& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
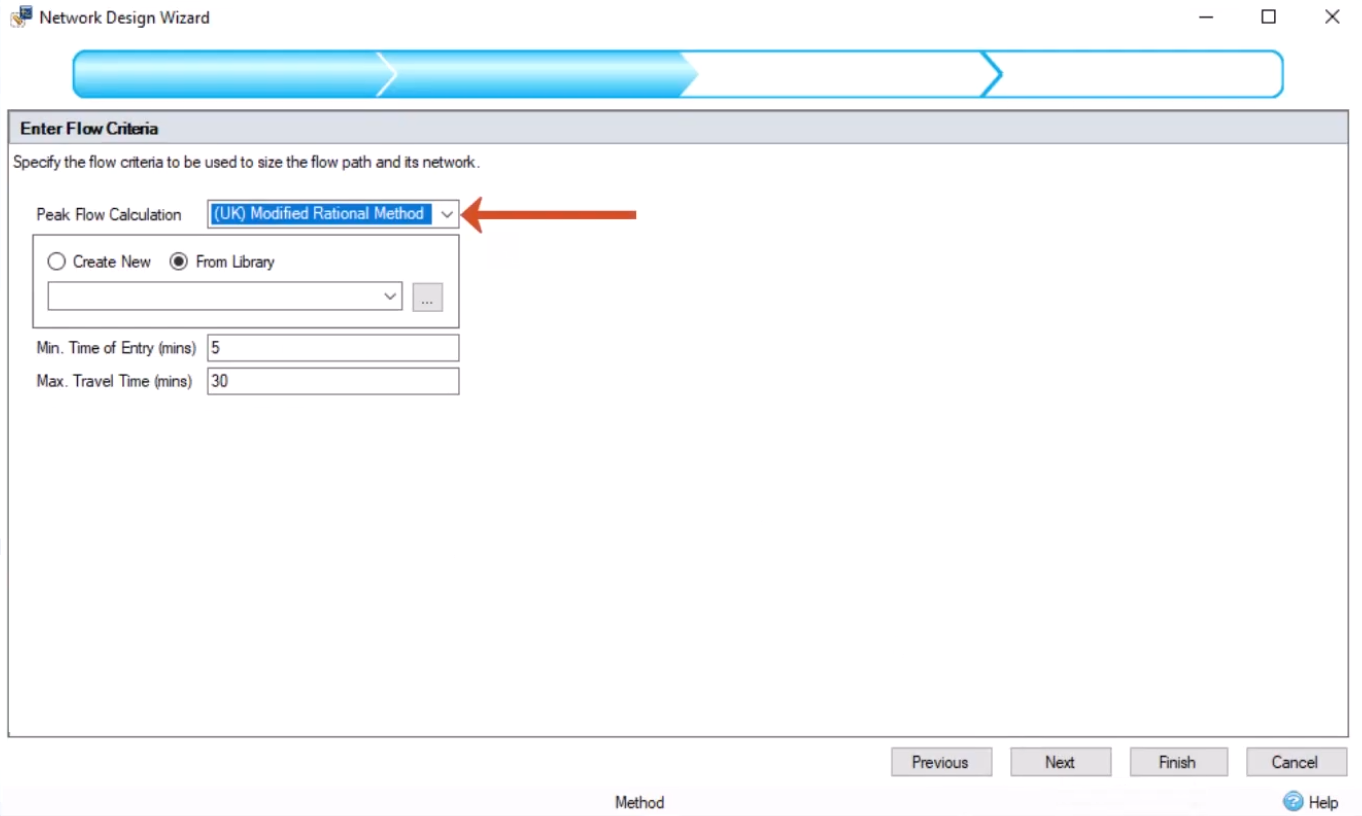
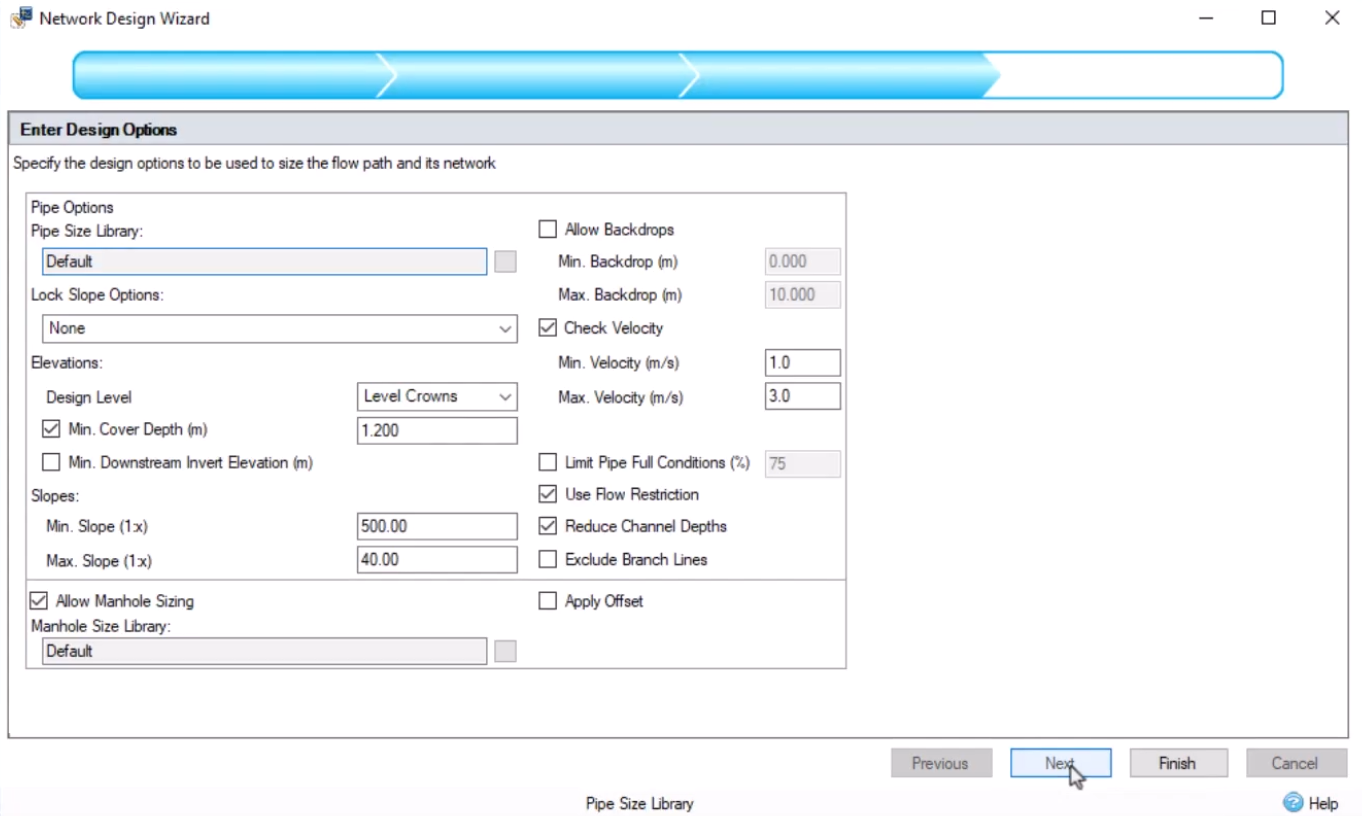
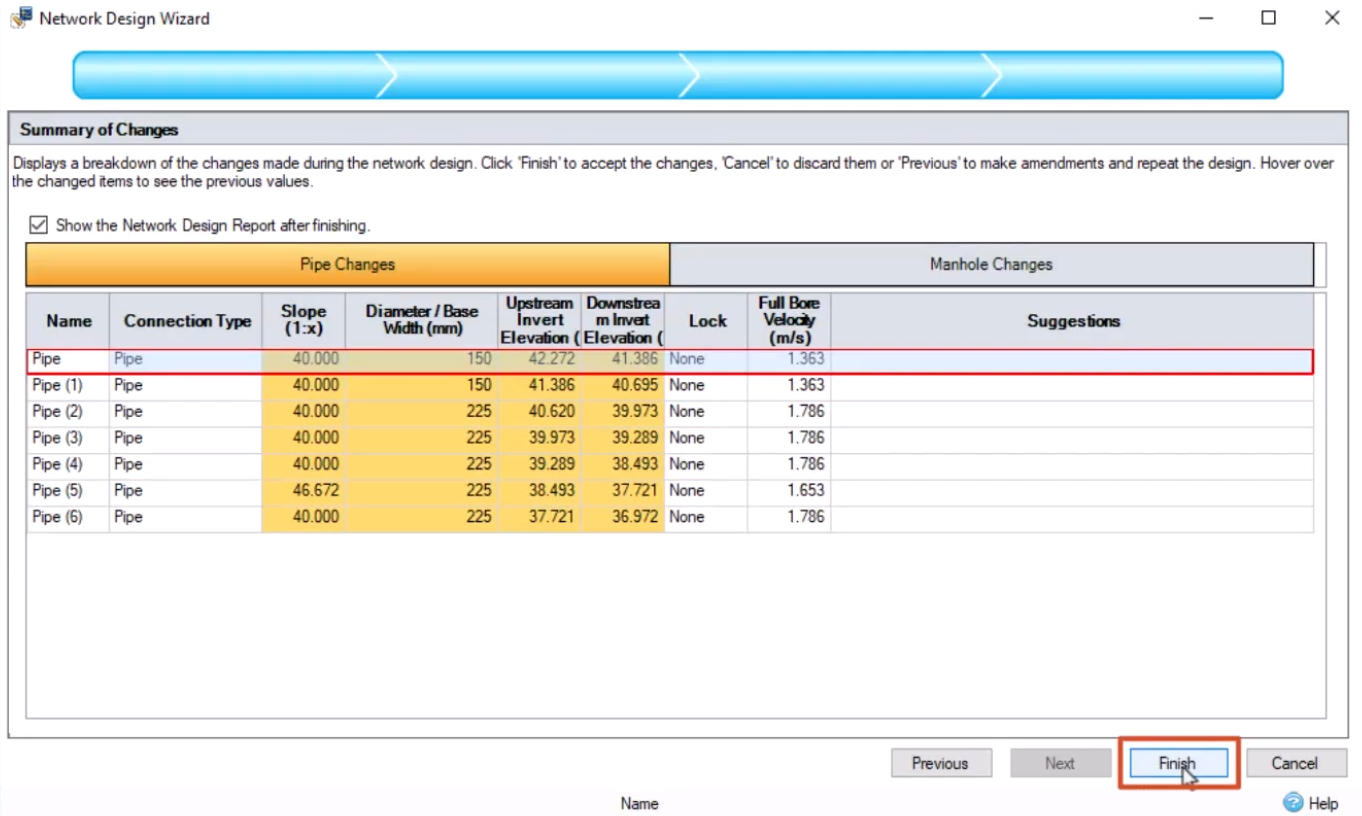
Once you have defined the Network Design criteria, as has been done in this example, you then simply need to run the Network Design Wizard to apply that criteria.
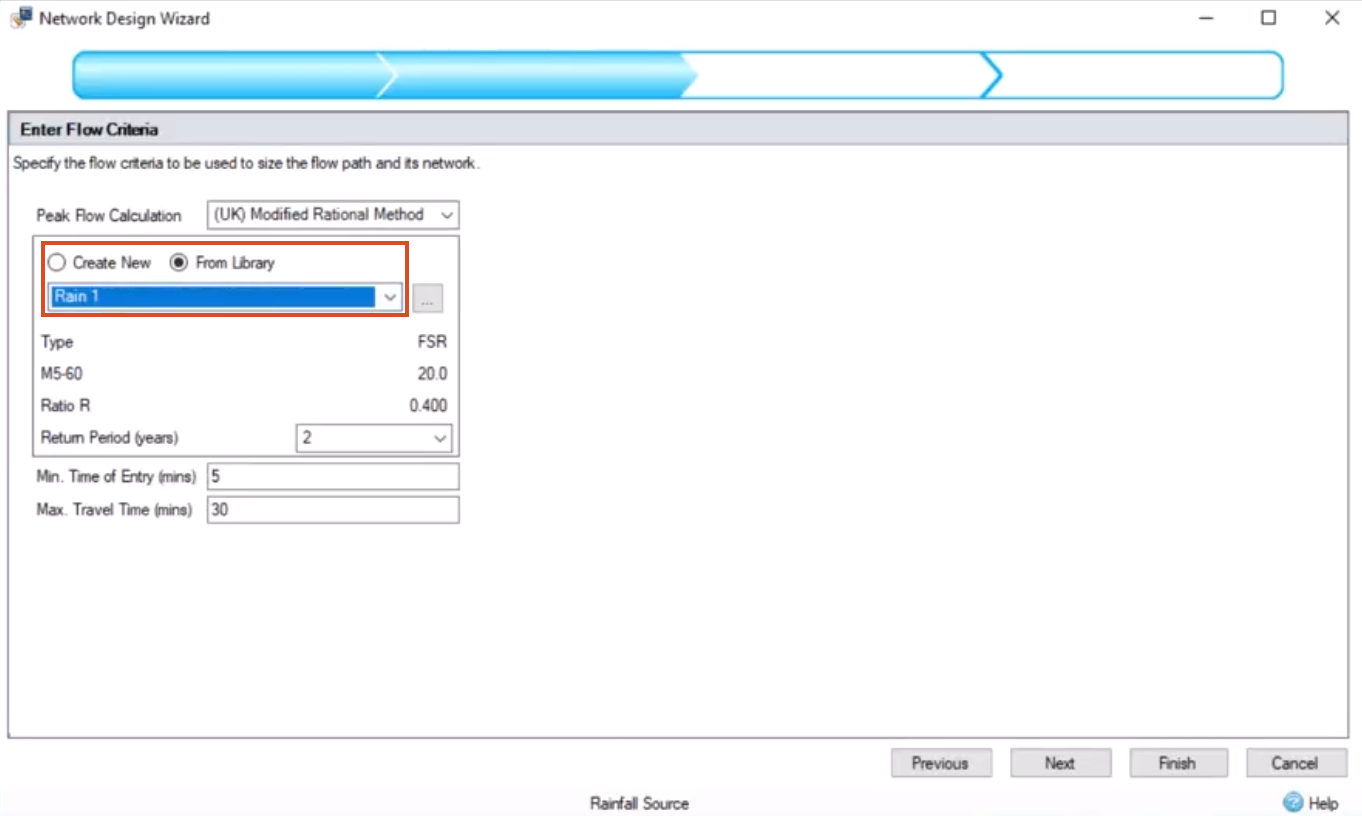
First, load the rainfall study if it is not already:
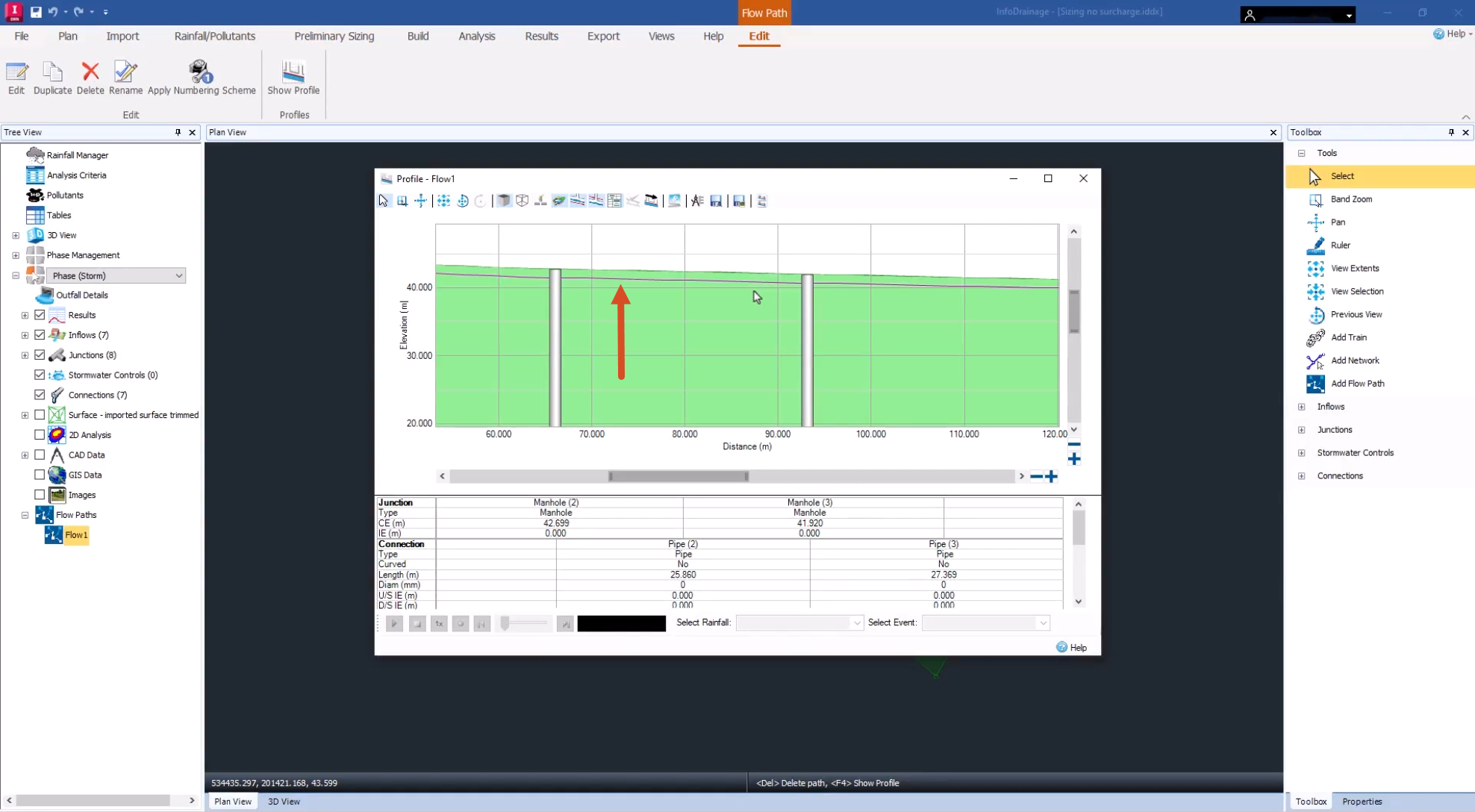
In the Profile – Flow1 dialog box, notice that the pipes are currently laid along the top of the catchment surface.
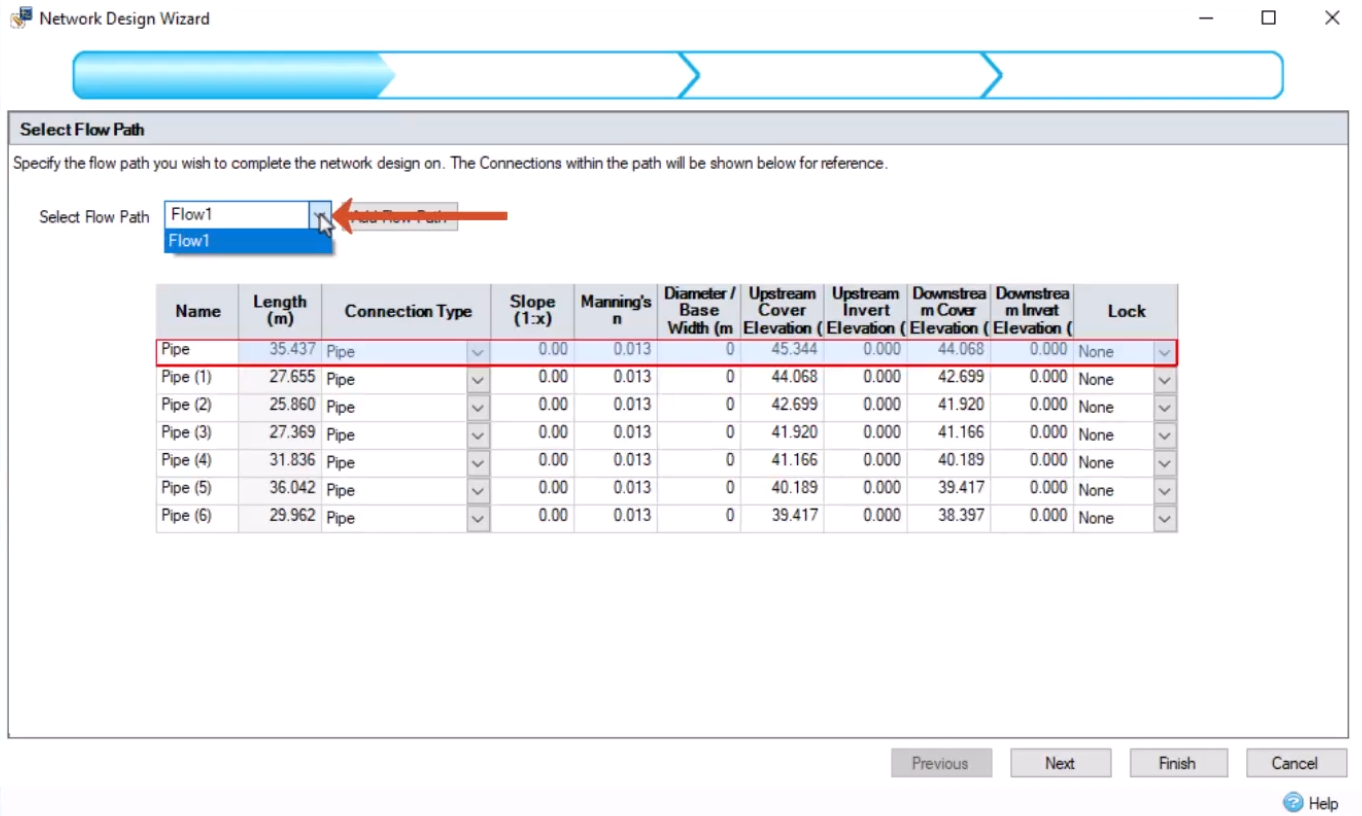
To specify the flow path and assign a depth to the pipes:
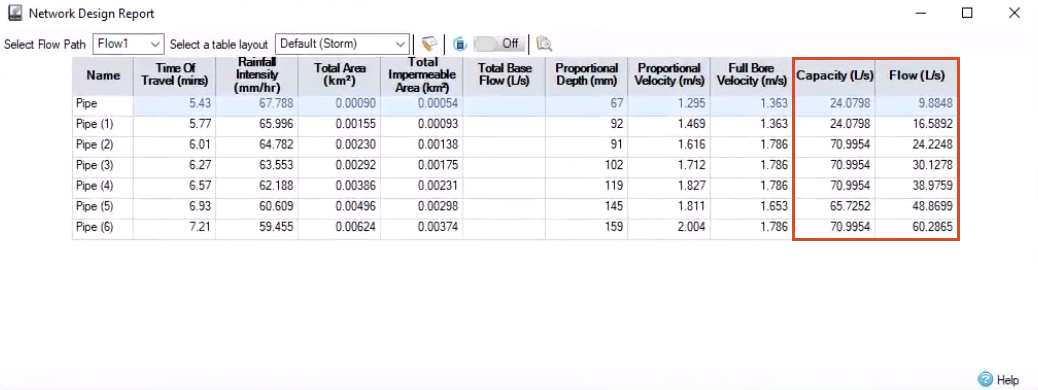
For the first catchment area, the capacity of 24.08 liters per second far exceeds the flow of 9.88 liters per second, so this pipe is sized plenty big enough. If additional structures are to be built within that first area, it is likely that the pipe will be able to accommodate the increased flow.
Now look at the Pipe (2) values. Here, the flow is closer to the capacity, in which case, for those same additional structures in the first catchment area, this pipe may not be big enough to accommodate the greater flow.
After that, there is a big jump in the capacity of the next couple of pipes, likely from a greater size pipe.
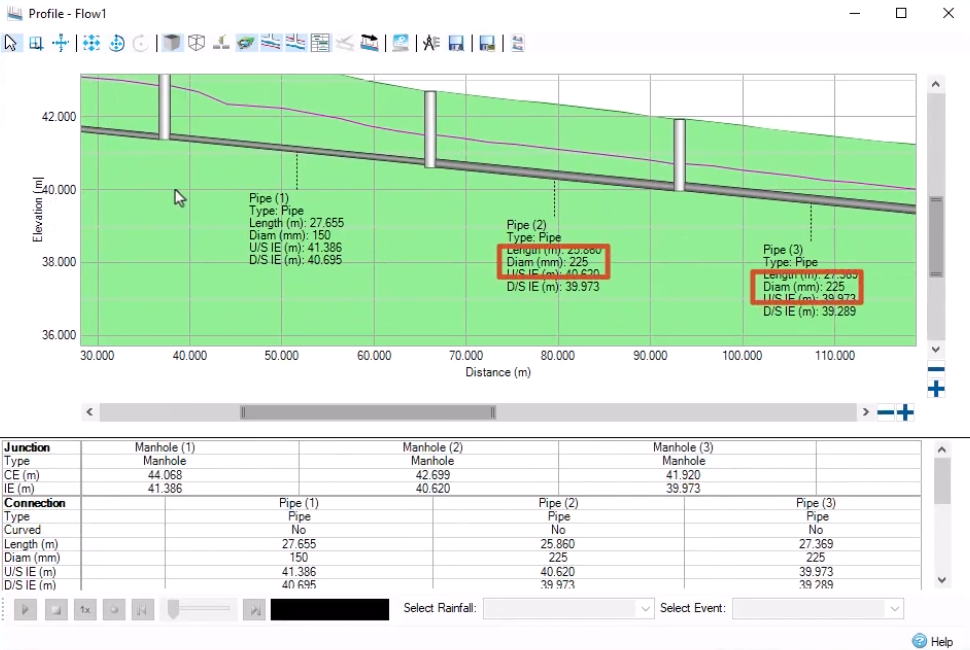
The pipes have been laid much deeper in the ground upslope than downslope. This is because the design had to meet either the slope criteria or the velocity criteria that was specified.