& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
7 min read
Want to learn about the render workspace in Fusion 360? Look no further. This guide will walk you through all you need to know to get started!
Renders allow you to see what your product would look like in a more detailed realistic way. These renders can be an excellent resource for product marketing, conceptualization, and visualization.
To switch over to the render workspace, simply click on the work environment you are in and select Render.
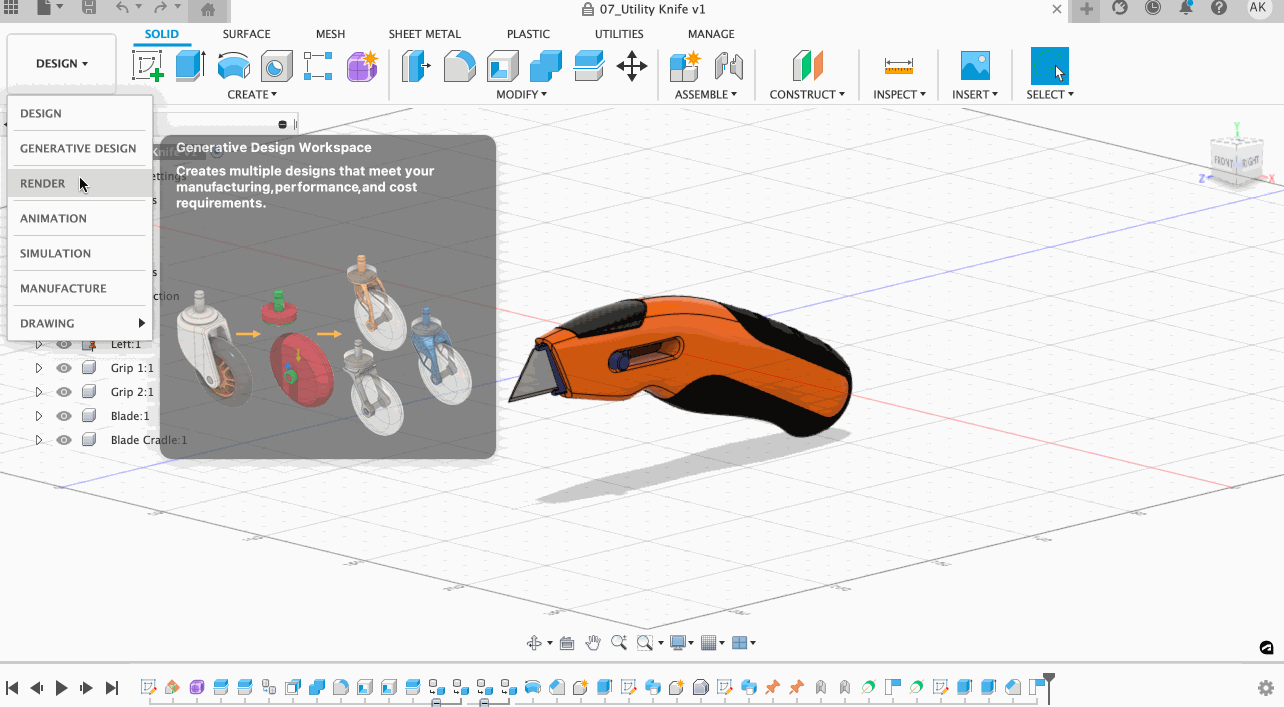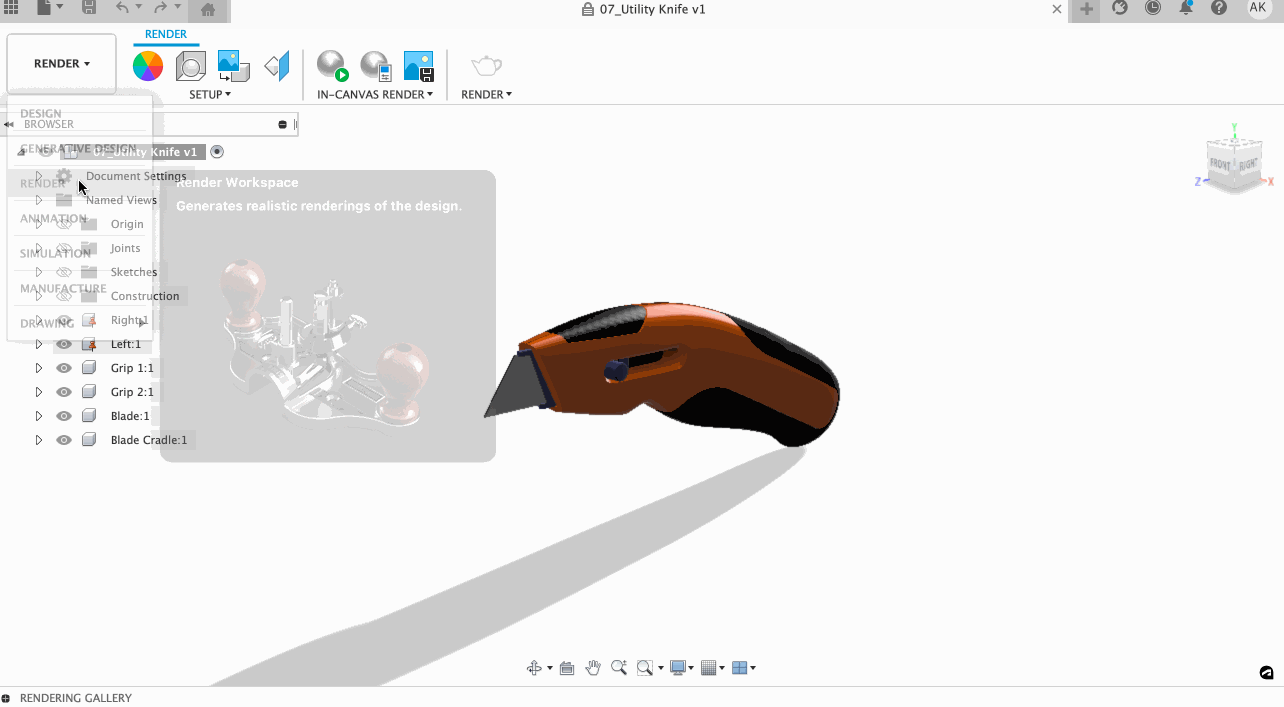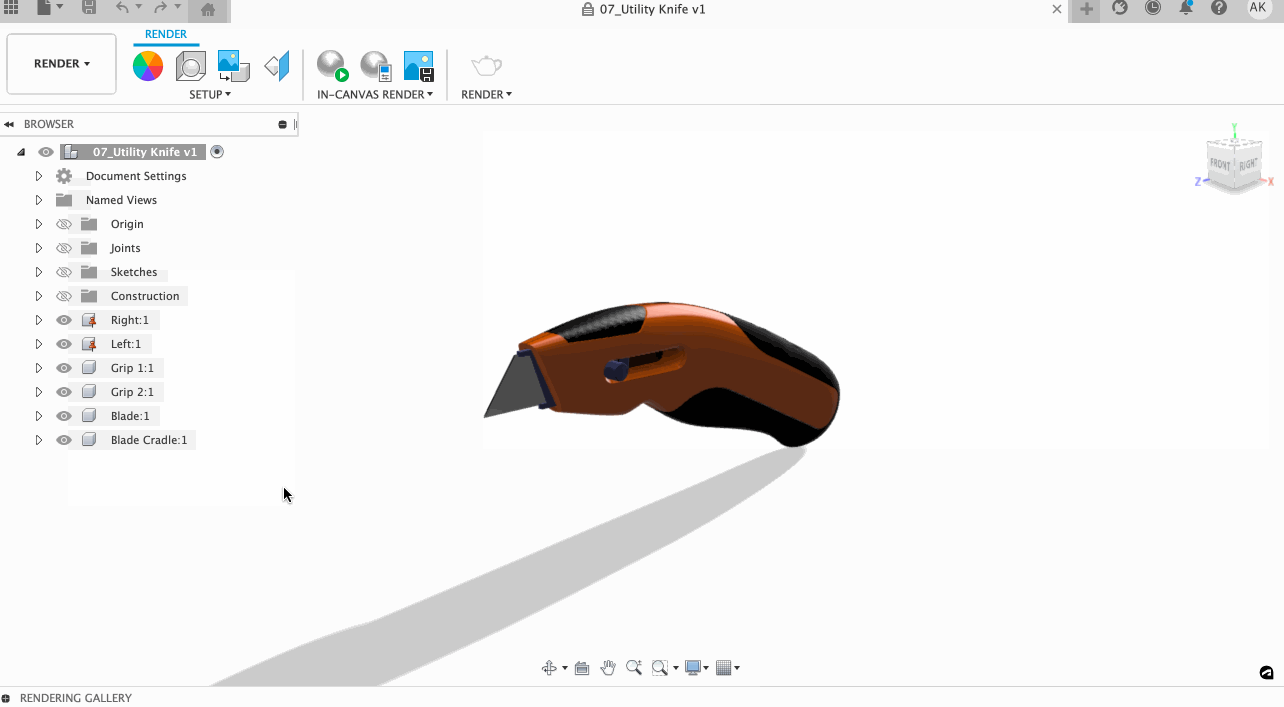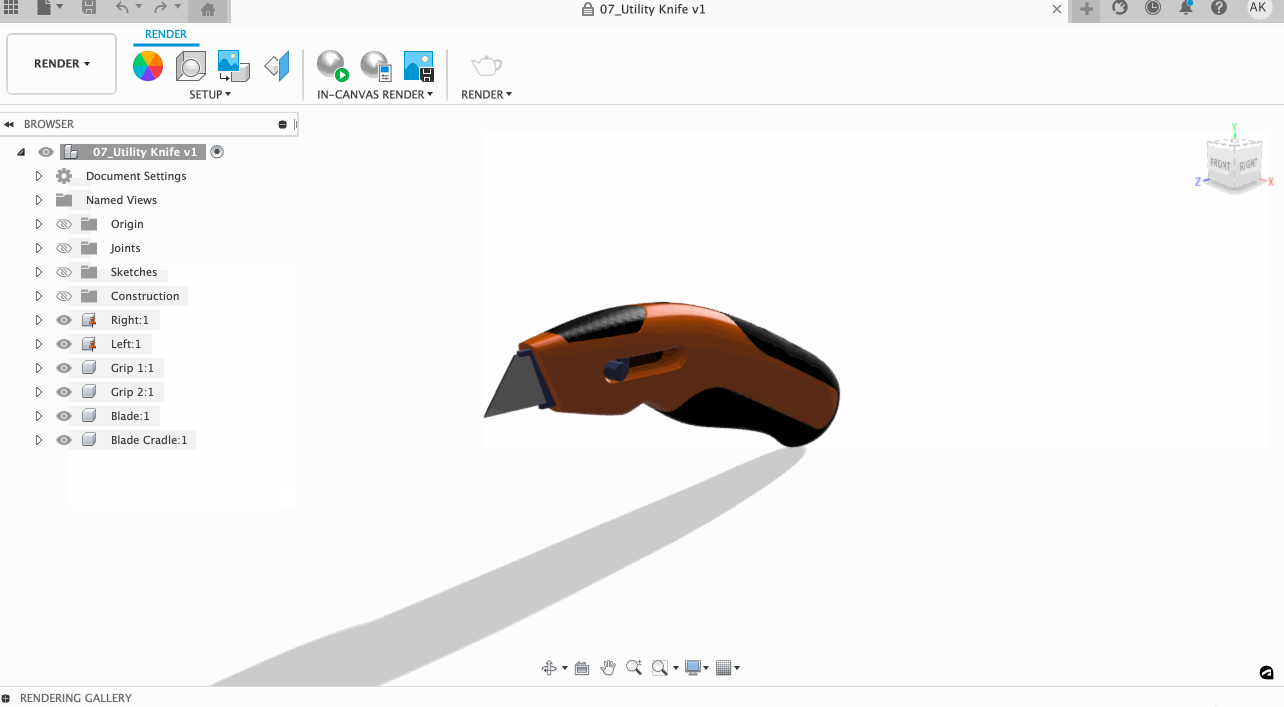
You will immediately notice a drastic difference in how your model appears. To understand how to use this space, let’s look at the commands.
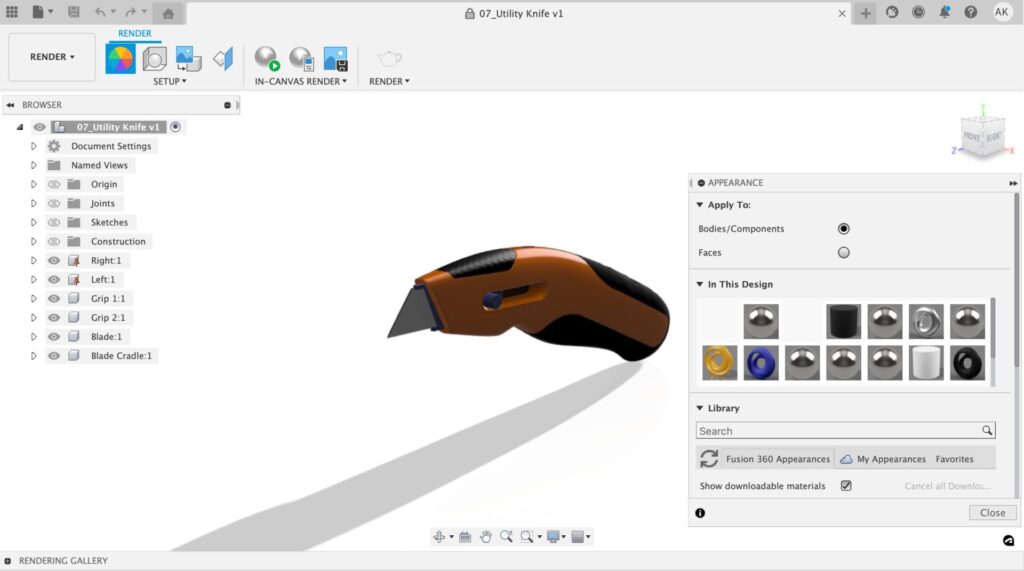
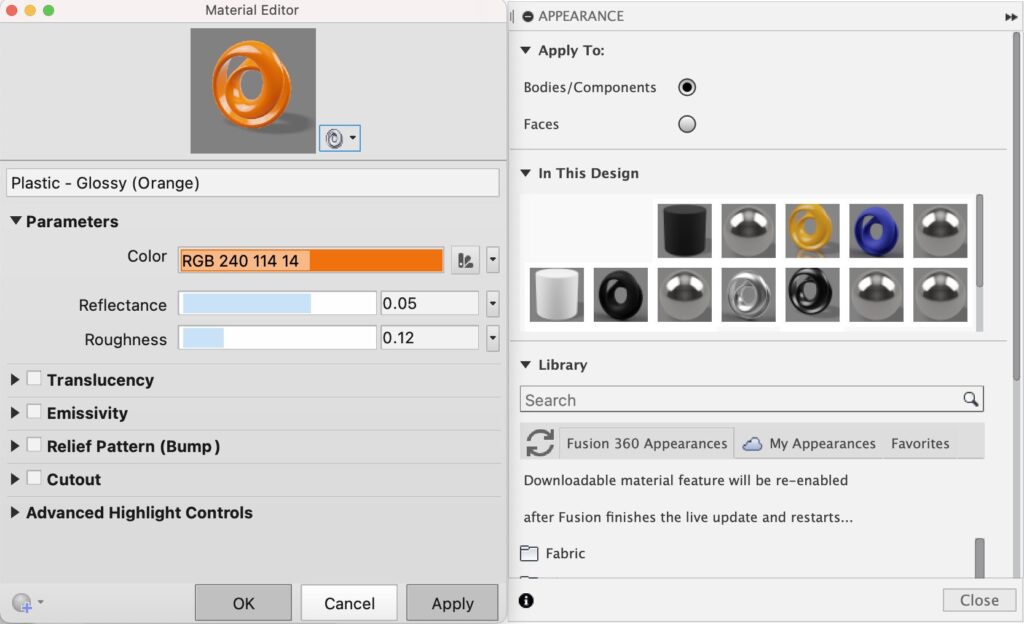
The Appearance command is where you can modify what materials your model is comprised of. Aside from choosing between options like leather, liquid, metal, plastic, wood, stone, and more, you can also adjust the color, texture, and feel of your material within this menu.
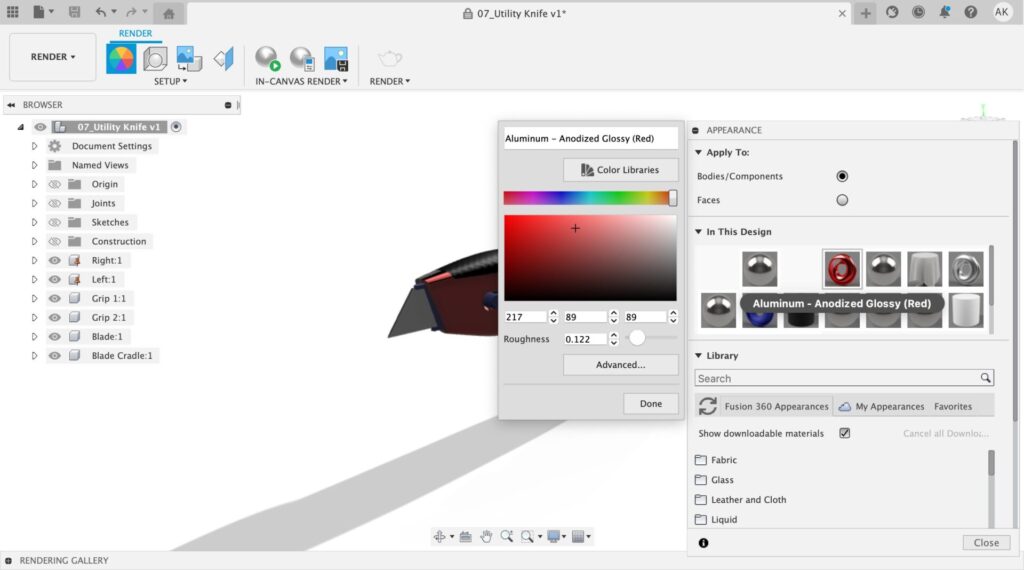
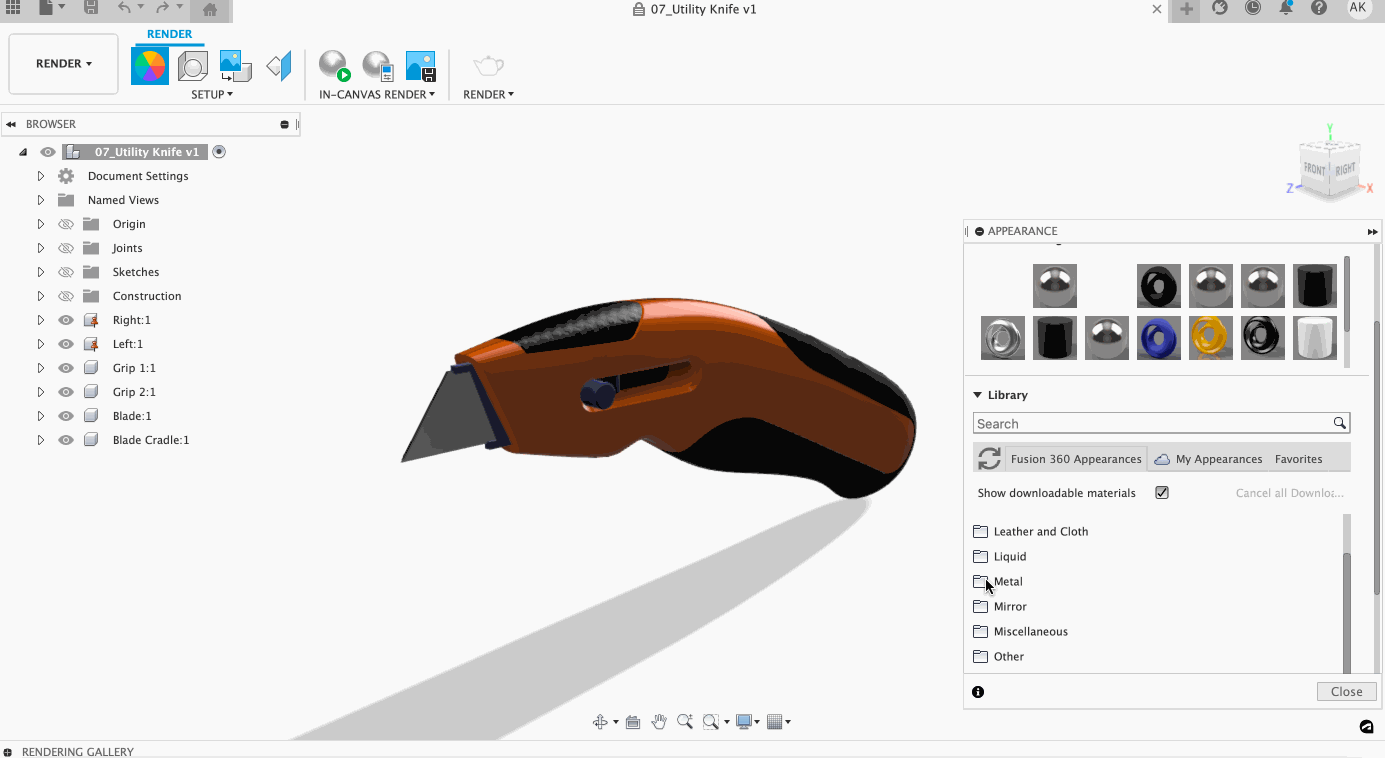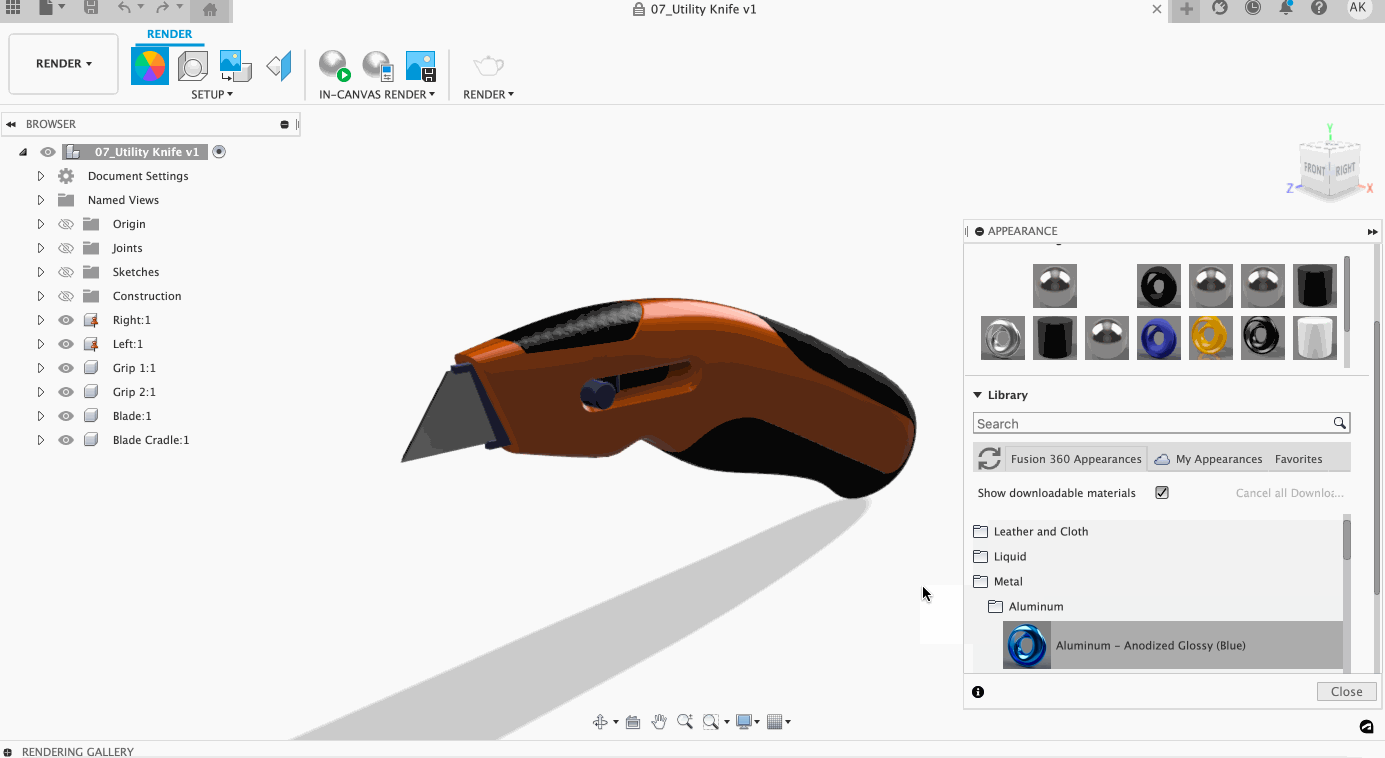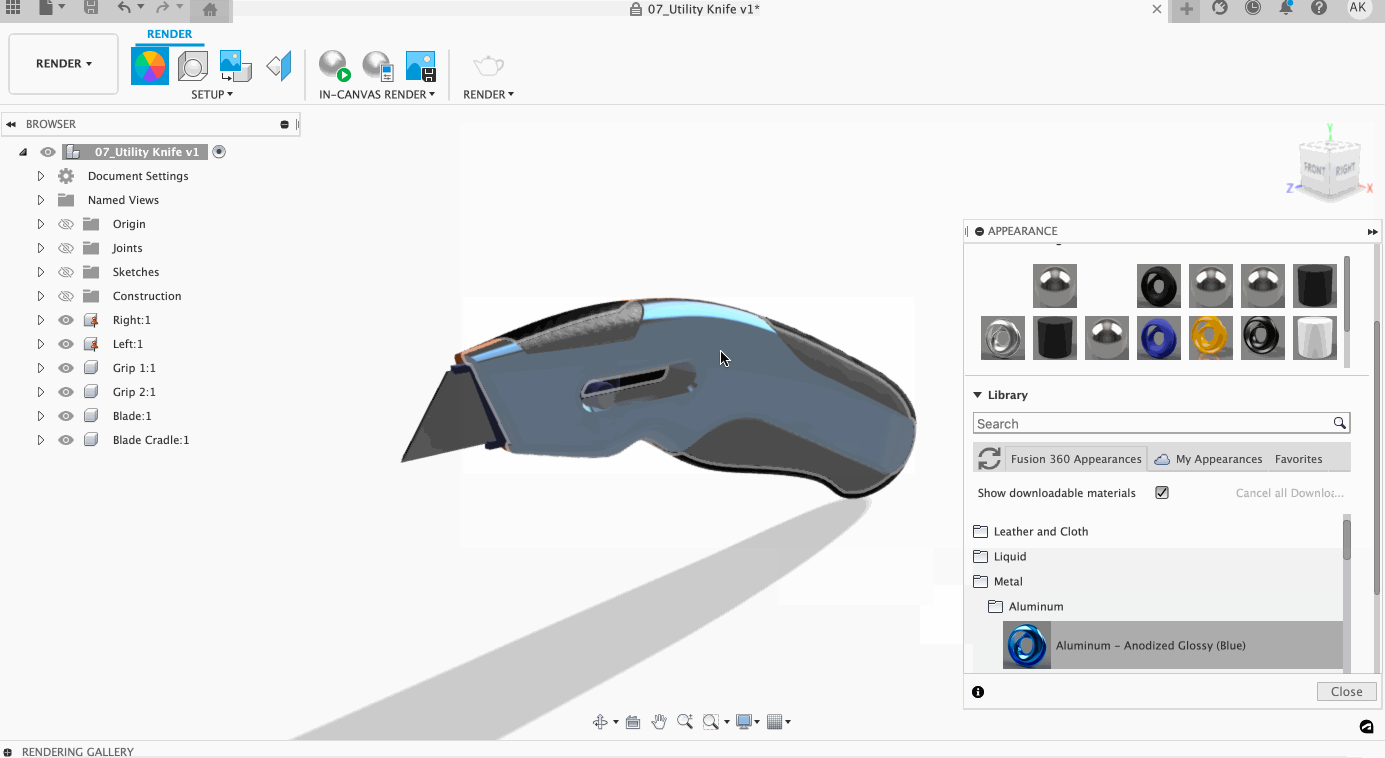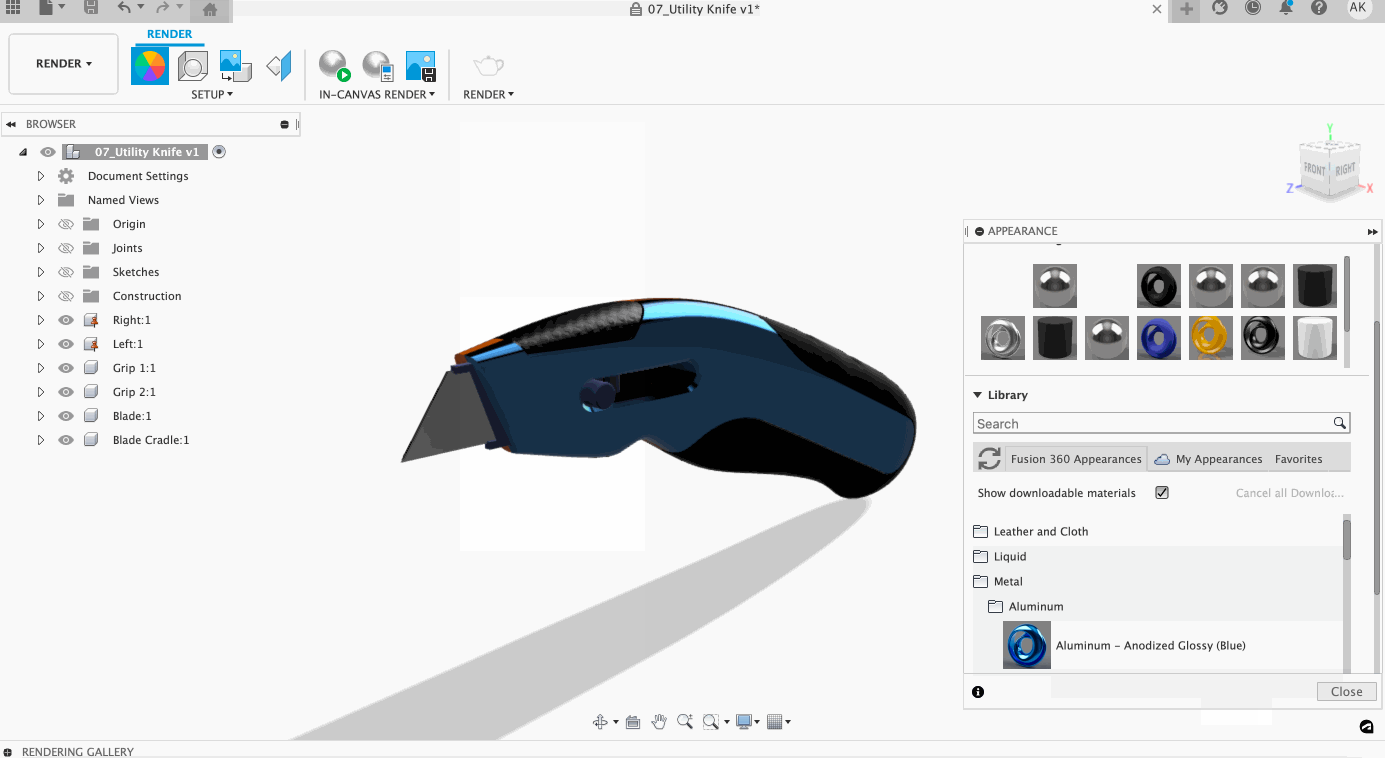
Assigning a material is easy! To assign a material, select the material you would like to use and then click and drag the material onto the body. If you wish to replace multiple bodies, pre-select the bodies in the browser and then drag the material on one of the selected bodies. If you want to replace a material on a face, select Faces within the Apply To settings of appearance, click, and drag.
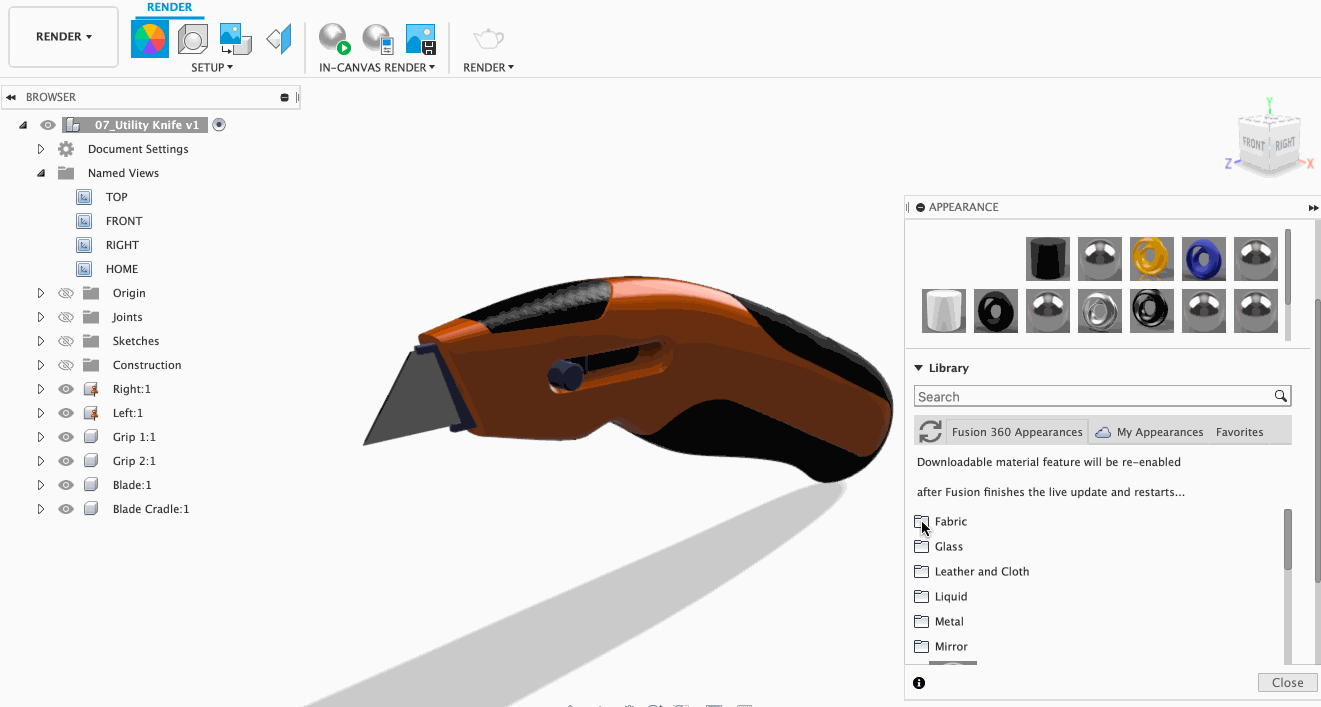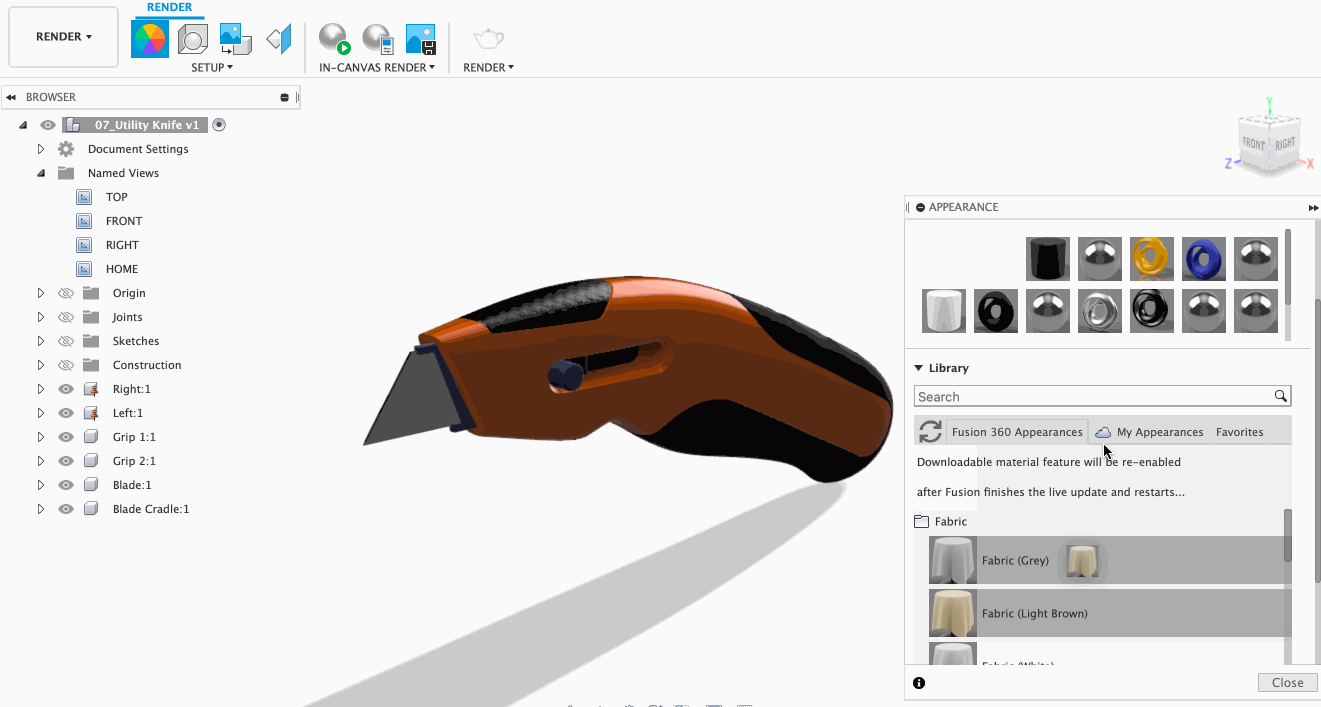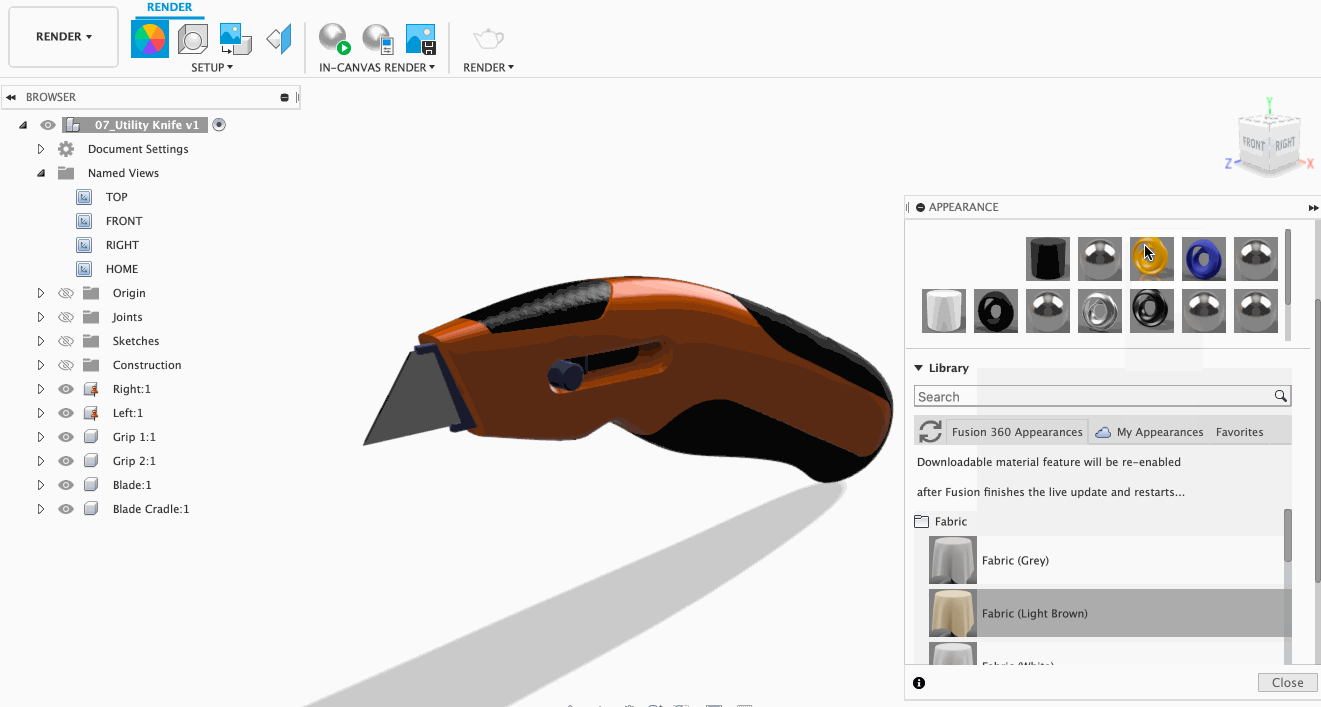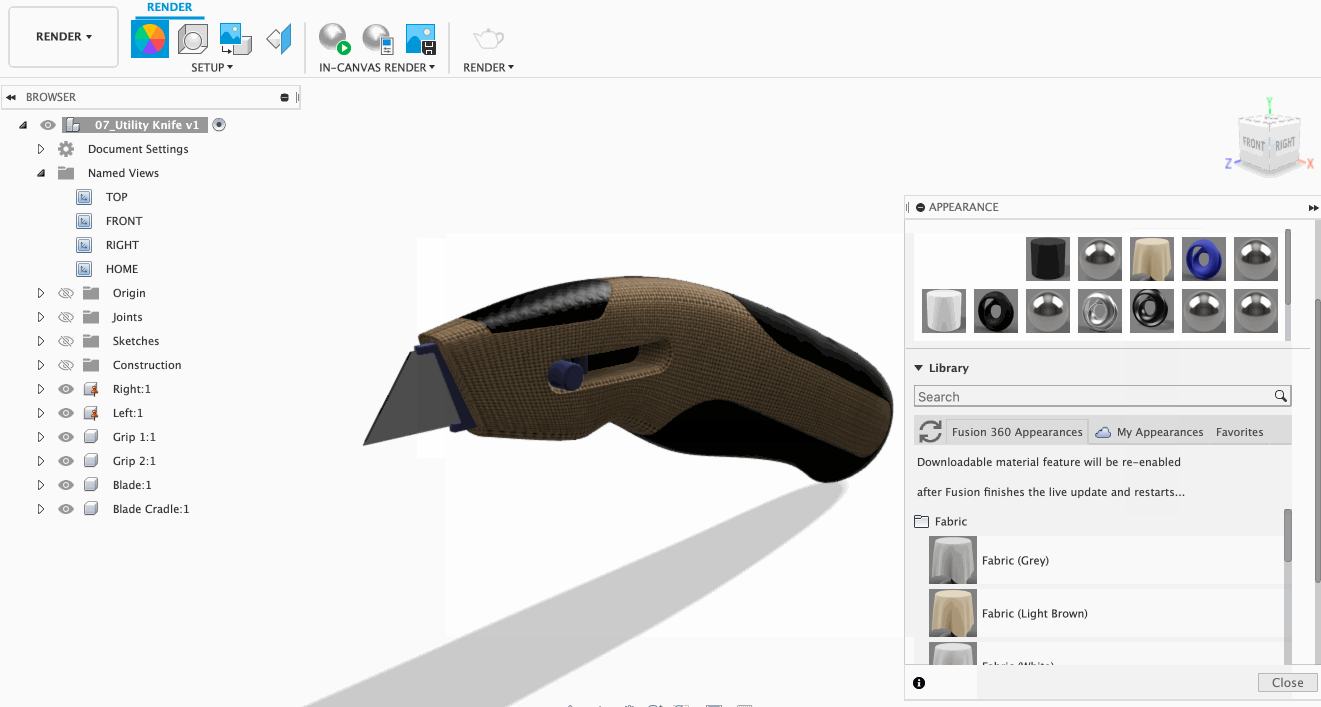
Need to change materials at the last minute? No worries. With this feature, you can easily change all instances of certain texture with a different texture of your choice! To do this, select the new material you want and then drop it on an existing material in the In This Design section of the appearance dialog. This will ensure all of the objects that have the old material applied are replaced.
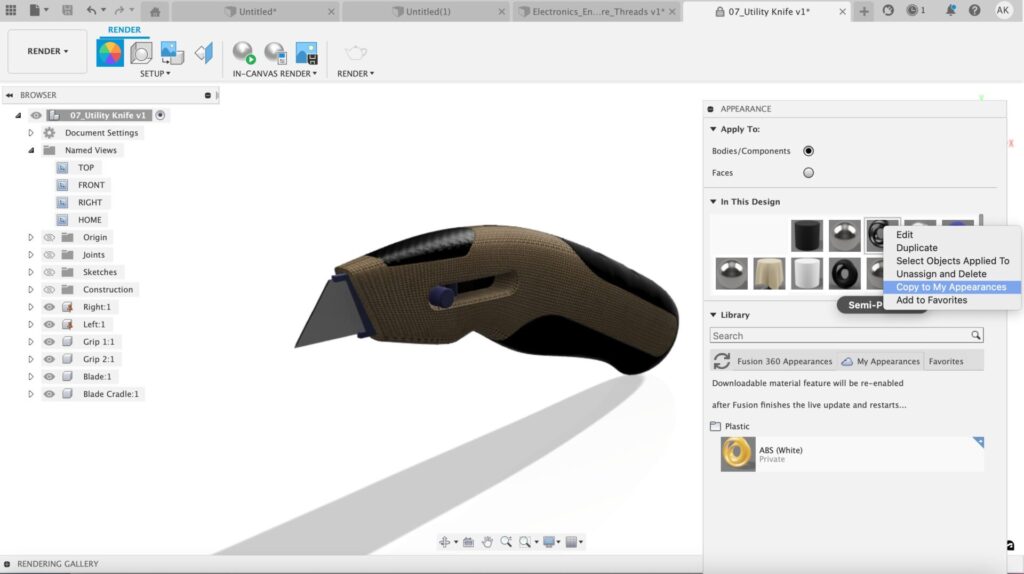
Finally, you created the perfect custom material that suits all your needs. Save this material for later by right-clicking it and selecting Copy to My Appearances. This will store the appearance on your cloud and allow you to access it later on from whatever device you’re accessing your account!
Learn more about Materials and Appearances here.
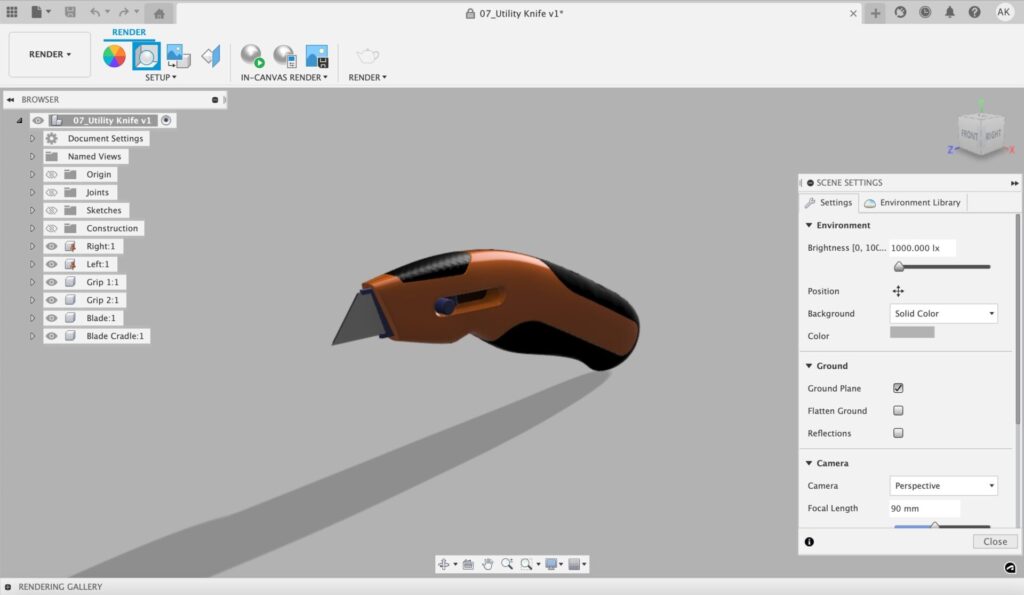
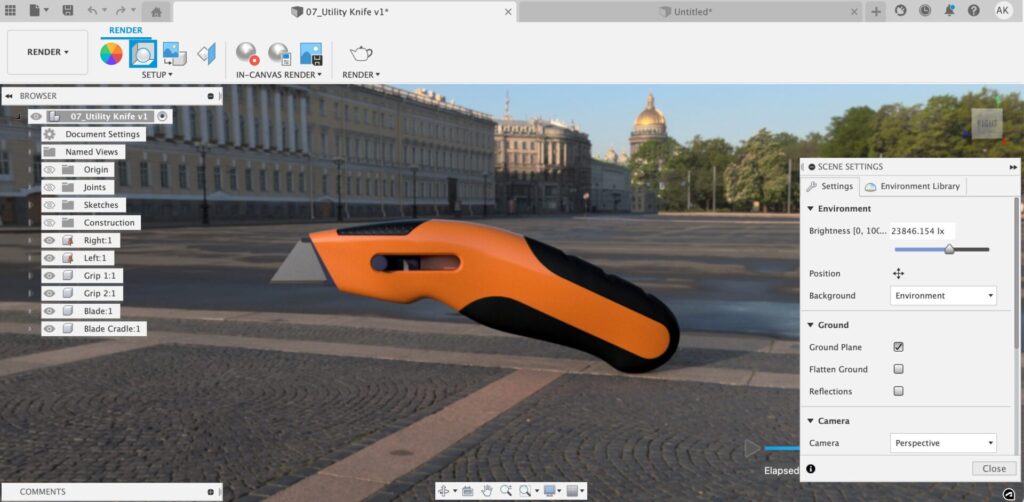
First off, we have Environment, which consists of three basic settings: Brightness, Position, and Background.
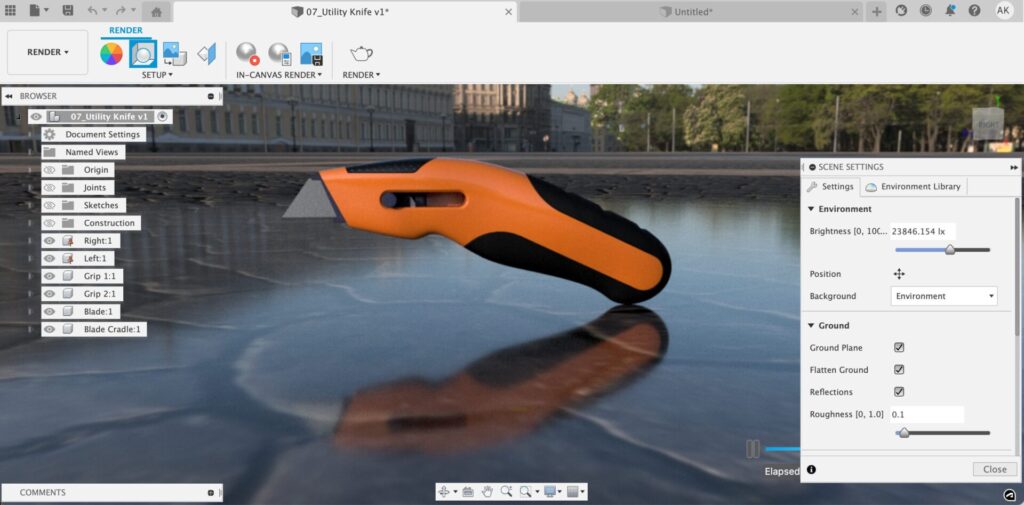
After selecting your preferred Environment settings, you can now move down to the Ground settings. Ground allows you to create a surface for your model to rest on, to ground your model select ground plane. The flatten ground command stretches out your ground plane, this can help make your model appear as though it is resting on a surface, be careful however, this command is not always the best option in grounding your model. Reflection serves to reflect your CAD model off of the ground plane.
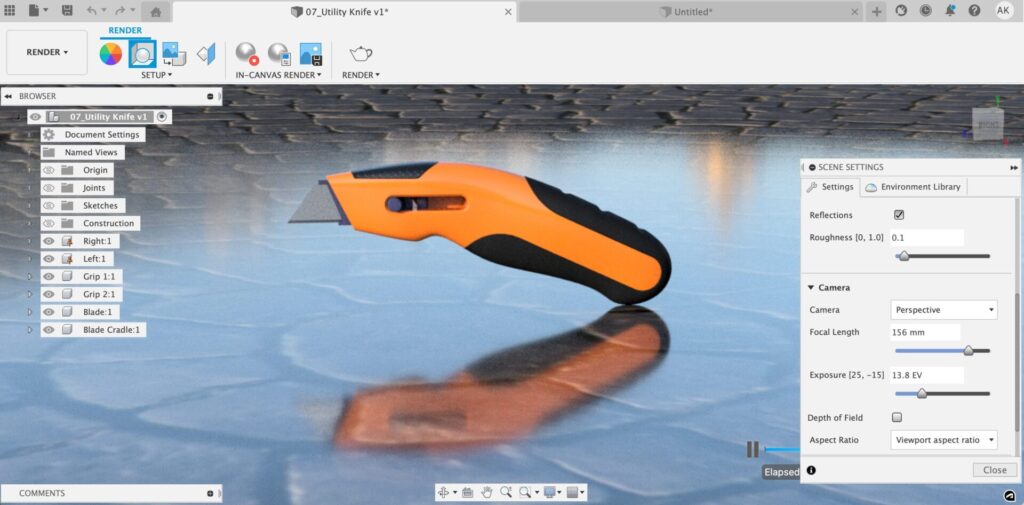
As you move down the settings dialog, you will see the Camera settings. These settings work very similarly to how a physical camera operates. Within this section of the dialog, you can select between camera types and adjust your focal length, exposure, and aspect ratio. You can also create a depth of field to focus on one part of your image while blurring the rest.
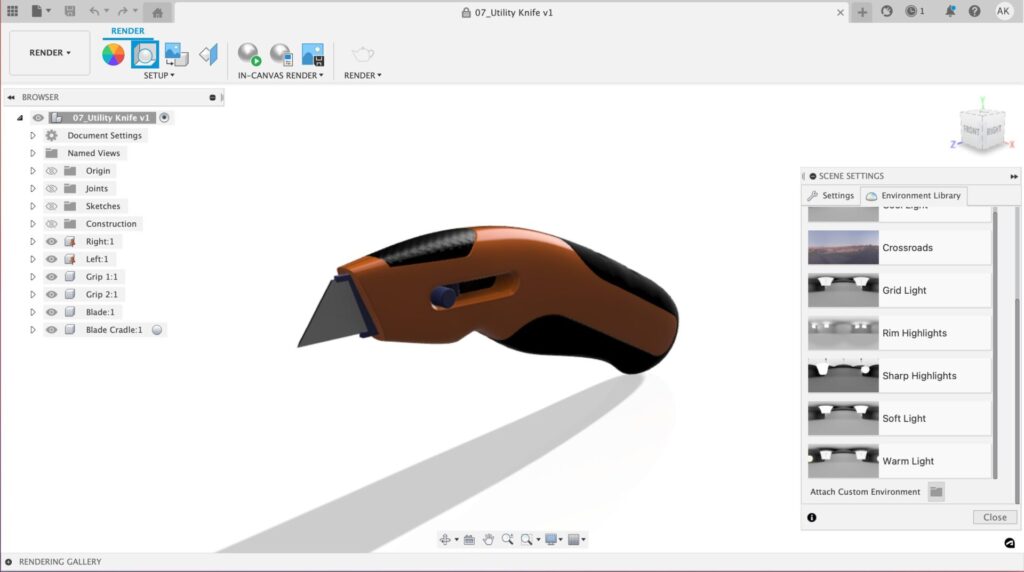
To attach a custom environment first go to the environment library within the scene settings dialog. Next scroll down to the bottom of the dialog and select “attach custom environment”. From here you can upload the HDR image of your choice. Once you are finished, go back to the settings tab and make sure everything is to your liking.
Learn More about Scene Settings here.
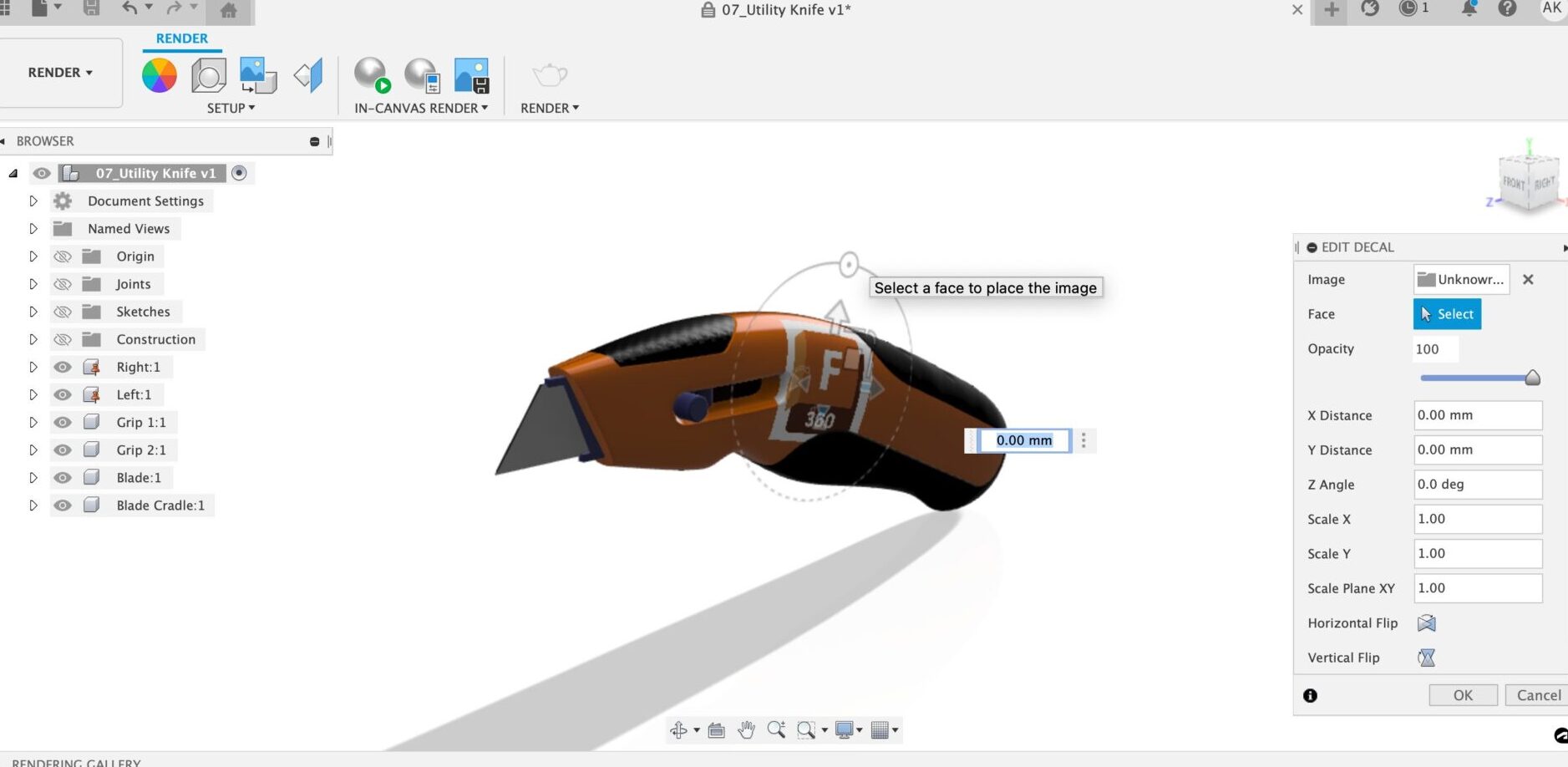
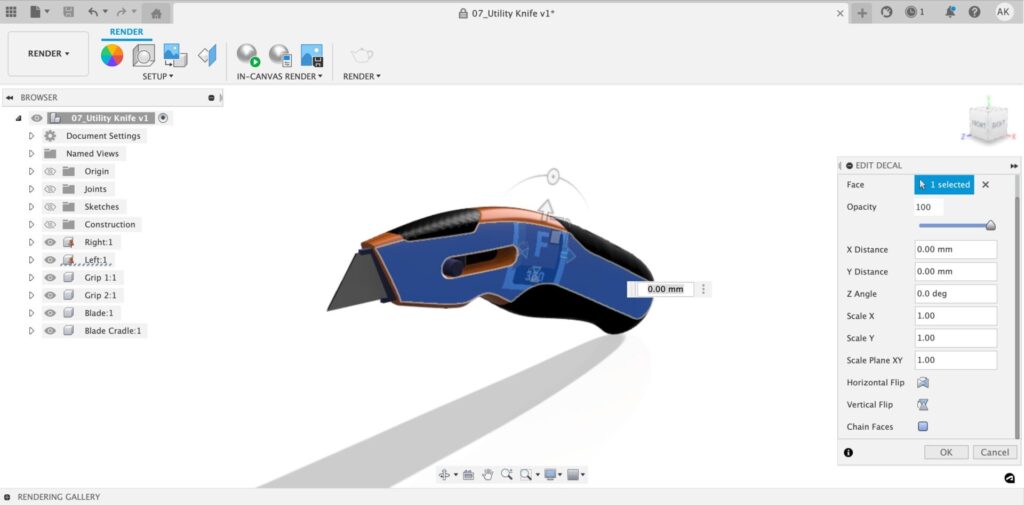
Want to insert a decal? Simply head over to the decal icon located in the tool bar and select your image. Once you select your image select the face you would like to place your image on. From here you will be able to adjust the location, size, opacity, and position of your decal!
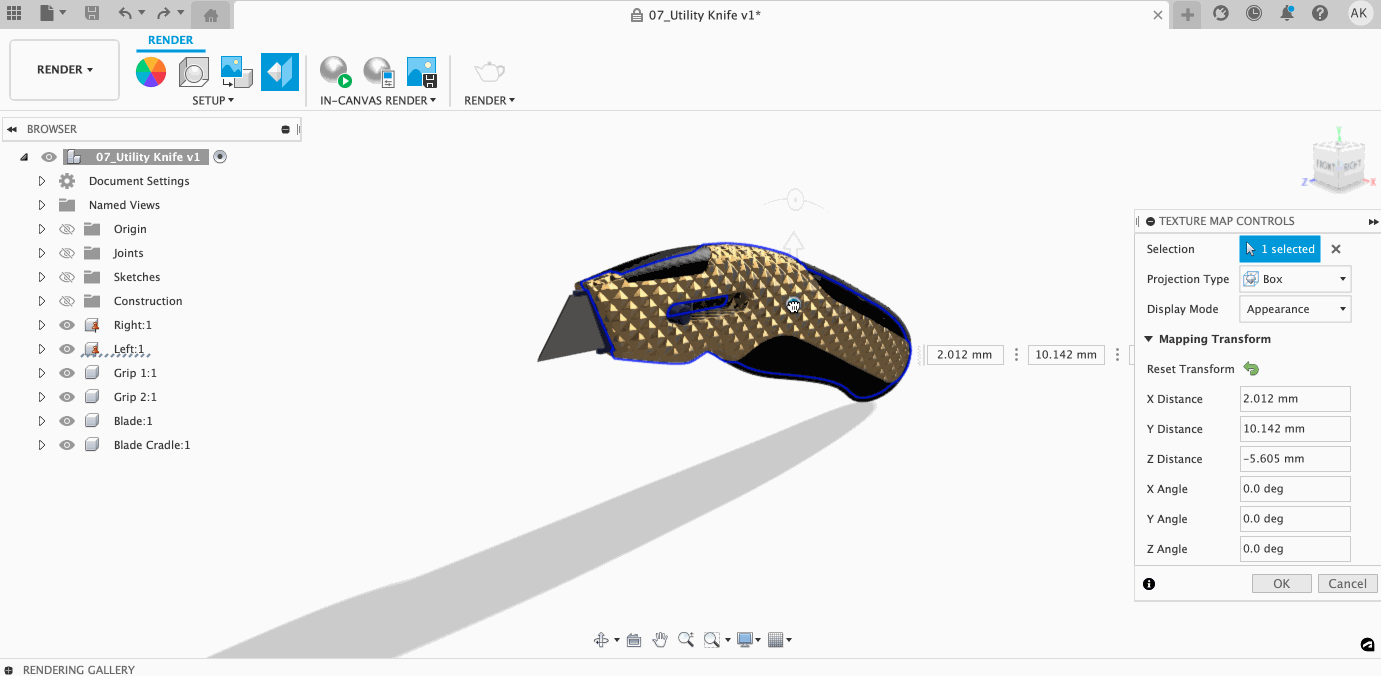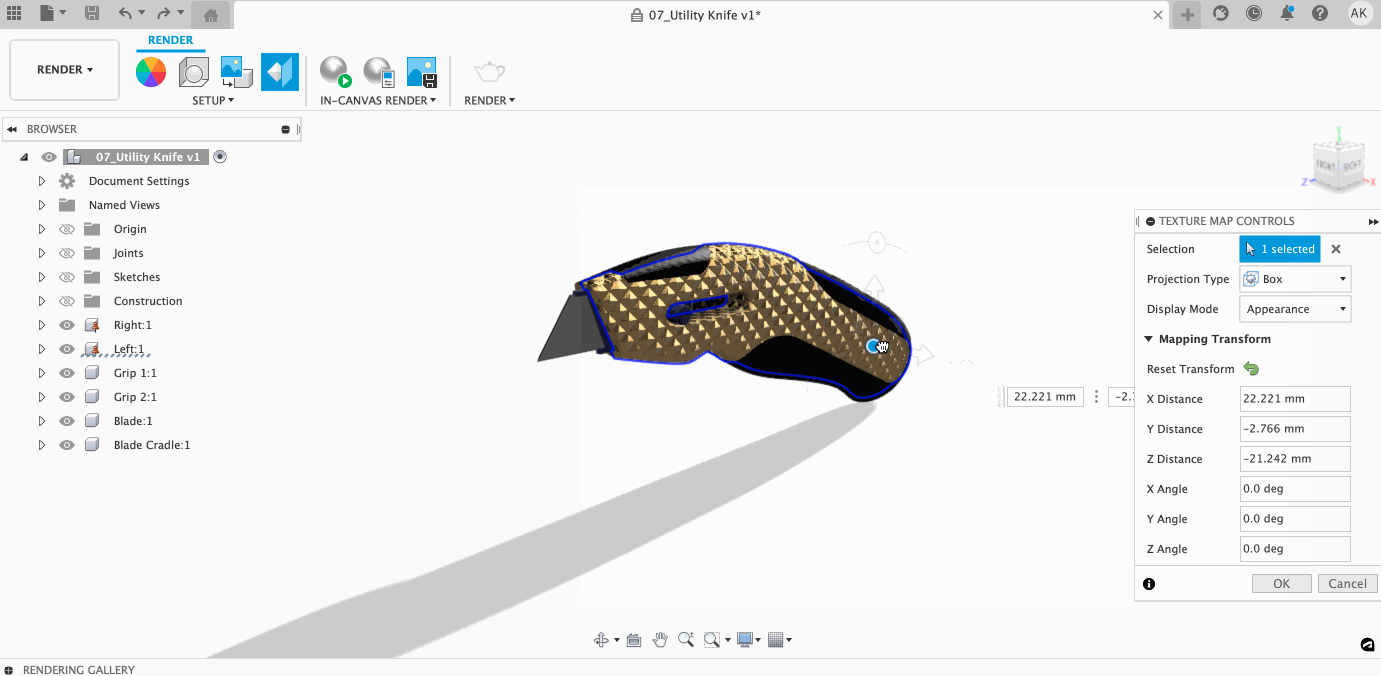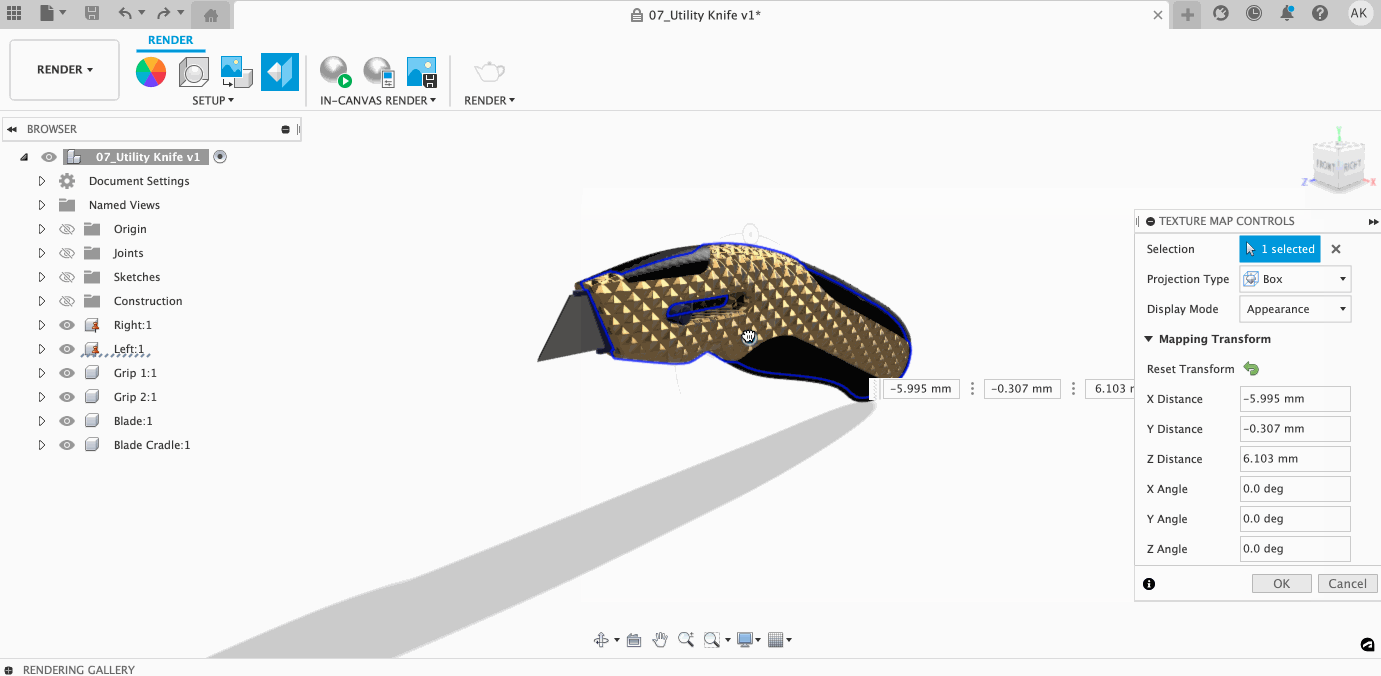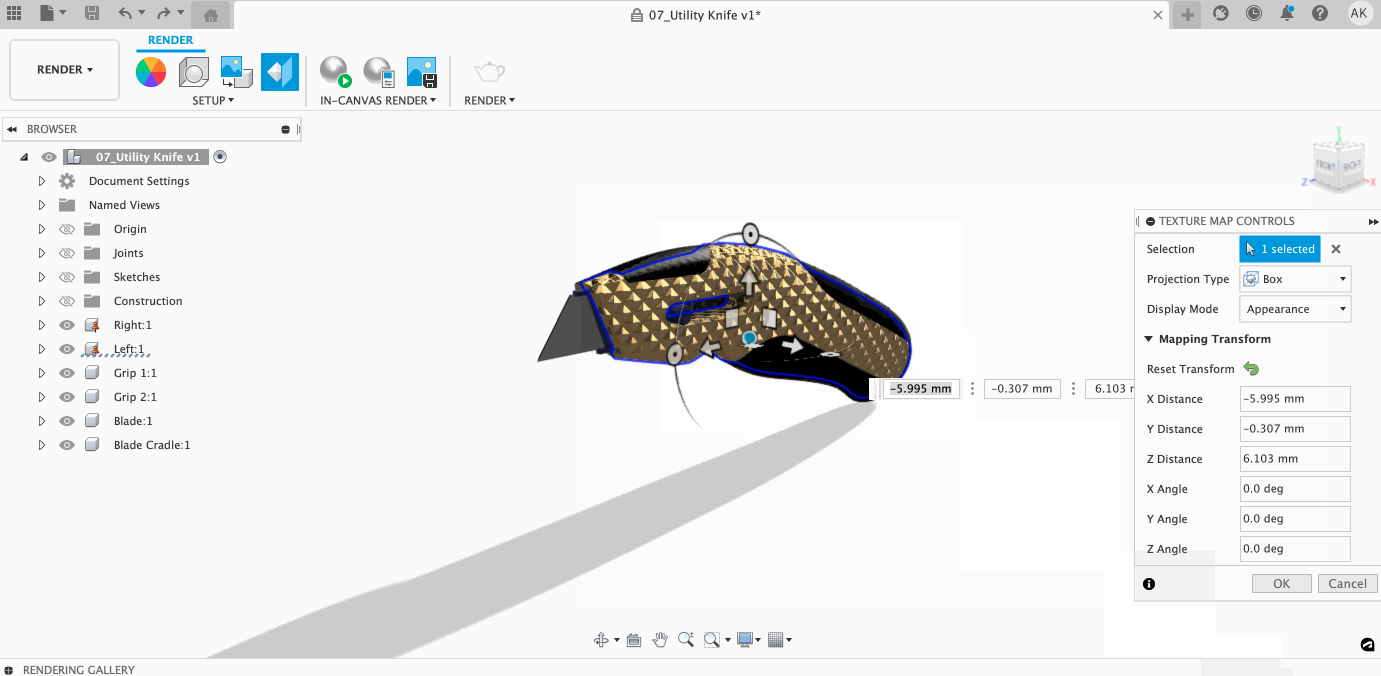
Within the Texture Map Controls dialog, you can control how your texture lays on your model. Once you select a projection type, you can access a variety of controls to make sure your projection is perfect.
Learn more about adjusting Texture Mapping here.
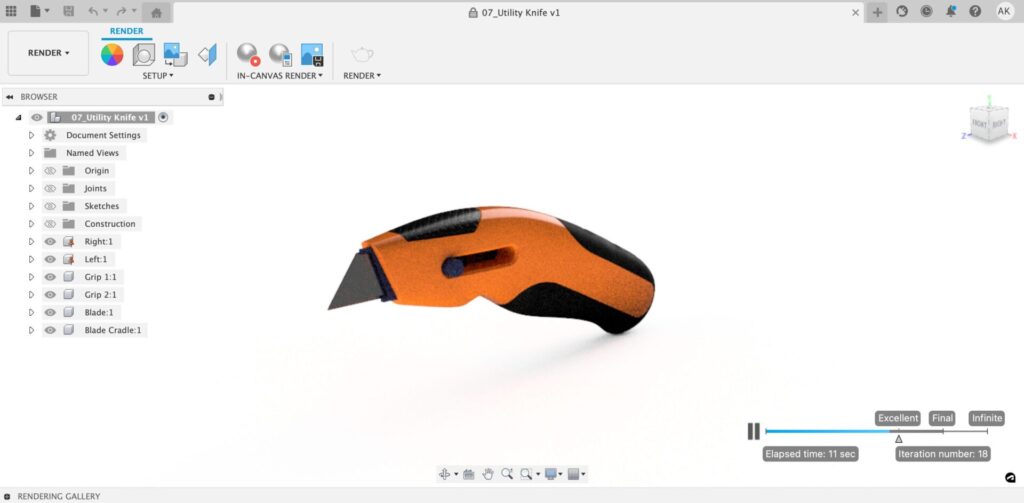
In-Canvas Render and Render commands both render your image over a set amount of time and give you the opportunity to download your render. They serve to get you an amazing final image you can be proud of.
What differentiates In-Canvas Render is the ability to render directly within the Fusion 360 canvas. To use In Canvas render, there are three commands you need to familiarize yourself with:
Once you get the hang of these, you will be able to quickly generate a quality render whenever you want!
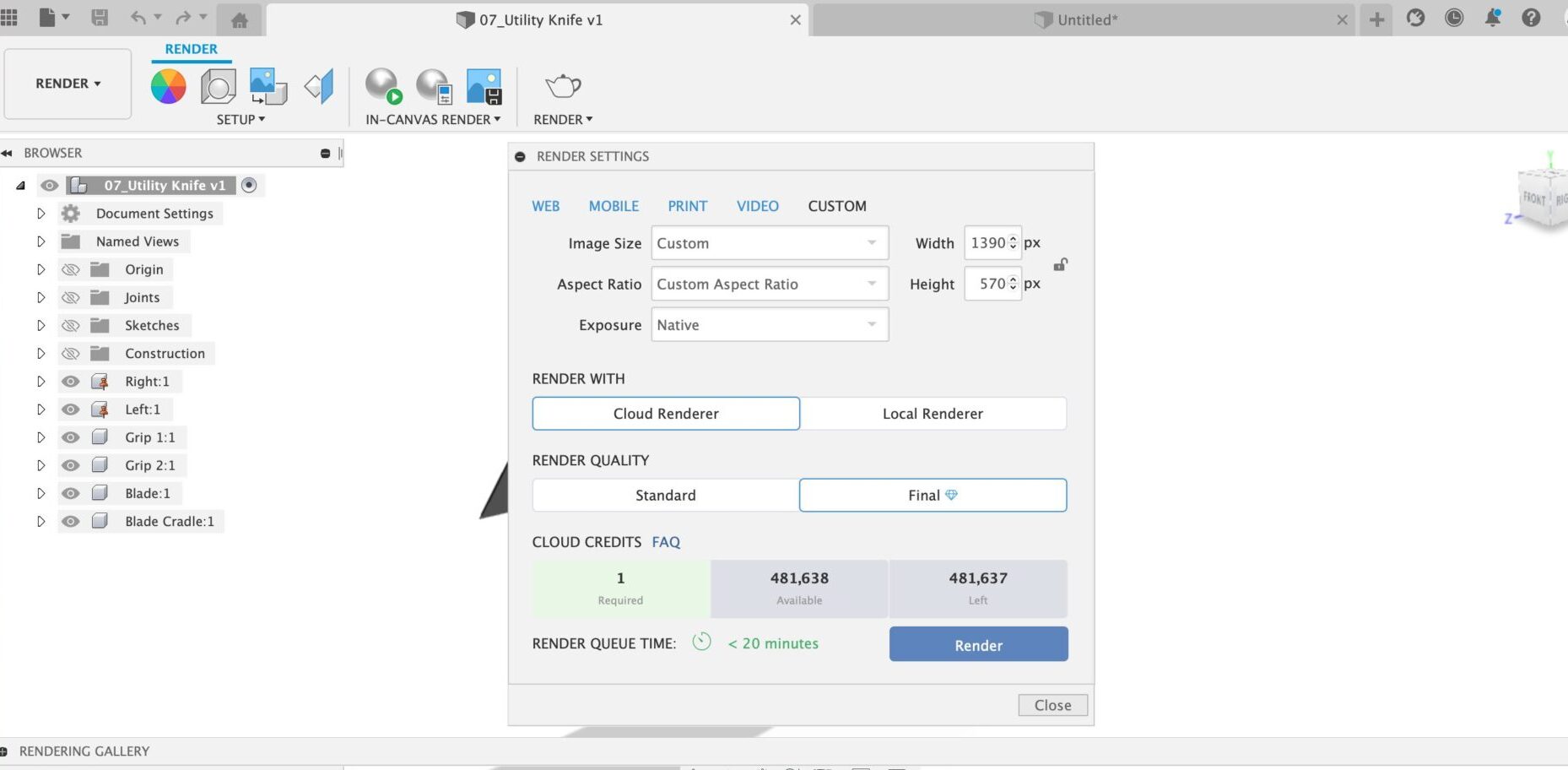
Render gives you greater flexibility in what you do with the final render generated. Once you select the Render icon, you’ll be brought to a settings dialog where you can choose between a cloud renderer or a local renderer. Cloud rendering lets you configure your rendering settings and then send it to process in the cloud. Local rendering enables you to configure your rendering settings and perform the rendering on your machine. While your render is completing, you have the flexibility to move around the workspace and complete other tasks.
When your final render is ready, check out the Rendering Gallery, where you can:
Learn more about the Render command here.
Check out these tutorials to learn more:
Ready to put your rendering skills to the test? Try Fusion 360 today.

By clicking subscribe, I agree to receive the Fusion newsletter and acknowledge the Autodesk Privacy Statement.
Success!
May we collect and use your data?
Learn more about the Third Party Services we use and our Privacy Statement.May we collect and use your data to tailor your experience?
Explore the benefits of a customized experience by managing your privacy settings for this site or visit our Privacy Statement to learn more about your options.