& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Transcript
00:04
In order to properly use info works. WS pro
00:07
you need to understand how it stores and orders data in a database.
00:12
Everything within the database is considered an
00:14
object and these objects can be grouped.
00:17
A group acts like a folder
00:19
groups can also be grouped.
00:22
Some objects are version controlled specifically network
00:26
control and live data configuration objects.
00:31
Most objects can only be created within the correct group type.
00:35
For example, a demand diagram, an object must be in a demand diagram group.
00:41
Generally,
00:42
there are two ways in which databases are stored by purpose and by area or location.
00:49
For example,
00:50
there may be an operational or future
00:52
planning database with areas listed as subgroups.
00:56
There may also be area databases with operational or planning models as subgroups.
01:02
Keep in mind there is no correct or recommended way
01:05
to structure databases that will depend on your company's preferences.
01:10
You will encounter several different types of groups and objects in info works.
01:14
WS pro
01:16
for example, you may have a model group,
01:18
a high level folder that can store most other objects and groups.
01:23
You may also have the following
01:25
a network which is the infrastructure of the model,
01:28
the control which depicts the behavior of the model.
01:31
The demand diagram which contains the demand profiles for the model,
01:36
a run group which holds the configurations of
01:39
particular simulations including their duration accuracy type and more
01:45
results which are the results of a simulation.
01:48
Some simulations may produce multiple sets of results
01:52
and a selection list which is a saved selection of objects.
01:57
Common object types within a network include nodes and links.
02:02
Nodes consist of nodes, fixed heads
02:05
reservoirs
02:06
hydrants
02:07
and transfer nodes.
02:09
Links consist of pipes,
02:11
pump station valves, float valves or inlets,
02:15
non
02:16
return valves and meters.
02:19
It is worth noting that this is how info works W S pro handles objects.
02:23
But that other software programs may classify these objects differently.
02:28
It is also important to understand the modeling workflow
02:31
in its simplest form, the workflow consists of the following steps,
02:36
make changes,
02:38
validate model,
02:39
save changes,
02:41
create run
02:43
run simulation
02:45
view results
02:47
based on the results.
02:48
You may want to make additional changes to and
02:51
create new iterations of the components of your model.
Video transcript
00:04
In order to properly use info works. WS pro
00:07
you need to understand how it stores and orders data in a database.
00:12
Everything within the database is considered an
00:14
object and these objects can be grouped.
00:17
A group acts like a folder
00:19
groups can also be grouped.
00:22
Some objects are version controlled specifically network
00:26
control and live data configuration objects.
00:31
Most objects can only be created within the correct group type.
00:35
For example, a demand diagram, an object must be in a demand diagram group.
00:41
Generally,
00:42
there are two ways in which databases are stored by purpose and by area or location.
00:49
For example,
00:50
there may be an operational or future
00:52
planning database with areas listed as subgroups.
00:56
There may also be area databases with operational or planning models as subgroups.
01:02
Keep in mind there is no correct or recommended way
01:05
to structure databases that will depend on your company's preferences.
01:10
You will encounter several different types of groups and objects in info works.
01:14
WS pro
01:16
for example, you may have a model group,
01:18
a high level folder that can store most other objects and groups.
01:23
You may also have the following
01:25
a network which is the infrastructure of the model,
01:28
the control which depicts the behavior of the model.
01:31
The demand diagram which contains the demand profiles for the model,
01:36
a run group which holds the configurations of
01:39
particular simulations including their duration accuracy type and more
01:45
results which are the results of a simulation.
01:48
Some simulations may produce multiple sets of results
01:52
and a selection list which is a saved selection of objects.
01:57
Common object types within a network include nodes and links.
02:02
Nodes consist of nodes, fixed heads
02:05
reservoirs
02:06
hydrants
02:07
and transfer nodes.
02:09
Links consist of pipes,
02:11
pump station valves, float valves or inlets,
02:15
non
02:16
return valves and meters.
02:19
It is worth noting that this is how info works W S pro handles objects.
02:23
But that other software programs may classify these objects differently.
02:28
It is also important to understand the modeling workflow
02:31
in its simplest form, the workflow consists of the following steps,
02:36
make changes,
02:38
validate model,
02:39
save changes,
02:41
create run
02:43
run simulation
02:45
view results
02:47
based on the results.
02:48
You may want to make additional changes to and
02:51
create new iterations of the components of your model.
InfoWorks WS Pro stores and orders data within a database. Everything within the database is considered an object, and these objects can be grouped. A group acts like a folder. Groups can also be grouped.
Network, Control, and Live Data Configuration objects are version-controlled.
Most objects must be created within the correct group type, i.e., a Demand Diagram object must be created within a Demand Diagram Group.
The different Groups and Objects in InfoWorks WS Pro include:
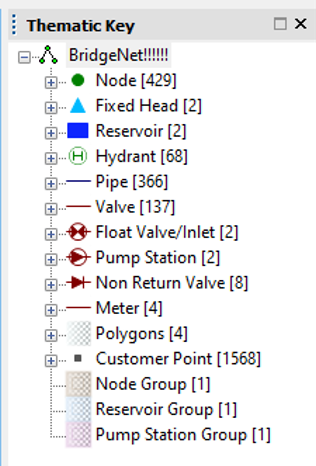
Within a Network, object types include Nodes and Links
Nodes include:
Links include:
The modeling workflow in InfoWorks WS Pro in its simplest form includes the following steps:
After reviewing results, you can make changes or create iterations of the components of your model.
How to buy
Privacy | Do not sell or share my personal information | Cookie preferences | Report noncompliance | Terms of use | Legal | © 2025 Autodesk Inc. All rights reserved
Sign in to start learning
Sign in for unlimited free access to all learning content.Save your progress
Take assessments
Receive personalized recommendations
May we collect and use your data?
Learn more about the Third Party Services we use and our Privacy Statement.May we collect and use your data to tailor your experience?
Explore the benefits of a customized experience by managing your privacy settings for this site or visit our Privacy Statement to learn more about your options.