3D Printing
Learn about 3D printing, and access 3D printing software, customer case studies, and 3D printing learning resources for students and teachers.

What is 3D printing?
3D printing, also called additive manufacturing, is a family of processes that produces objects by adding material in layers that correspond to successive cross-sections of a 3D model. Plastics and metal alloys are the most commonly used materials for 3D printing, but it can work on nearly anything—from concrete to living tissue.
What's 3D printing used for?
Efficiently make one-off parts and create highly complex geometries that are only possible with 3D printing.
-
![]()
Prototyping
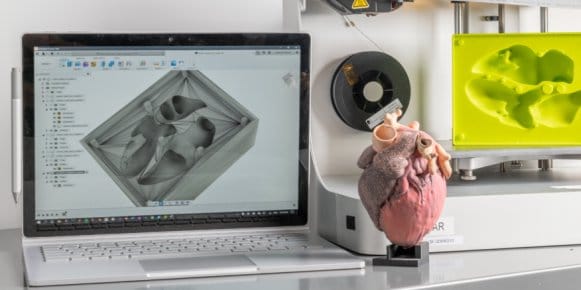
3D printing has long been used to quickly create prototypes for visual aids, assembly mockups and presentation models.
-
![]()
Lightweight parts
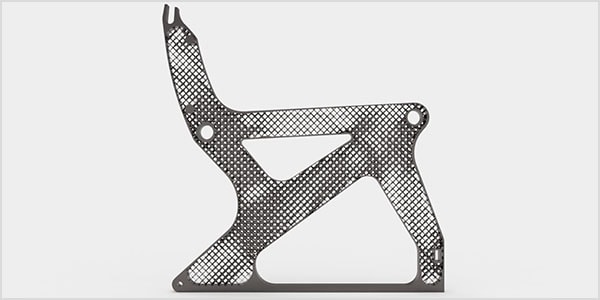
Fuel efficiency and emissions reductions are driving the need for lightweight parts via 3D printing in aerospace and automotive applications.
-
![]()
Functionally enhanced products
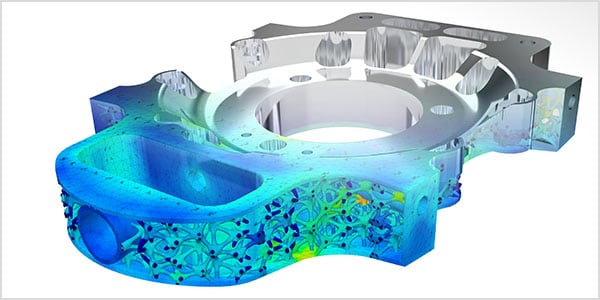
3D printing removes many of the constraints imposed by traditional manufacturing processes that prevent engineers from truly designing for optimal performance.
-
![]()
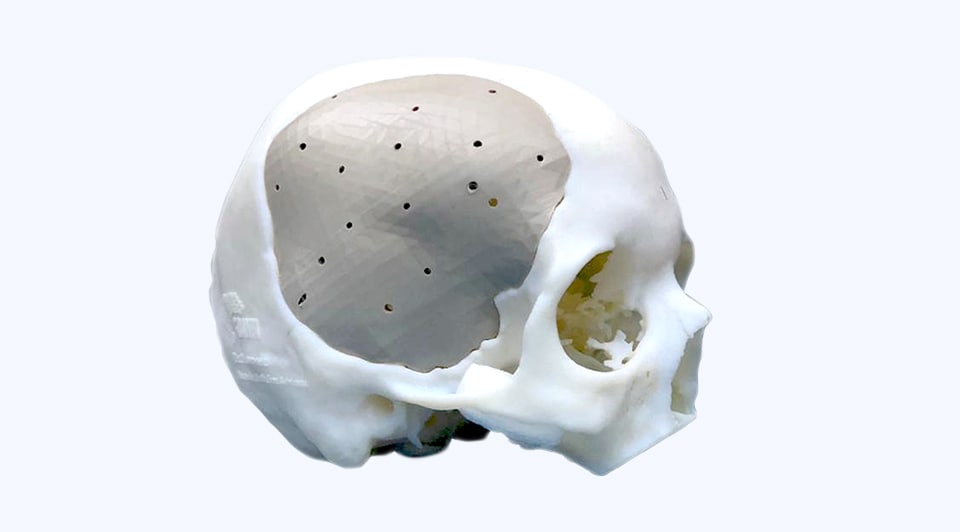
Custom medical implants
To achieve osseointegration, manufacturers are using 3D printing to precisely control surface porosity to better mimic real bone structure.
-
![]()
Toolings, jigs and features
3D printed composite tooling and machining fixtures are often cheaper and faster to produce and conformally cooled inserts for injection moulds can dramatically reduce cycle times.
-
![]()
Metal casting patterns
Combining 3D printing with metal casting bridges the gap between generatively designed parts and proven manufacturing approaches for large metal objects.
3D printing processes & materials

Understanding the different additive manufacturing processes
Explore different additive manufacturing processes and technologies to help you to find the right one for your workflow.

What materials can be 3D printed?
Using the right material for your 3D printed project can make or break a product. This article will cover what materials can be 3D printed.
How is 3D printing software used?
-
![]()
Granta
Mexico City start-up disrupts medical-implant manufacturing
Mexico City start-up Granta is changing medical implant design and fabrication for patients who suffer head trauma.
Image courtesy of Granta
-
![]()
Airbus
Airbus bionic partition
Airbus uses generative design (US Site) and 3D printing to create a strong yet light cabin partition for the A320—and takes the first step toward the plane of the future.
Image courtesy of Airbus
-
![]()
Stanley Black & Decker
A computer designed Stanley Black & Decker’s new tool
Using generative design and 3D printing, Stanley Black & Decker's Infrastructure Innovation Centre is exploring new approaches to creating high-performance industrial tools.
Image courtesy of Stanley Black & Decker
Future of 3D printing
-
![]()
What does the future of 3D printing look like?
3D printing has come a long way from the early days of desktop figurines. As technology continues to evolve, the future is brighter than ever.
-
![]()
How 3D printing is revolutionising the medical industry
Amidst a global healthcare crisis, 3D printing has become a flexible solution to modern medical challenges.
-
![]()
The future of additive manufacturing in aerospace
Learn about how aerospace companies are buying into additive manufacturing and what it means for the industry’s ongoing success.
3D printing tutorials
-
![]()
How to SLICE 3D Prints with Fusion 360
Fusion 360 can slice models for 3D printing, without the need to save the file as an STL. In this tutorial, we'll take a design model into the Manufacture workspace. From there, we'll slice it, simulate the 3D print and save the Gcode.
-
![]()
Fusion 360 Additive for your Ultimaker 3D printer
This video details the FFF workflow along with tips and tricks to utilise Fusion 360 Additive FFF for an Ultimaker 3d printer.
-
![]()
Fusion 360 for 3D printing FDM technology workflow
Learn more about the design process using fused deposition modelling (FDM) 3D printing technology through the power of a very flexible modelling workflow in Fusion 360 software.
3D printing & sustainability

How sustainability and Fusion 360 can help you to save money and the planet
Find out how you can use Fusion 360 software to drive efficiencies and innovation in your processes that will benefit your bottom line and the planet.

Three environmental considerations for the FFF 3D printing process
Every manufacturing process, including FFF 3D printing, has an environmental impact. Learn how to reduce your parts' environmental footprint.
Frequently asked questions
How long has 3D printing technology been around?
3D printing is much older than you might think! The first patents for an additive manufacturing process are dated all the way back to the 1970s. The first true additive manufacturing patent that led to a product is dated to 1984. The first real-world applications of additive manufacturing are in the dental industry, printing out masks of teeth as a replacement for plaster casting from moulds.
What are the benefits of 3D printing?
3D printing is a rapid prototyping (US site) process, mass customisable manufacturing process and a technology that enables the creation of complex geometries previously not possible through other manufacturing processes. It’s also a digital manufacturing technology that requires no tooling changes for revised parts, which means there’s no downtime between product revisions or manufacturing entirely new products.
How much does it cost to 3D print something?
3D printing a part is a combination of the material you wish to use and the volume. Because 3D printing can output using a plethora of plastics and metals, the cost of a part can vary dramatically depending on what you are using, but it can be more affordable per part than other processes.
What 3D printing services does Autodesk offer?
Autodesk offers Netfabb as a dedicated additive manufacturing prep, analysis and simulation tool, as well as Fusion 360, which has a dedicated additive manufacturing space, marrying design, engineering, simulation and manufacturing all together.
Fusion 360 is an excellent choice for creating CAD models for 3D printing. It allows you to create not only “prismatic” models such as gears or brackets, but it also allows you create more “organic” models using T-Splines, including characters, plants and vehicles. You can use Fusion 360 to create and then edit your objects for 3D printing. Bring in models from other software and make modifications, such as de-featuring them by removing small features or blends. Fusion 360 can export as an OBJ or STL file format that is read by most 3D printing software. It also has the ability to print directly to your 3D printer. In addition, Fusion 360 even allows you to edit mesh or STL data that is brought in from a laser-scan or other source. Before printing, you can reduce or increase the surface count, edit out features, fill holes etc.
CAD 3D printing software allows you to conceptualise, design and optimise your models for fitting production technologies
Free resources for 3D printing
-
Access a variety of resources designed to help you to identify how you can add value to your products with additive manufacturing.
-
Learn how to use Tinkercad to model, align and group parts, cut holes, add customised text and specify dimensions. Tinkercad allows you to export and download designs for laser cutting and 3D printing to send designs to Autodesk® Fusion 360.
-
Learn how to take your ideas to reality through the use of design in Fusion 360 software and how to utilise 3D printing to manufacture your idea.
-
Get product updates and enhancements, useful Fusion 360 tips and tutorials, roadmap updates and community stories.
-
Stay current with the latest in 3D printing trends and Netfabb software updates.
-
Learn how to print a PPE face shield in under four minutes and large-scale additive manufacturing.