& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
10 min read
Let’s see a show of hands – Who loves the self-checkout lines at the grocery store? Yeah, they don’t work all the time, and still require some human intervention. But the benefit of being able to scan your stuff, bag it up just the way you like, and walk out the door without having to deal with a cashier or those long lines is priceless.
Amazon looks to be showing us the way towards an even more automated grocery store experience in the future with their new Amazon Go concept. But did the ecommerce giant and their technology just kill the retail employee and a method of doing business that has largely been the same since the 1800s? It’s the automation dilemma.
Amazon Go’s tagline is pretty compelling – “Just Walk Out.” This new retail concept is Amazon’s first foray into the world of brick-and-mortar business, and it seems to be making some waves. What’s the big deal? Think about a grocery store without all of the problems, like waiting in line, waiting to have your items scanned one-by-one, comments about each item you are purchasing, waiting again to have your stuff bagged up, then not having your credit card work, and finally trying to make your credit card work with a plastic bag (sound familiar)? Man, that sounds really inefficient.

Now, imagine all of these problems disappearing, leaving you only the essence of the grocery store experience – getting what you need, and getting out. In an Amazon Go store, you simply grab the stuff you want to purchase, put it in your bag, and walk out. On your exit, all the stuff in your bag will automatically be deducted from your Amazon account. Does all of this sound too good to be true? Here it is in action:
While Amazon Go is only open to Amazon employees in a beta program until early 2017, it’s set to completely shift how retail works in the future, thanks in part to technologies like artificial intelligence, RFID, sensors, and machine learning algorithms. And while we do find it rather odd how hush-hush Amazon is about how the whole operation works, we do know one thing – RFID is going to be huge.
RFID, or Radio-Frequency Identification, was created back in 1948 by scientist and inventor Harry Stockman and was used primarily for military applications. Today, RFID is just about everywhere. Here are a few of the most popular uses that you may or may not know about:
These are just a few of the most common uses for RFID, but these microchips are used in so many other applications it’s almost mind-boggling. Ever check in your baggage at an airport? That’s all handled with RFID. Or those packages that get delivered to your doorstep in two days? Yep, RFID. And one we didn’t quite know about – agriculture uses RFID tags on a cow’s ear to track all of their livestock.
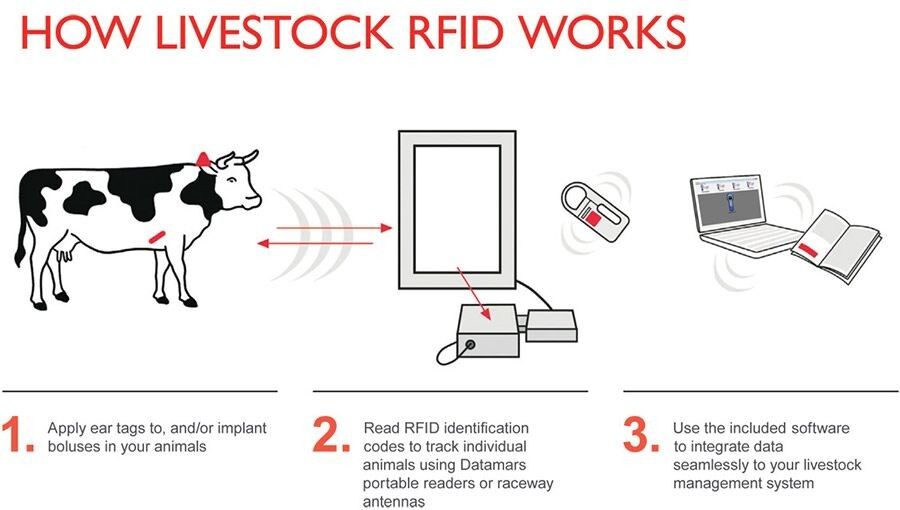
As we get deeper into our digital world, nearly everything will start to connect and transmit data using RFID or some other form of communication. The numbers don’t lie – RFID is projected to grow at 22.4% through 2018, and the smart label market is expected to be valued at $10 billion by 2020.
RFID works on a simple premise, using radio waves and microchips that can both read and capture information. To get all the information you need from a RFID, they use what’s called a tag, which can send and receive information from RFID readers with the help of an antenna as shown below:
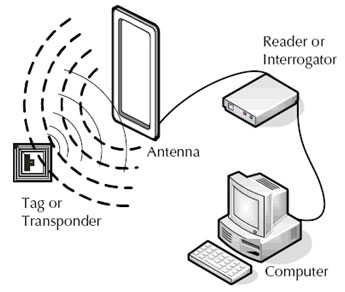
These RFID tags consist of both a processor that can store and interpret the information, along with an antenna that allows the IC to communicate with its home base. There are two types of RFID tags to know about:
These RFID tags also have several class designations that define their capabilities. You’ll find what’s called RFID Class-1, Generation-2 being used in retail operations today. The Class part refers to the functionality of the tag, and the Generation refers to the physical and logical standards of the software. Here’s a quick breakdown of all the classes you’ll need to know about if you find yourself working with RFIDs in the future:
From a public perception, RFID has a ton of privacy concerns. Ever heard of Spy Chips? This is another name for RFIDs, and the conspiracy goes that corporations and governments will use this technology to plan and track your every move. Whether or not this is true, you can’t deny that there is an inevitable loss of privacy and control when it comes to using RFID, seeing as how they can be read without needing to be swiped or directly scanned, and are invisible now.
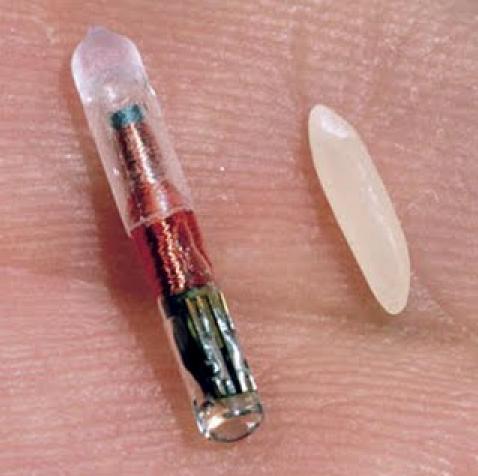
There are also some technical problems to address. Since RFID uses electromagnetic waves like WiFI and cellphones, it’s easy to jam when using the right frequency. This could be a huge nightmare if an entire RFID system gets jammed in a retail situation like Amazon Go, and can even be downright life threatening if the same situation happens in a hospital or military field operation.
RFID readers are also prone to collision issues when signals from two or more readers happen to overlap. But more and more systems are starting to use anti-collision protocols, which allows tags to take turns when sending information to a single reader.
Despite all of these problems that RFID has to overcome it also has many benefits and is a vast improvement over the barcode. Here’s why:
The question on everyone’s mind – is Amazon Go and RFID going to automate away the need for having retail employees? This is a big problem for our economy. The more we automate, the fewer jobs we create. Is the solution to keep pushing forward with advancements in automation at the expense of our jobs, or is there a middle ground out there somewhere? We’re all a little bit nervous, and excited to see what will happen. Here are our predictions for the future:
Rather than killing off the retail employee, we will see stores like Amazon Go reprioritizing how employees are used. Maybe instead of having to check out customers, employees can focus on replenishing stock or assisting customers with product knowledge. So yeah, there might be fewer employees needed to operate a store, but that’s just efficiency at its finest.
This new retail experience is a huge goldmine of data for Amazon and any other company that capitalizes on the opportunity. Amazon Go has a RFID system linked to your Amazon account and sensors in the store that show exactly what you’re looking at and what items you put in your bag, or even put down. Your entire shopping experience is monitored, and Amazon will know exactly what products you buy and how. Is this too much?
We’re already starting to see RFIDs the size of a grain of rice integrate into an ecosystem with other sensors and communication devices. And then some RFIDs can sense temperature, moisture, pressure and vibration. So what’s next? Heartbeat monitors, blood pressure sensors? There’s even talk about RFID “dust” that can be inhaled into the body and act as an internal monitoring system.
In the past, it was a bit of a pain to manage the influx of data flowing in from thousands of RFID tags with a self-managed system. But with cloud-based services now universally available, we’ll start to see the deployment of centrally managed solutions for retail, healthcare, and manufacturing sectors that would have otherwise been a nightmare to monitor and maintain.
We’ve already seen RFIDs getting a bad rap in the past as some kind of crowd control device by governments and corporations. Will we see the government start to get involved in how RFIDs can be used and regulated in various industries? It’s already happening with drones, so it’s only a matter of time.
If there is one thing that Amazon Go can manage to do those other retailers haven’t quite figured out, it’s able to link individual products to individual consumers through their smartphones. Doing this error-free is no easy task, but if there’s one company that can do it, it will probably be Amazon. Until Amazon Go arrives in early 2017, we’ll be keeping our eyes glued to see what kind of magic can be done with RFID and machine learning. And before you go thinking that Amazon is a genius for their new retail concept, you better watch this IBM video. We think someone owes IBM a big thank you.
Subscription to Autodesk EAGLE today and help shape the future of retail, using RFID!
By clicking subscribe, I agree to receive the Fusion newsletter and acknowledge the Autodesk Privacy Statement.
Success!
May we collect and use your data?
Learn more about the Third Party Services we use and our Privacy Statement.May we collect and use your data to tailor your experience?
Explore the benefits of a customized experience by managing your privacy settings for this site or visit our Privacy Statement to learn more about your options.