& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
2 min read
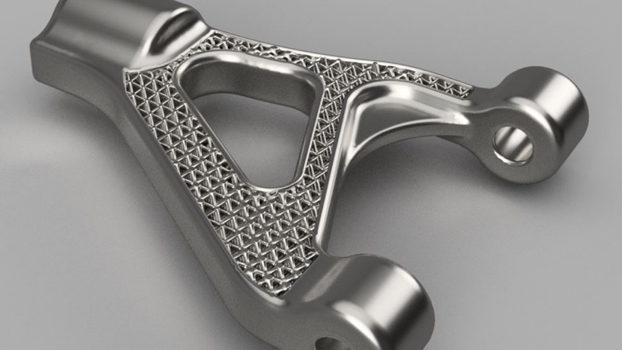
Additive manufacturing made a splash in the consumer market nearly a decade ago, but 3D printing has been around much longer than that. Now that 3D printers are available and functional for anybody with the internet and $200, they have become a necessary tool in most engineering environments. But what about manufacturing?
Metal 3D printers used to cost millions of dollars, and the material wasn’t much less, but they helped make unique parts that could only be 3D printed in the high-end aerospace and automotive industries. With the cost of this technology dropping, these printers are emerging in more industrial spaces.
These printers have the ability to help machine shops save money. Similar to casting a part, metal printers can create parts without purchasing billet, which can then be machined to a refined tolerance or finish. Having this ability to essentially create a cast without a mold provides some unique opportunities for a machine shop.
Printing with PLA or ABS plastic provides the opportunity for fairly quick and inexpensive prototyping. While you might think that should be left to an engineering firm, but prototyping in a machine shop can save you headaches by getting a part in-hand before cutting (and potentially wasting) raw material.
Moving from CAD to prototype to CAM to machining is an efficient workflow that can help not only make parts faster, but it can help make better parts more efficiently. What’s more, it’s helps to demonstrate workholding needs and manufacturing challenges that you can easily present to a customer.
Speaking of workholding, there are a number of opportunities to utilize a 3D printer for workholding. Creating softjaws is quick and easy with a 3D printer, so long as you aren’t planning to machine with a lot of force.
Printed workholding is also a great way to hold odd-shaped parts or if you want the workholding to be more sacrificial than aluminum.
Similar to the perks of prototyping in a machine shop with a 3D printer, they can also help simplify the process of designing for manufacturing. As the gap continues to close between designers/engineers and manufacturers, the need for properly designing parts for manufacturing is more apparent than ever.
3D printing in the machine shop provides the opportunity to test and vet designs before they are ever CAMed up.
While the need for 3D printers in the machine shop may be a new thing, they are far from replacing traditional manufacturing. 3D printing has become much less expensive in the last decade, and now they are the perfect tool to help more the machine shop more efficient and productive.
By clicking subscribe, I agree to receive the Fusion newsletter and acknowledge the Autodesk Privacy Statement.
Success!
May we collect and use your data?
Learn more about the Third Party Services we use and our Privacy Statement.May we collect and use your data to tailor your experience?
Explore the benefits of a customized experience by managing your privacy settings for this site or visit our Privacy Statement to learn more about your options.