& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Transcript
00:03
To run a steady state analysis.
00:05
You must first set boundary conditions such as pump status or tank levels.
00:11
In this exercise, you define pump operations and assign an initial level to the tank
00:17
to begin.
00:18
Double click the desired project dot APR X file to open
00:22
Agis Pro.
00:24
Once the project starts,
00:26
click the info water pro tab to open the info water Pro ribbon
00:30
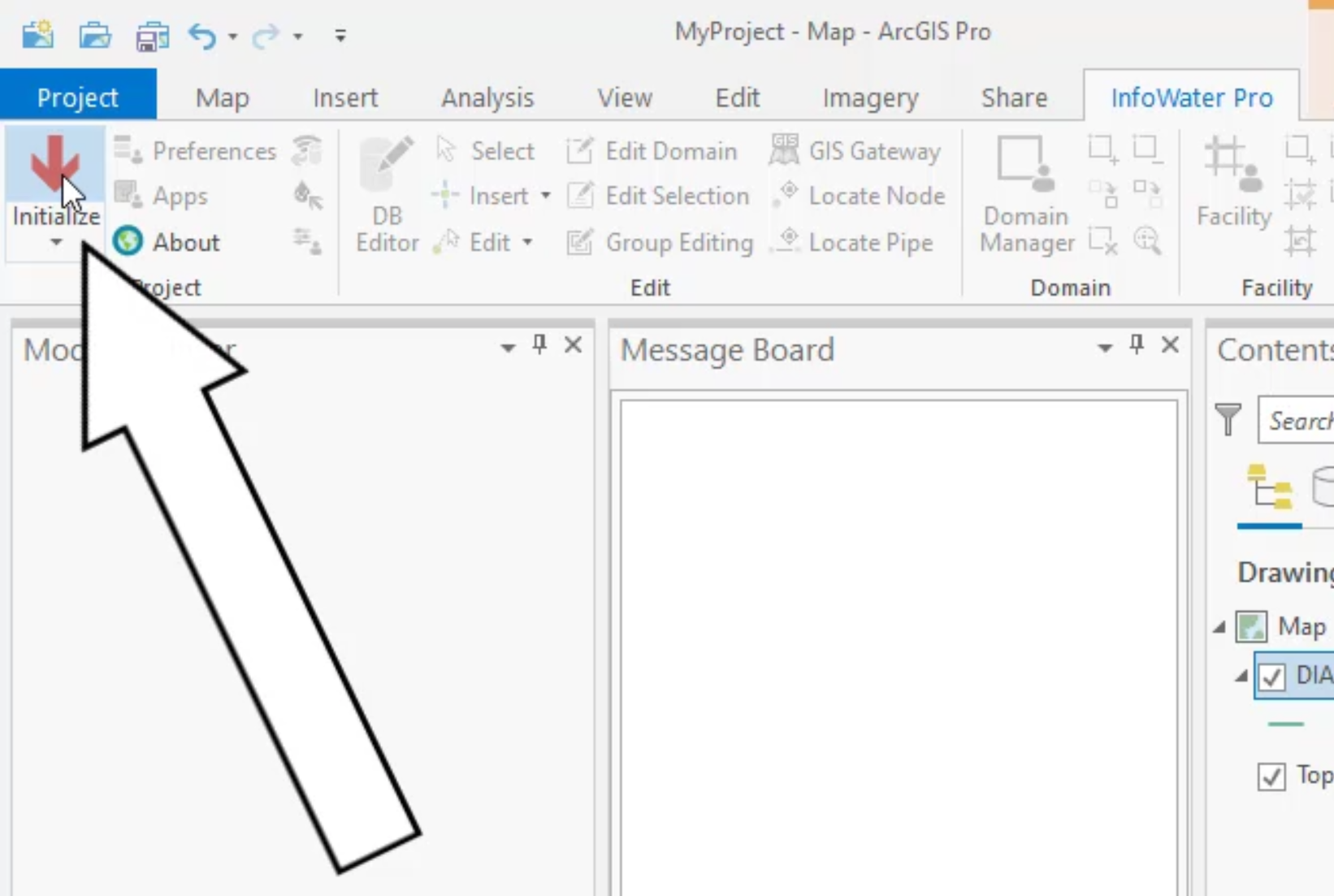
in the project panel, click initialize
00:35
to start zoom to the north tank with an ID of T 5004
00:41
from the info water pro ribbon
00:43
edit panel, click the select tool, then select tank T 5004.
00:51
If you are having trouble finding this tank in the model,
00:54
you can use the model explorer to help locate it
00:58
in the attribute tab. Enter T 5004 in the name field,
01:03
press enter
01:04
and then click zoom to an active element
01:08
with tank T 5004 selected
01:10
from the model explorer
01:12
attribute tab
01:13
enter an initial level of 120.
01:17
This means that this tank will have a hydraulic grade line
01:20
or H G L of 120 ft above the ground.
01:23
Surface. During this static analysis,
01:30
locate in zoom to the south tank with an id of T 5000 and select it
01:36
again
01:37
in the attribute tab of the model explorer enter an initial level of 90.
01:44
This tank will have an HGL of 90 ft above the ground surface.
01:47
During this static analysis,
01:51
locate in zoom to the treatment plant with an ID of W T P 100
01:56
select it
01:58
in the attribute tab of the model explorer. Enter ahead of 5880.
02:03
This treatment plant operates at a constant HGL of 5880 ft.
02:09
During this static analysis
02:12
now add pumps, P 100
02:14
P 120 to the domain which are the pumps located downstream of the reservoir.
02:21
On the info water pro ribbon in the domain panel, click the enlarged domain icon,
02:26
then select both pumps near the reservoir to add them to the domain.
02:31
The pumps and adjacent pipes will be selected,
02:35
click the reduced domain icon and then select the
02:38
adjacent pipes to remove them from the domain.
02:42
Only the pumps should remain
02:44
on the info water pro ribbon in the edit panel,
02:47
click group editing to open the group editor,
02:51
select pump slash valve status. Make sure that the initial status is set to close
02:56
and click. Apply
02:59
when you are prompted to confirm click. OK. And then close. The group editor
03:05
on the info water pro ribbon
03:07
in the domain panel. Click the clear domain icon.
03:11
Now, the pumps and tank are ready for a steady state analysis.
Video transcript
00:03
To run a steady state analysis.
00:05
You must first set boundary conditions such as pump status or tank levels.
00:11
In this exercise, you define pump operations and assign an initial level to the tank
00:17
to begin.
00:18
Double click the desired project dot APR X file to open
00:22
Agis Pro.
00:24
Once the project starts,
00:26
click the info water pro tab to open the info water Pro ribbon
00:30
in the project panel, click initialize
00:35
to start zoom to the north tank with an ID of T 5004
00:41
from the info water pro ribbon
00:43
edit panel, click the select tool, then select tank T 5004.
00:51
If you are having trouble finding this tank in the model,
00:54
you can use the model explorer to help locate it
00:58
in the attribute tab. Enter T 5004 in the name field,
01:03
press enter
01:04
and then click zoom to an active element
01:08
with tank T 5004 selected
01:10
from the model explorer
01:12
attribute tab
01:13
enter an initial level of 120.
01:17
This means that this tank will have a hydraulic grade line
01:20
or H G L of 120 ft above the ground.
01:23
Surface. During this static analysis,
01:30
locate in zoom to the south tank with an id of T 5000 and select it
01:36
again
01:37
in the attribute tab of the model explorer enter an initial level of 90.
01:44
This tank will have an HGL of 90 ft above the ground surface.
01:47
During this static analysis,
01:51
locate in zoom to the treatment plant with an ID of W T P 100
01:56
select it
01:58
in the attribute tab of the model explorer. Enter ahead of 5880.
02:03
This treatment plant operates at a constant HGL of 5880 ft.
02:09
During this static analysis
02:12
now add pumps, P 100
02:14
P 120 to the domain which are the pumps located downstream of the reservoir.
02:21
On the info water pro ribbon in the domain panel, click the enlarged domain icon,
02:26
then select both pumps near the reservoir to add them to the domain.
02:31
The pumps and adjacent pipes will be selected,
02:35
click the reduced domain icon and then select the
02:38
adjacent pipes to remove them from the domain.
02:42
Only the pumps should remain
02:44
on the info water pro ribbon in the edit panel,
02:47
click group editing to open the group editor,
02:51
select pump slash valve status. Make sure that the initial status is set to close
02:56
and click. Apply
02:59
when you are prompted to confirm click. OK. And then close. The group editor
03:05
on the info water pro ribbon
03:07
in the domain panel. Click the clear domain icon.
03:11
Now, the pumps and tank are ready for a steady state analysis.
To run a steady state analysis, you must first set boundary conditions, such as pump status or tank levels. In this exercise, you define pump operations and assign an initial level to the tank. Note that a steady state analysis has already been created.


TIP: If you are having trouble finding this tank in the model, use the Model Explorer to locate it. In the Attribute tab, enter T5004 in the name field, press ENTER, and then click Zoom to an Active Element.

Tank T5004 will now have a hydraulic grade line, or HGL, of 120 feet above the ground surface during the steady state analysis.
Tank T5000 will now have an HGL of 90 feet above the ground surface during the steady state analysis.
Treatment plant WTP100 will now operate at a constant HGL of 5880 feet during the steady state analysis.




Note that only the pumps should be selected.



The pumps and tank are now configured and ready for the steady state analysis.
How to buy
Privacy | Do not sell or share my personal information | Cookie preferences | Report noncompliance | Terms of use | Legal | © 2025 Autodesk Inc. All rights reserved
Sign in to start learning
Sign in for unlimited free access to all learning content.Save your progress
Take assessments
Receive personalized recommendations