Step-by-step Guide
In InfoWorks WS Pro, models must be validated to ensure that they are hydraulically sound before simulations can be run. The validation process involves finding errors and warnings—if any exist—and then fixing them one at a time.
To open a transportable database:
- Click File > Open > Open transportable database.
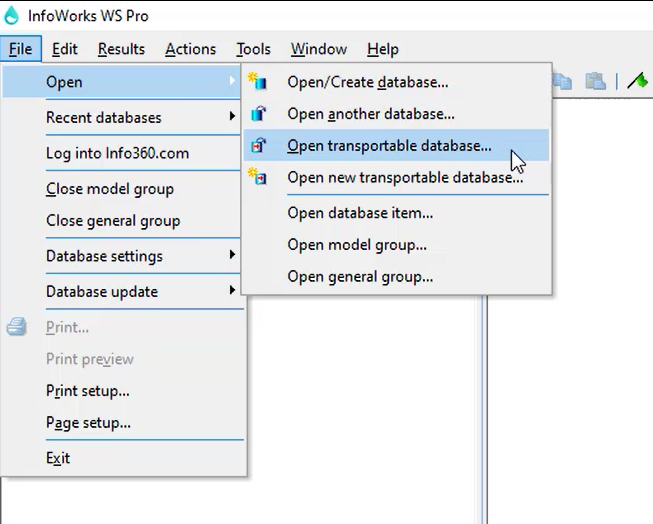
- In a file browser, open the Session 3 folder.
- In the Session 3 folder, open the Data folder.
- Select “Validating Models.wspt”.
- Click Open.
- On your keyboard, press and hold SHIFT.
- In the transportable database window, click the Session 03 model group.
- Click the Session 03 – Lock model group.
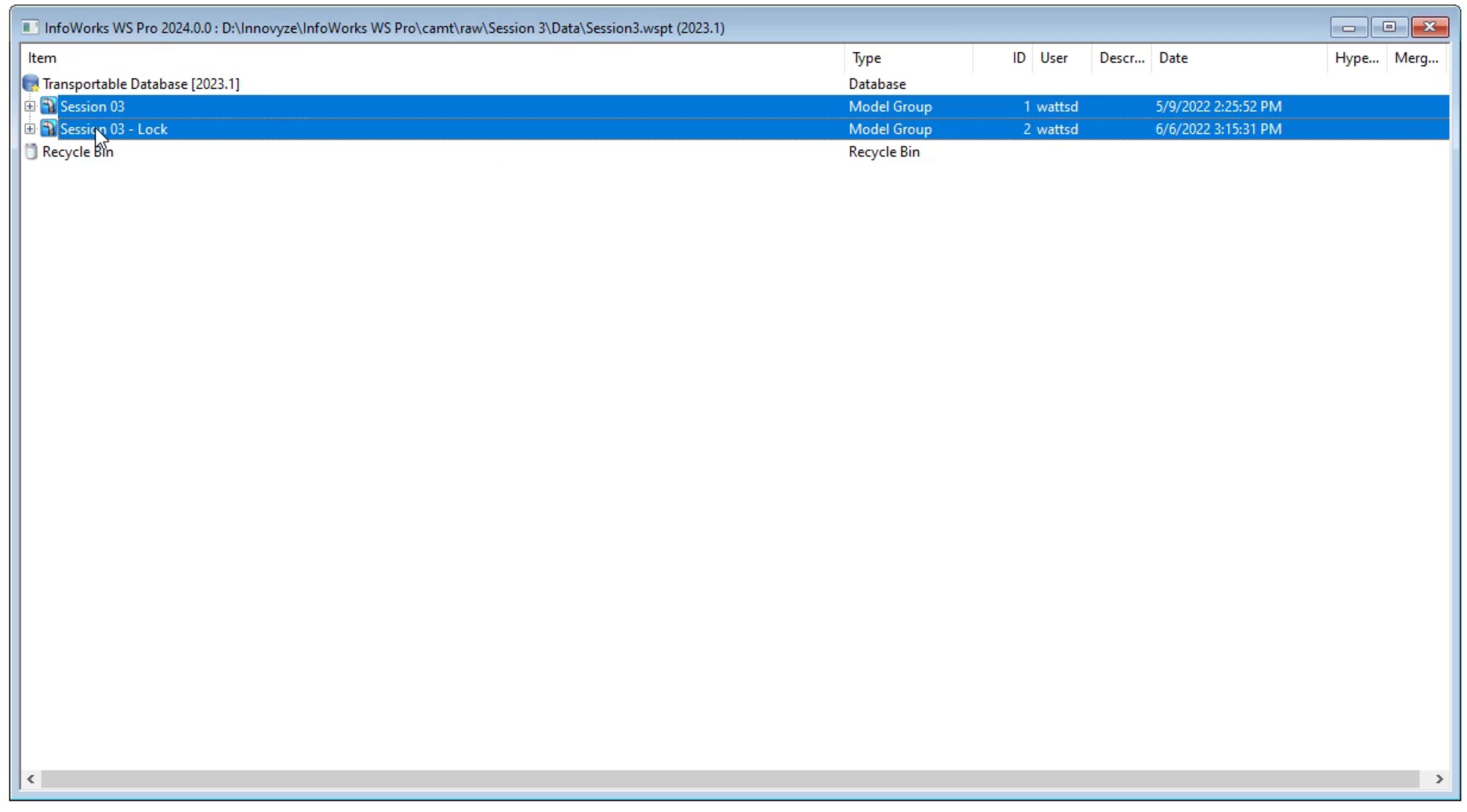
- Right-click the selected model groups and select Copy.
- In the Model Group window, right-click Database and click Paste all.
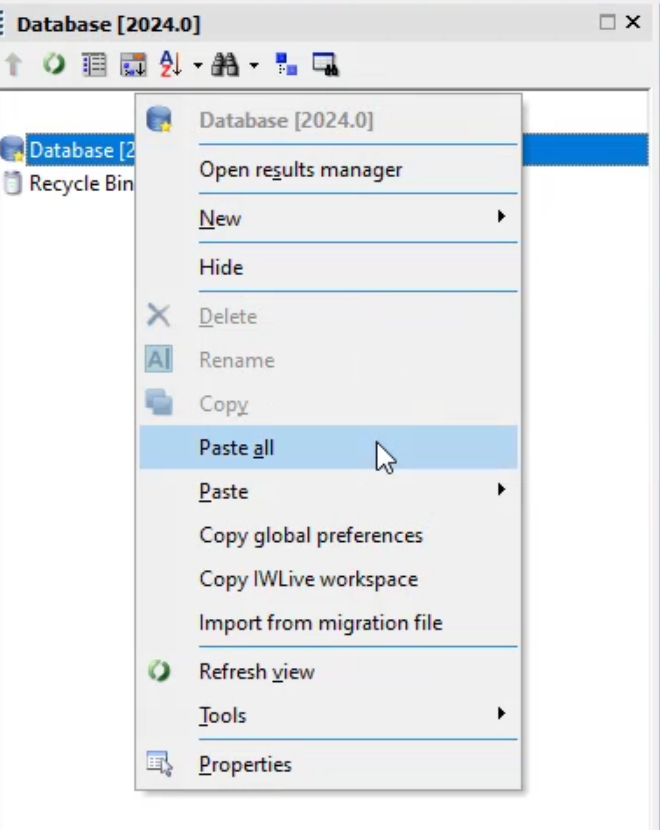
- Close the transportable database window.
To start the validation process:
- In the Model Group window, expand the Session 03 model group.
- Drag-and-drop BridgeNet into the workspace to open the GeoPlan.
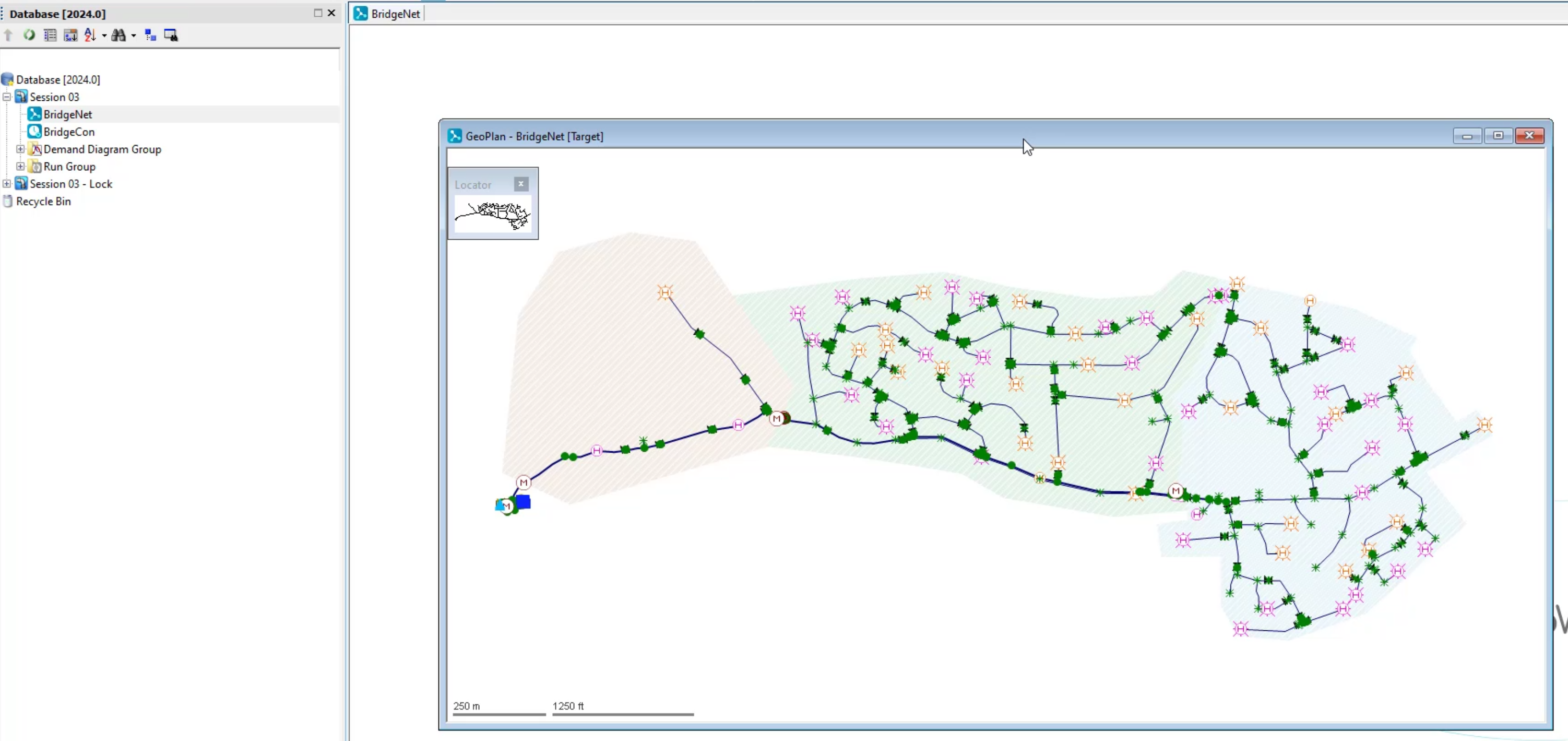
Note: If you have the control and demand diagram already associated with the network, they will open with the network. Skip to Step 18.
- From the Model Group window, drag-and-drop the BridgeCon control into the workspace.
- Expand the Demand Diagram Group.
- Drag-and-drop the BridgeTown demand diagram into the workspace.
To validate the network:
- In the menu bar, select Network > Validate Network.
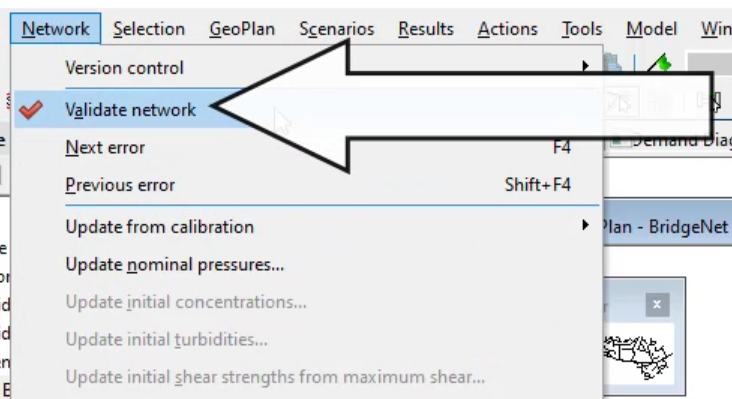
- From the Model Group window, drag the BridgeCon control into the Validate Network dialog box and drop it into the Control group box.
- From the Model Group window, drag BridgeTown ADAW into the Validate Network box and drop it into the Demand Diagram group box.
- Click OK.
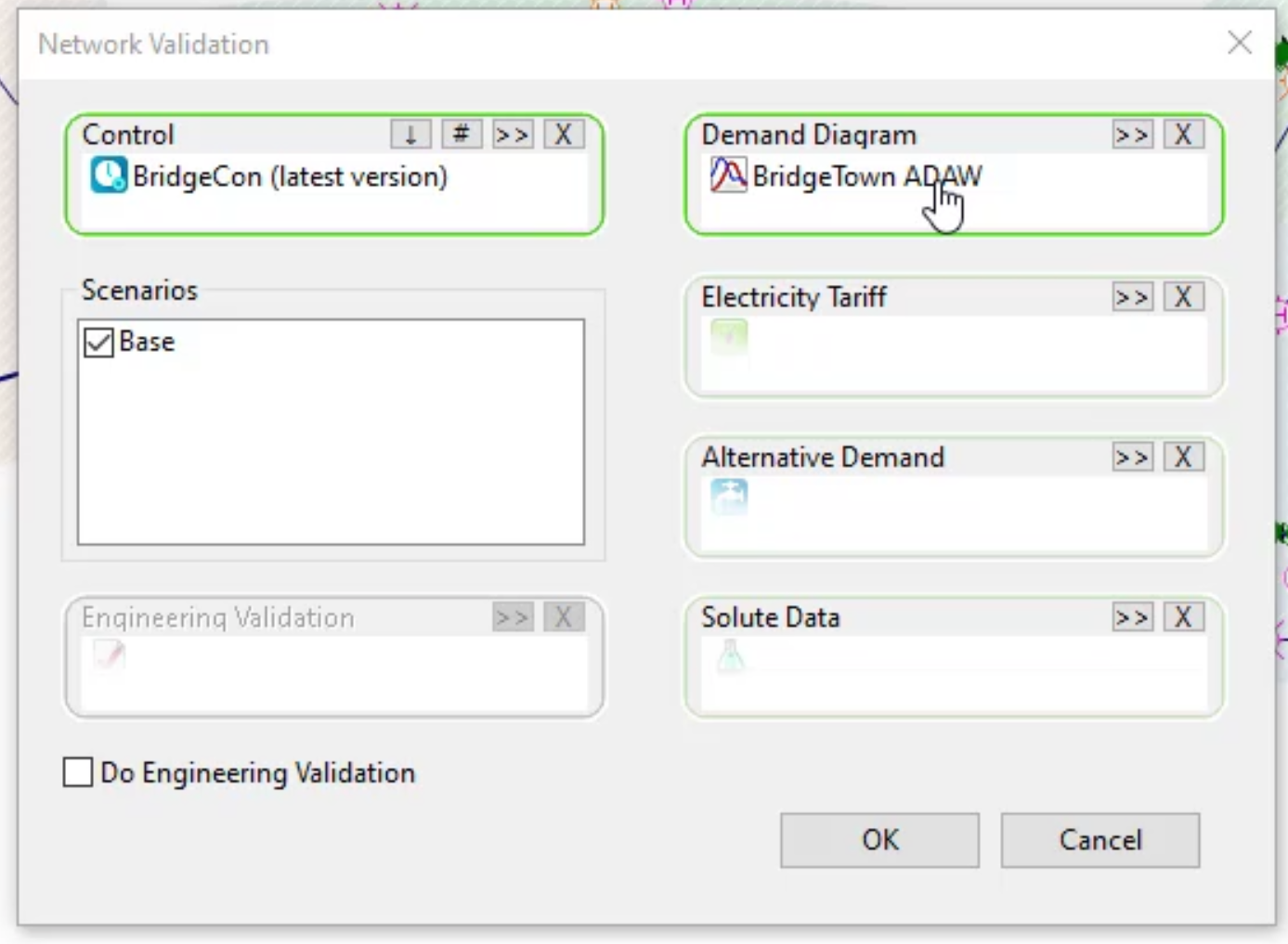
- In the Output Window, review the list of errors and warnings.
- A red circle with an exclamation mark (!) indicates an error. The model will not run until it is resolved.
Note: Re-validate the model after fixing each error. Sometimes, resolving one error will solve others linked to it.
- A yellow circle with an exclamation mark (!) indicates a warning. The model will run, but something is outside of default parameters.
Note: You may not need to resolve a warning if it represents a change or setting you intended.
- Double-click error E0040 and notice that nothing happens, because it is a Connectivity issue, as listed in the Field column.
- In the Output Window, double-click error E0208, and a grid appears showing the exact location of the problem.
To resolve a connectivity error:
- In the ribbon, select GeoPlan > Tracing tools > Connectivity trace.
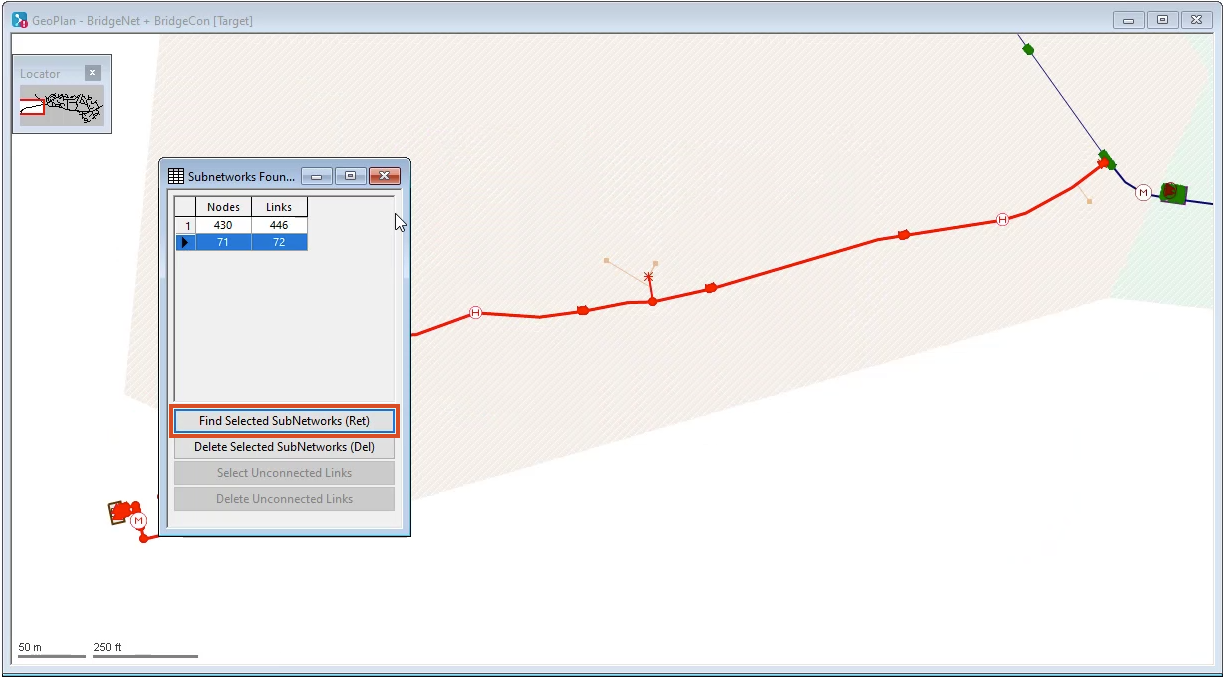
In the Subnetworks Found dialog, notice there are two subnetworks, meaning a single connectivity break in the network is separating it into two subnetworks.
- Click either of the subnetworks to select it.
- Click Find Selected SubNetworks (Ret).
- In the GeoPlan, review the subnetwork, highlighted in red, for the source of the connectivity issue.
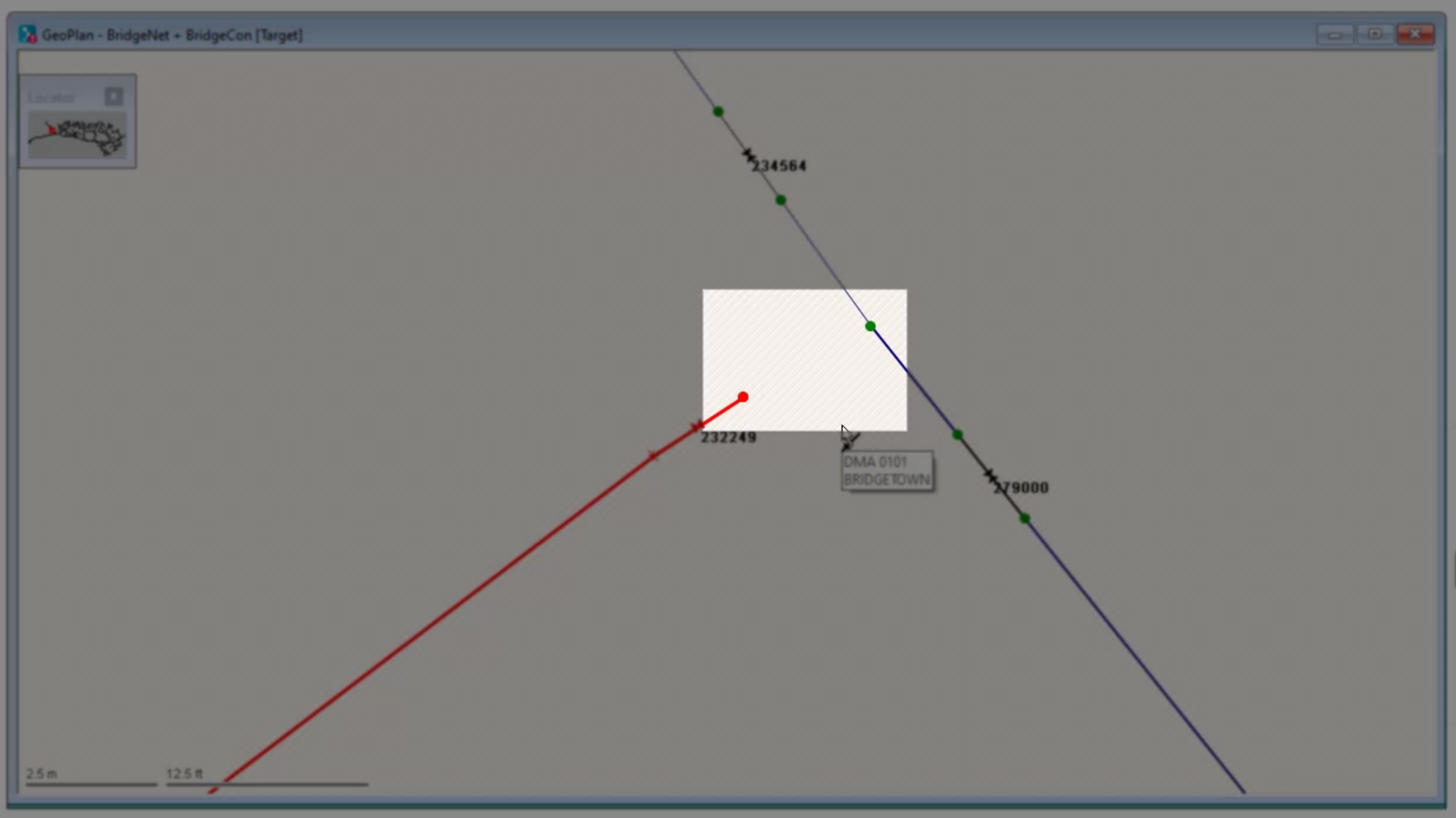
- Zoom in to see the error in more detail.
In this example, a junction is not complete, so water cannot flow from the reservoir upstream past this point.
- In the Tools toolbar, expand the Object category drop-down and select Link.
- In the Tools toolbar, click New object.
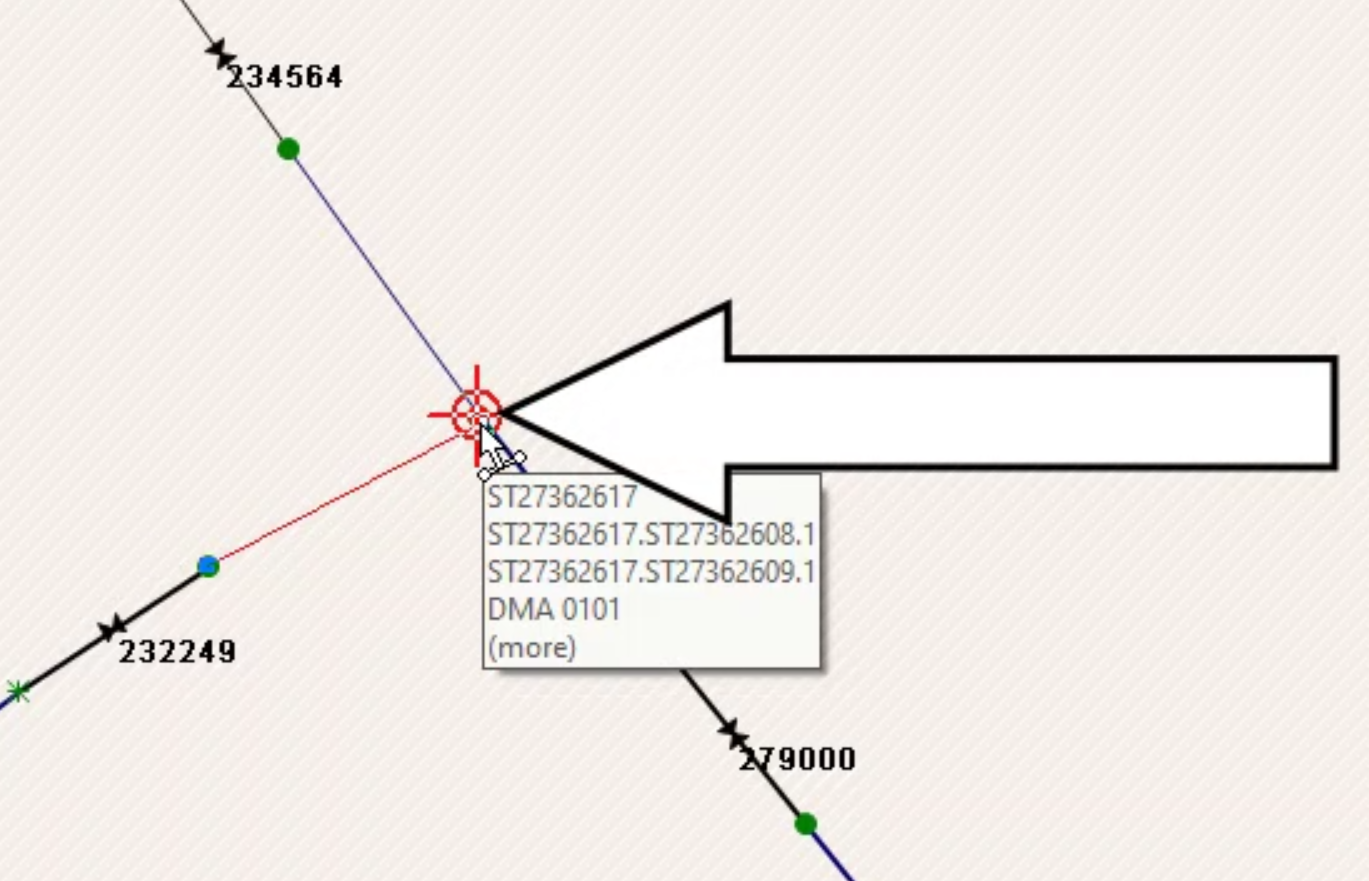
- In the GeoPlan, click the node at the end of the upstream portion of the network to place a start point.
- Click again on the node across from the start point.
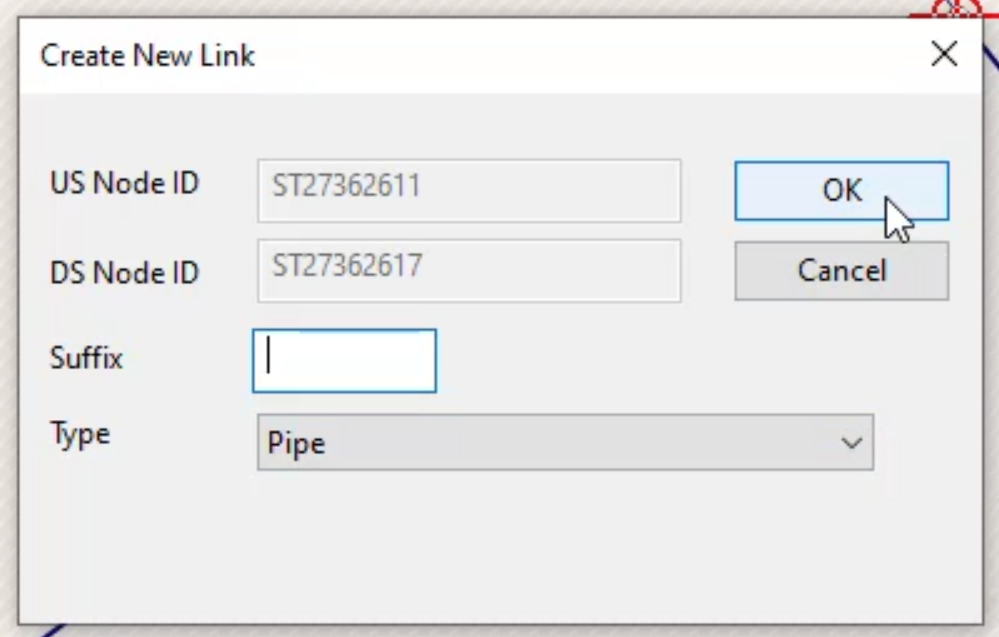
- In the Create New Link dialog, in the Type drop-down, select Pipe.
- Click OK.
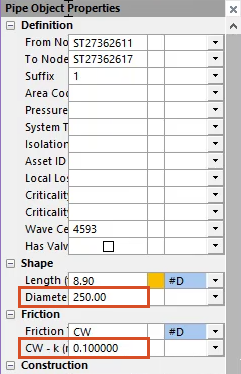
- In the Properties panel, review the properties for the pipe just created.
Note: In this example, the small cells next to the Diameter (mm) and CW - k (mm) fields are red. This means you are required to enter values for those properties.
- In the Diameter (mm) field, enter “250” to set the diameter of the pipe.
- In the CW – k (mm) field, enter “0.1” to set the friction coefficient.
- Close the Properties panel.
- Repeat Step 18 to validate the model again.
Notice the Output Window only lists three errors, as the connectivity issue is solved. Solving that issue also resolved the warning that had previously appeared here. Also, notice the Reservoir error is now at the top of the list.
To resolve a reservoir error:
- In the Output window, drag either window edge outward until you can see Top Water Level (ft AD) listed at the top of the Field column.
- Double-click reservoir error E0208 to view its details in a grid.
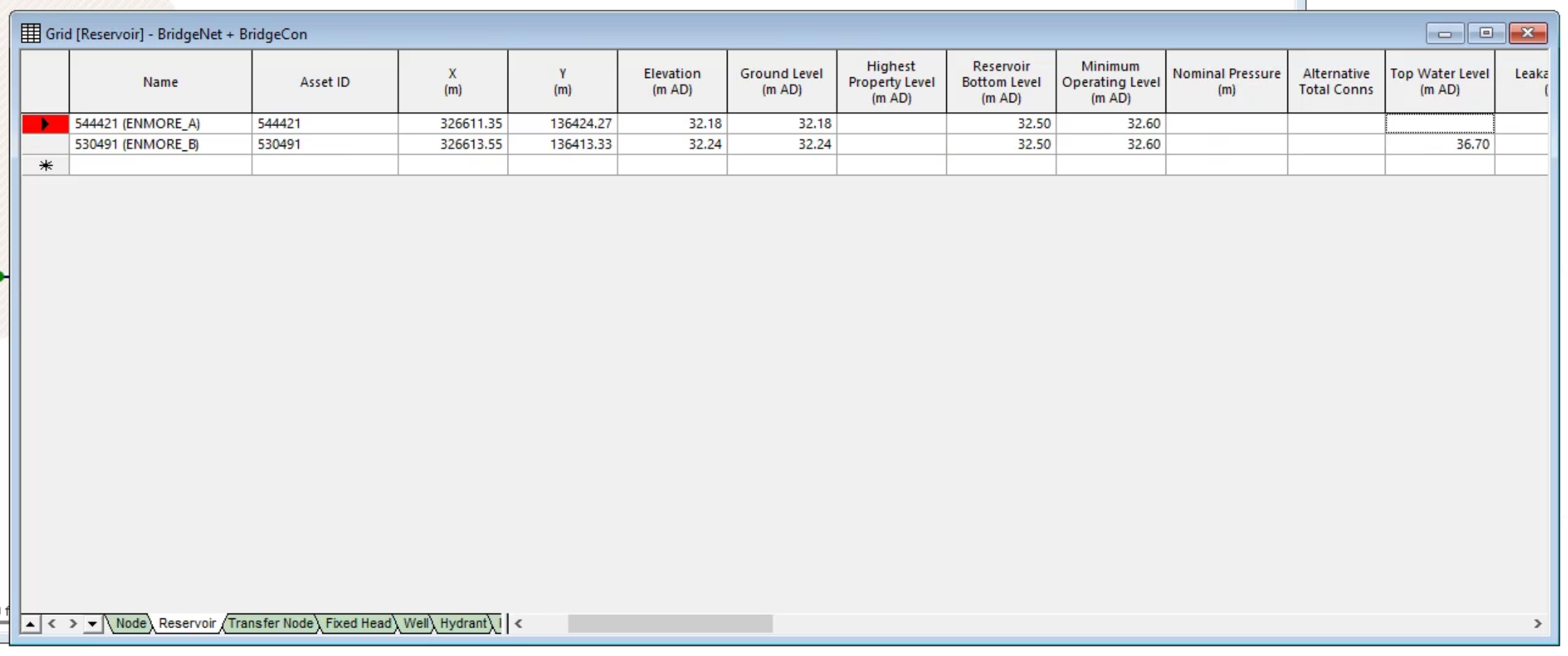
In the Grid window, in the Top Water Level (m AD) column, notice the first cell is blank. This is a common error that often happens when importing data from other sources, such as GIS.
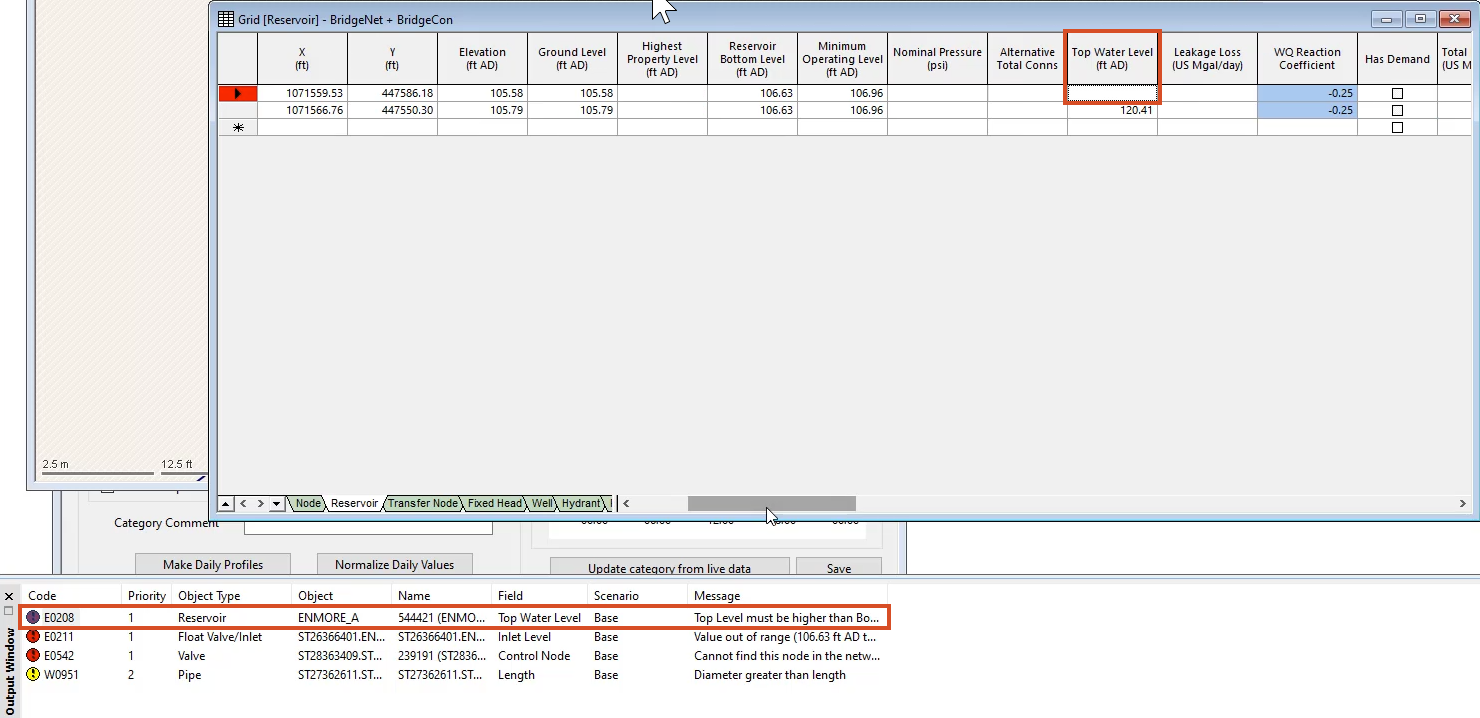
- In the Grid window, in the blank Top Water Level cell, enter the same value listed below it.
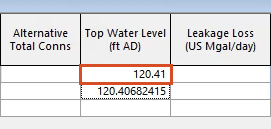
- Click in another cell to confirm that the new value has been saved.
- Close the window.
- Validate the model again, as in Step 18.
Notice the Output Window now lists only one error, again emphasizing that fixing one error can solve another.
To resolve a valve error:
- In the Output Window, double-click the valve error to view its details.
Note: You can fix the error in the grid, but sometimes, it is easier to use the GeoPlan.
- In the Grid window, at the bottom of the left column, right-click the green cell with the black arrow, and click Select and find in GeoPlan.
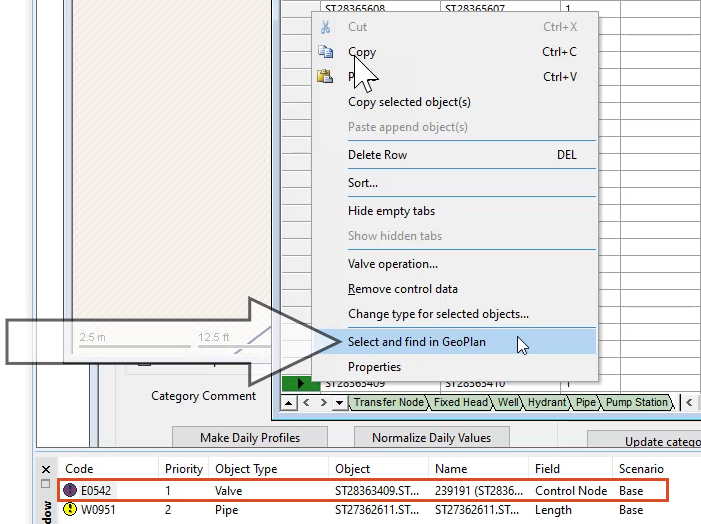
Notice this changes the window from a grid to a zoomed-in view of the GeoPlan with the valve highlighted in red.
- In the Tools toolbar, click Properties.
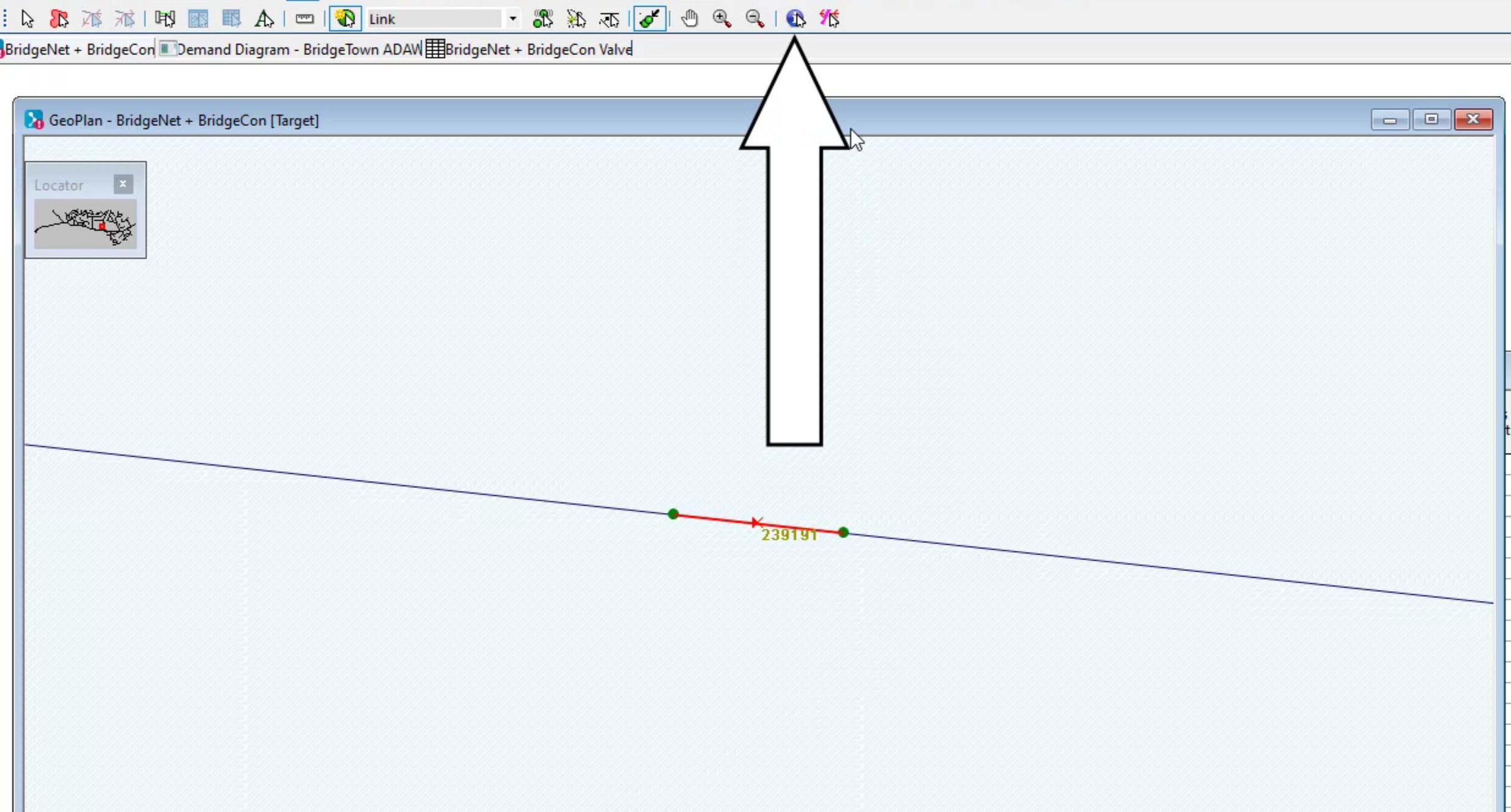
- Click the valve to view its properties.
Note: Because this is a pressure-reducing valve (PRV), it requires a control node. In this example, the node immediately downstream is used as the control.
- At the top of the Properties panel, under Definition, select the To Node, ST28363410.
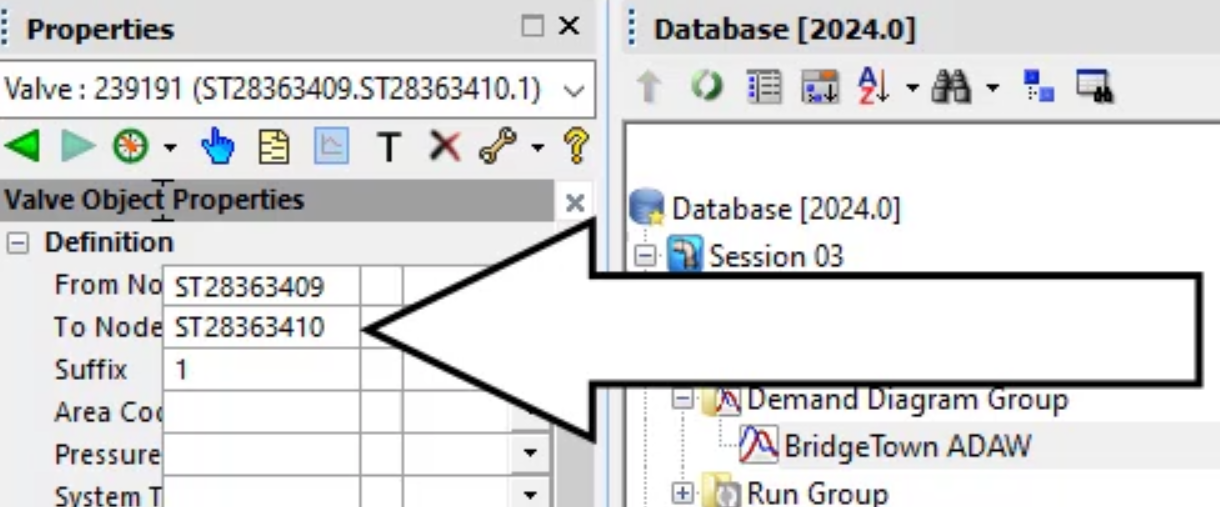
- Copy the value to the clipboard.
- In the Properties panel, under Valve Control, click to select the Control Node field.
- Paste the value into the field.
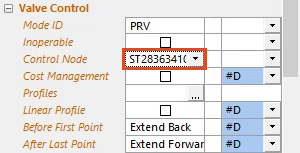
- Repeat Step 18 to validate the model again.
The Output Window is now cleared of all errors and warnings, meaning that the model is now hydraulically sound and ready to be run through simulations.
























