This post is also available in: Deutsch (German)
VR and AR provide virtual 3D environments for designers, engineers and clients to preview products before they hit the production line. In this article, you’ll learn about the different ways these technologies support the design and review process.

Popular culture has always been one step ahead of technological advancements in terms of creativity. The idea of virtual reality (VR) first emerged in a short story titled “Pygmalion’s Spectacles,” written by Stanley G. Weinbaum in 1935. Since then, VR has slowly emerged from the tech industry with varying degrees of success. The dream of any VR enthusiast is to “experience worlds within worlds,” as spoken by Keith David’s character in Season 6, Episode 2 of Community.
In the last ten years, VR has become a tangible reality for engineers and consumers. So what happened to that short augmented reality (AR) craze a few years ago? Well, AR has become more helpful in the design and manufacturing process than in the consumer market. AR gaming never quite got off the ground. However, designers and engineers have been able to use 3D models and renderings to examine products before production.
VR vs. AR
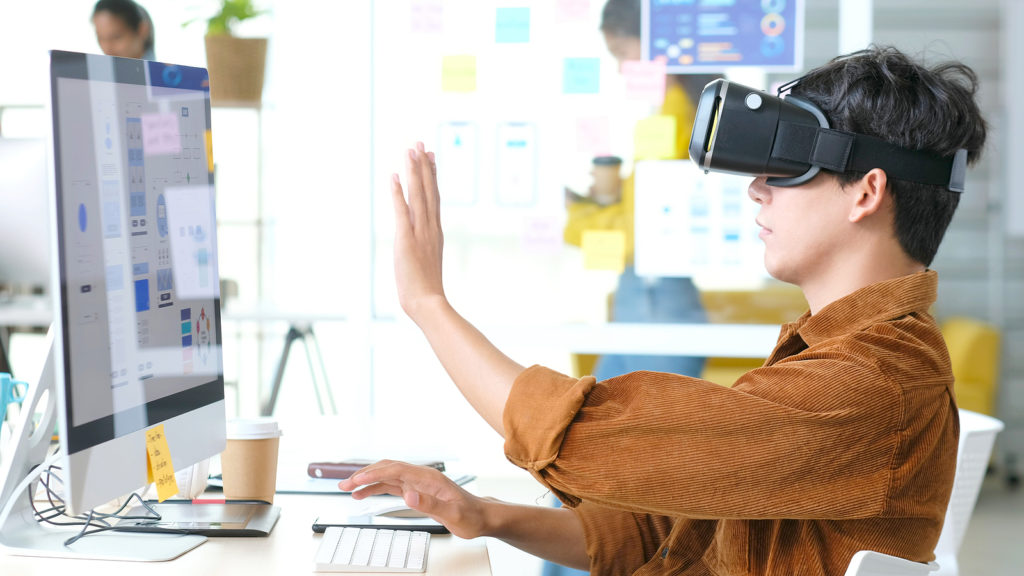
The main difference between VR and AR is immersion. Virtual reality utilizes a headset to immerse the user in a 3D digital environment completely. The user can see, hear, and virtually touch their surroundings while in the headset. Thus, virtual reality can have a very realistic aura.
On the other hand, augmented reality is a superimposed 3D graphic design that lays over a real-world picture. Usually, AR is used on a mobile device via the camera and USDz files — an unencrypted zip file that packages all data required for an AR rendering. AR is most beneficial to visualize a 3D design in a real 3D space.
Real-World VR Applications
One of the most readily known and, quite possibly, the most popular application for VR is set in the gaming industry. Sony, Microsoft, Facebook, Google, and Samsung — to name a few — are leading the charge in VR gaming technologies. But how is VR shaping other industries like the design industry?
One key benefit of VR is the ability to view products in their intended spaces without ever leaving the office. Virtual reality can help designers and engineers visualize the products with their clients in an immersive environment. It can also be used in the ideation phase thanks to VR sketching programs like Gravity Sketch.
VR is not limited to gaming and design. Other applications include:
- Virtual dining
- 360° video live streaming
- Virtual classrooms during a pandemic
- Vehicle and flight simulation
- Combat training
A startup company called OVR Technology is attempting to incorporate smell into the VR experience. VR can simulate sight, sound, and movement, but it lacks other senses like smell. Again, the ultimate goal of VR is to accomplish complete immersion.
Real-World AR Applications
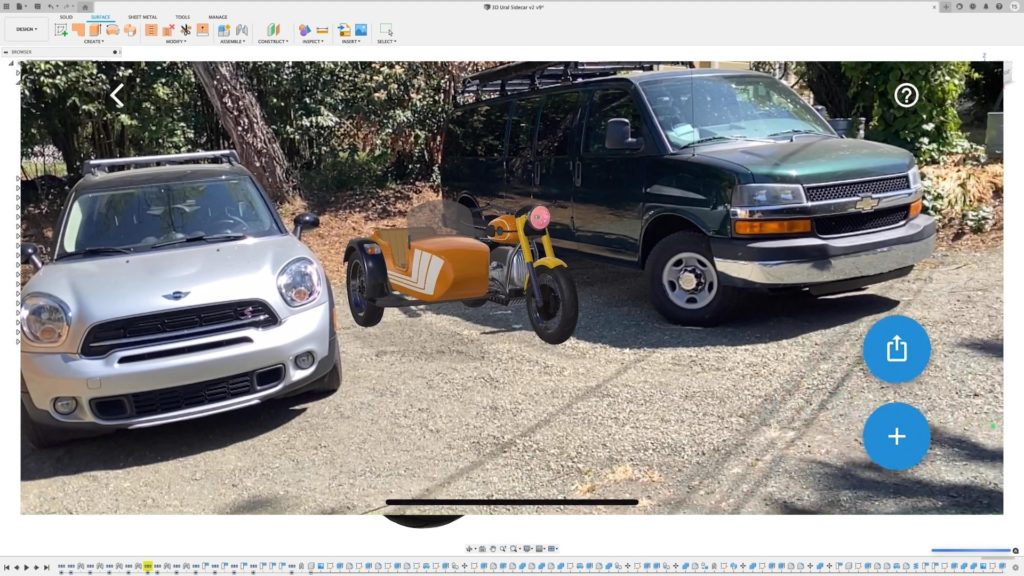
Unlike VR, augmented reality exists not in a prefabricated digital world but in our reality. Consider, for example, the benefits of 3D visualization of molecular geometry superimposed over a real-world live video feed. AR provides the next best thing to holding an object. In this way, AR helps engineers understand three-dimensional structures within their designs.
Augmented reality can be used to visualize furniture placement in someone’s apartment, molecular structure in a classroom, or 3D computer-aided designs in a lab.
Autodesk’s Fusion 360 recently added USDz export as a feature. Designers and engineers can now visualize their 3D models in real-life environments right from a mobile device or tablet (learn how here). Like VR applications, USDz files can be useful during the client review process, as clients can see how the product will interact with its environment in a more immersive way than a 2D sketch or render.
The Future of Visualization Technologies
AR and VR platforms will continue to change as innovations continue to arrive. Engineers and designers will inevitably find a way to incorporate more senses and introduce new applications to VR and AR sectors.

