes the curvature of the Earth into account.
This guide introduces you to the essential commands that you need to create 2D drawings in AutoCAD
Uncover the guide to the basic commands needed to create and modify surveys in Civil 3D.
See how the AEC Collection is used to for civil/survey consulting processes, proposals and workflows.
Discover how to use AutoCAD Civil 3D for various day-to-day operations of consulting engineering and surveying companies.
See how BIM is used to survey and map the world's largest twin-helix steel structure.
Use 5 real-world examples to help you to understand survey functionality within AutoCAD Civil 3D software.
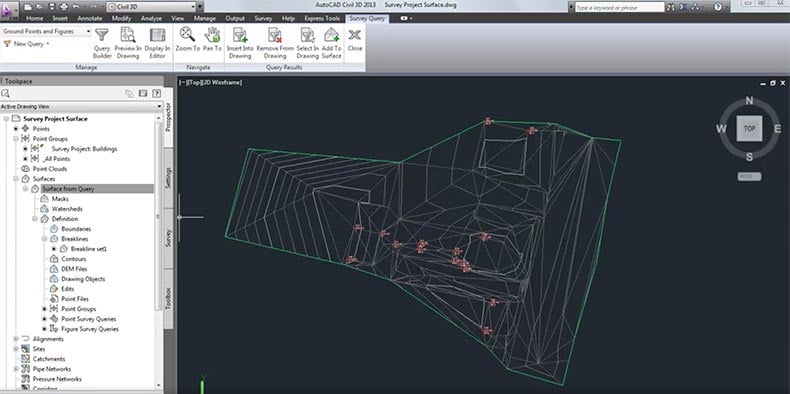
Learn how to create a model from external survey information, how to manipulate surface data and process multiple survey data into one model.
Get access to the latest news, tutorials and resources on civil infrastructure.
The first basic principle of surveying is that the position of any given point should be ascertained by measuring from at least two other reference points. The second is to work “from whole to part” - when surveying, the whole area to be surveyed should first be established with precision, using control points.
Land surveying is important for several reasons. It creates the legal basis and evidence for land ownership and can be used to settle property disputes. It is also vital in determining and planning the positions of new constructions such as roads and buildings and makes it possible to gather detailed knowledge and maps of large areas for a variety of purposes.
Land surveyors make extensive use of computer-aided design (CAD) software, as it allows them to accurately visualise and present information on the areas they are surveying. CAD modelling enables them to produce a virtual representation of the features of buildings, landscapes and more. It can even show how future construction and improvements will alter the area. CAD software is considered particularly flexible and time-efficient, as changes can be easily made at any point. It can also lead to greater accuracy.
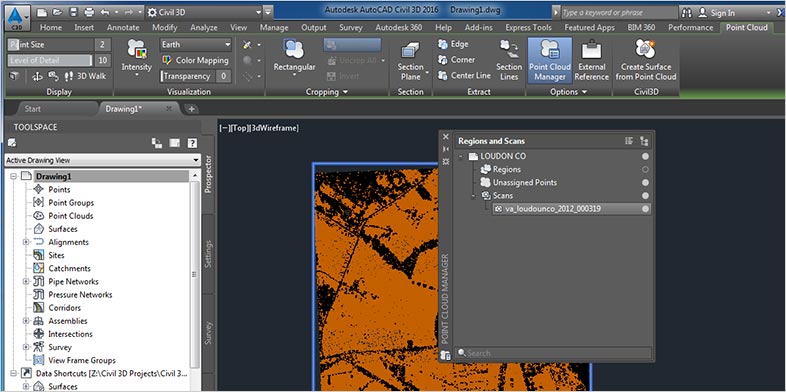
Laser scanning (US Site) is a popular land surveying method that can accurately measure and collect data from objects, surfaces, buildings and landscapes. Modern laser scanners can collect detailed point clouds and with point cloud processing software, these datasets can create digital 3D models of the scanned environment.
There are myriad types of land survey, including:
Yes. Please visit our knowledge network to read more about land surveying and Civil 3D survey features. This software contains a complete set of tools that surveyors can use to download and process survey information, perform adjustments on network and traverse data and import survey points into 3D drawings.