Product development requires careful planning, creativity, and iteration. Each step is crucial in bringing a product to life, from the initial design concept to the final manufacturing stage. This article explores the essential stages of product development, highlighting their significance and how they contribute to creating successful products. We’ll also dive into how Autodesk Fusion can support design and engineering teams every step along the way.
1. Design
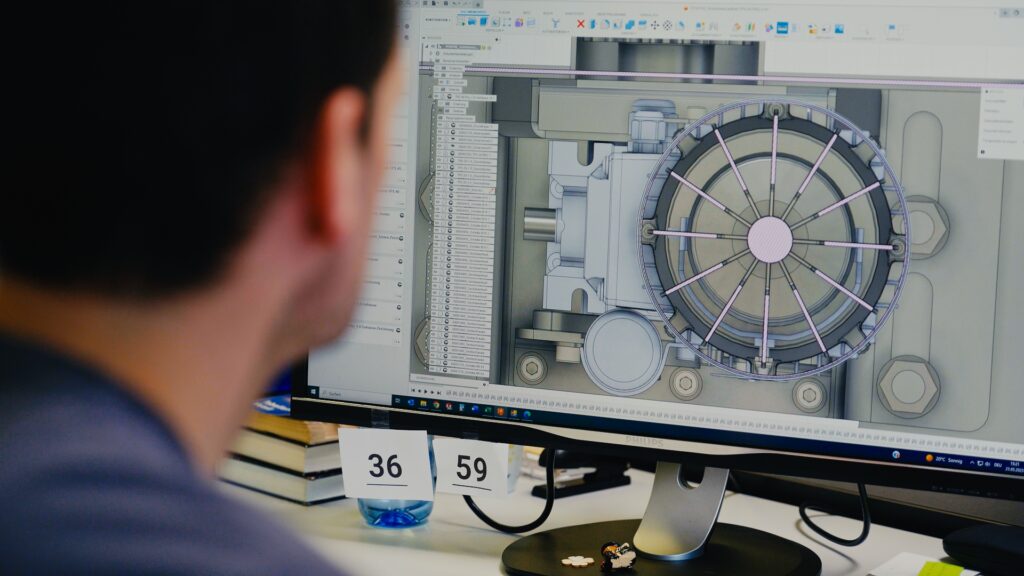

The design stage marks the inception of any product development process. It involves transforming an idea or a set of requirements into a tangible design. Designers work on conceptualizing the product’s form, functionality, and aesthetics, considering factors such as user experience, materials, and manufacturing feasibility.
This stage often includes a mix of physical sketching and 3D modeling to visualize and refine the product’s design before moving forward. An industry-standard tool for computer-aided design (CAD) is Autodesk’s Fusion, a powerful cloud-based 3D modeling and design software that combines various functionalities into a comprehensive product development platform. With tools like Fusion, designers can optimize their productivity for improved designs and less time spent in the design phase.
2. Prototyping
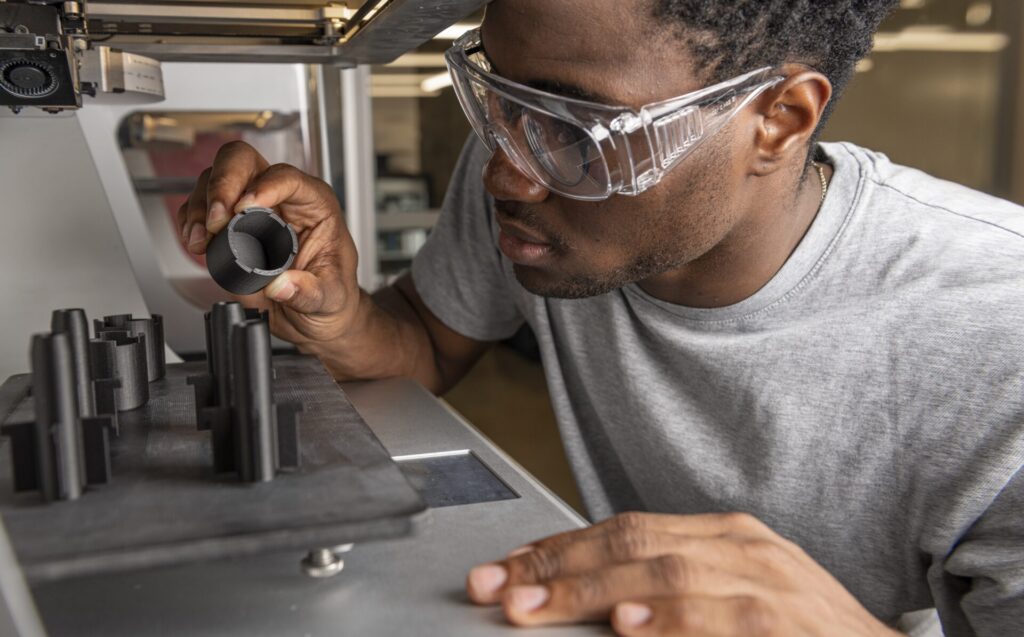

Once the design phase is finished, it’s time to move on to prototyping. Prototyping is a crucial step in the design process that bridges the gap between design and production. Design and engineering firms often employ rapid prototyping methodology to bring their ideas into testing even faster.
This stage involves further refining a design by creating physical and/or digital representations of the product to validate its functionality, ergonomics, and user experience. Prototypes can range from simple mock-ups to fully functional models, depending on the complexity of the product. Depending on the complexity and cost of the product, one may take up techniques like additive manufacturing to create prototypes.
With a physical prototype, designers are able to have a tangible representation of their design in their hands. As compared to digital prototyping, physical prototyping has the benefit of allowing designers to test and iterate their design in real-world conditions.
Digital prototyping gives teams an added layer of agility, as they can alter a 3D model as they run simulations or test physical prototypes. This saves time and sets the design up for the rest of the design process.
A mix of physical and digital prototyping is ideal to help designers and engineers uncover design flaws, improve features, and gather feedback to further refine the product.
3. Testing
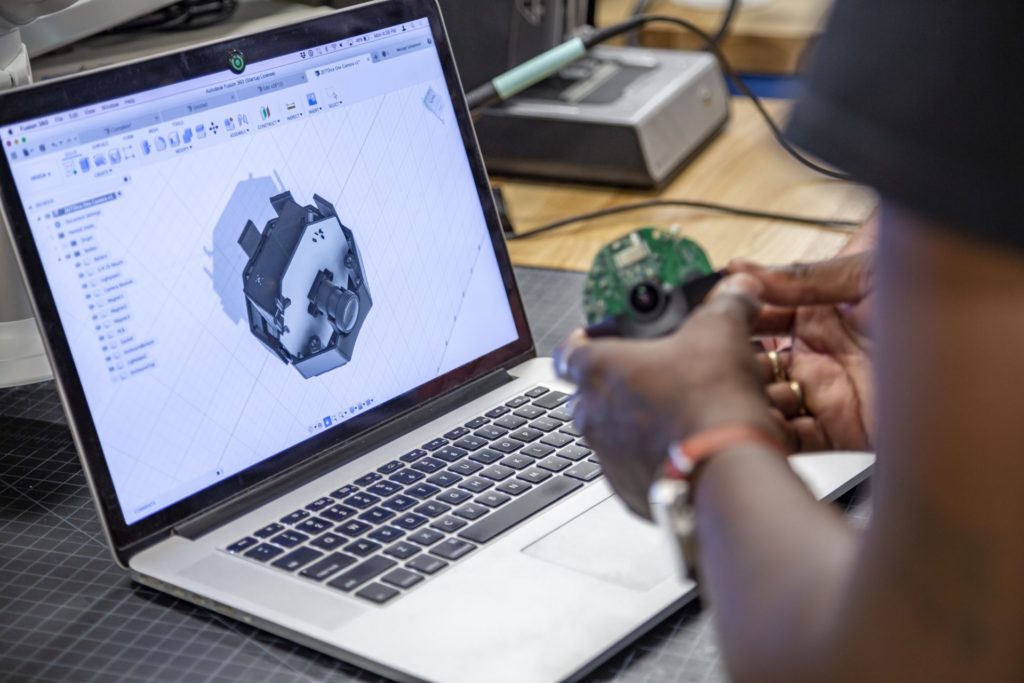
With your final prototype in hand, now it’s time for more official testing.
Testing is integral to product development, ensuring that the final product will meet the desired quality and performance standards. This stage involves subjecting prototypes or early production samples to rigorous testing, including finite element analysis (FEA) simulations and user testing. For connected devices, combining mechanical, electronic, and software design, the testing phase is also crucial for understanding system integration.
By evaluating the product’s performance and gathering user feedback, any necessary refinements or adjustments can be made before moving forward with production. This process can be one of the longest in the design lifecycle, as fully validating a design’s performance can be slow and arduous.
4. Fabrication
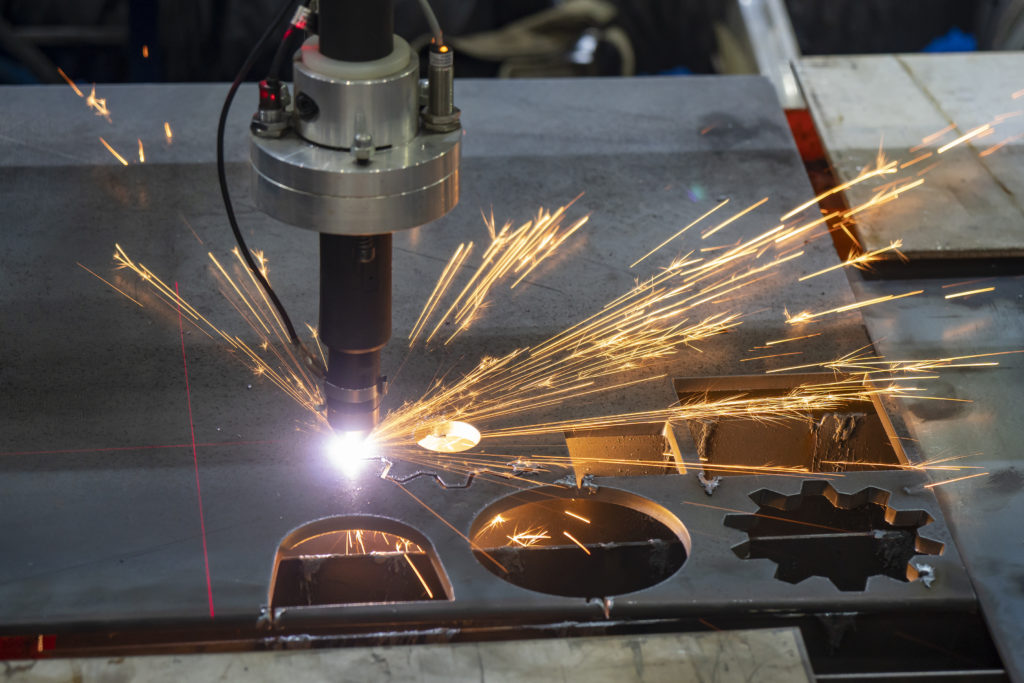

Once the design and prototypes have undergone thorough testing and refinements, the next stage is fabrication.
Different than manufacturing, fabrication involves transforming the finalized design into a production-ready format. This includes creating detailed technical specifications, determining materials and components, and establishing manufacturing processes. At this stage, collaboration between designers, engineers, and suppliers is crucial to ensure a smooth transition from prototyping to manufacturing.
Fusion has a wide range of features that make it an ideal tool for fabrication, including the Fusion Nesting & Fabrication extension, which enables the creation of optimized and associative multi-sheet layouts for material cutting on CNC machines.
5. Manufacturing
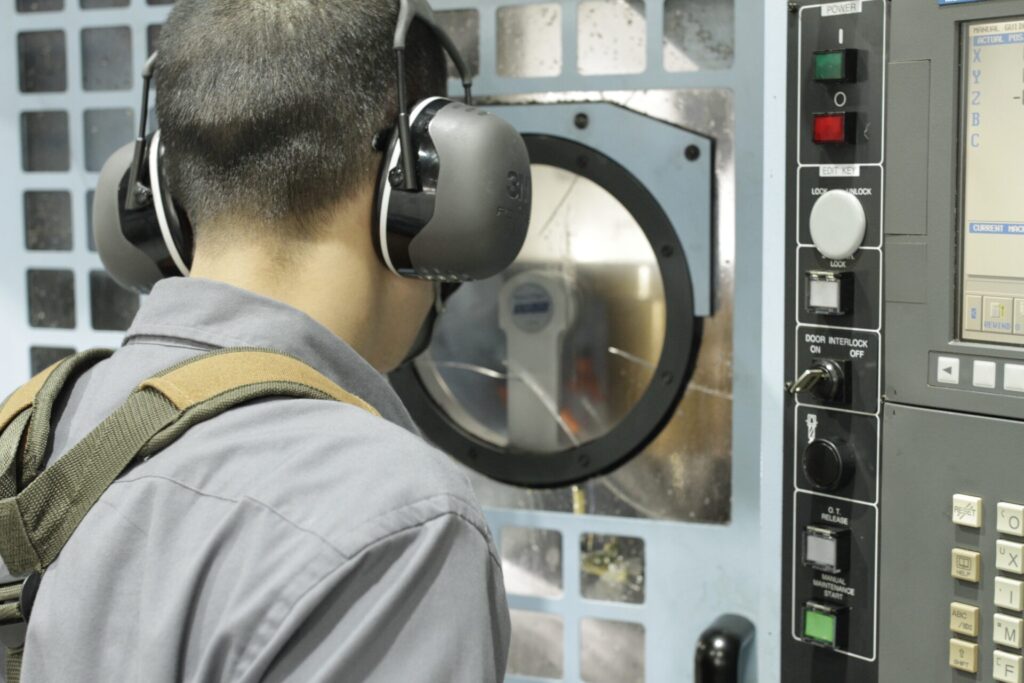

When your product is finally ready to hit the market, it’s time for the manufacturing stage.
Manufacturing is where product design becomes a physical reality. This process involves mass producing your product, including assembly, quality control processes, and new product introduction (NPI). Here, manufacturers use the finalized design and specifications to produce the product at scale. Because of this, close coordination between the design team and manufacturing partners is essential to address any production challenges and ensure the product is manufactured to the desired quality standards.
Autodesk Fusion covers the full spectrum of manufacturing, from quick design iterations to validation with simulation, all the way to manufacturing on your shop or factory floors.
6. Testing (again!)
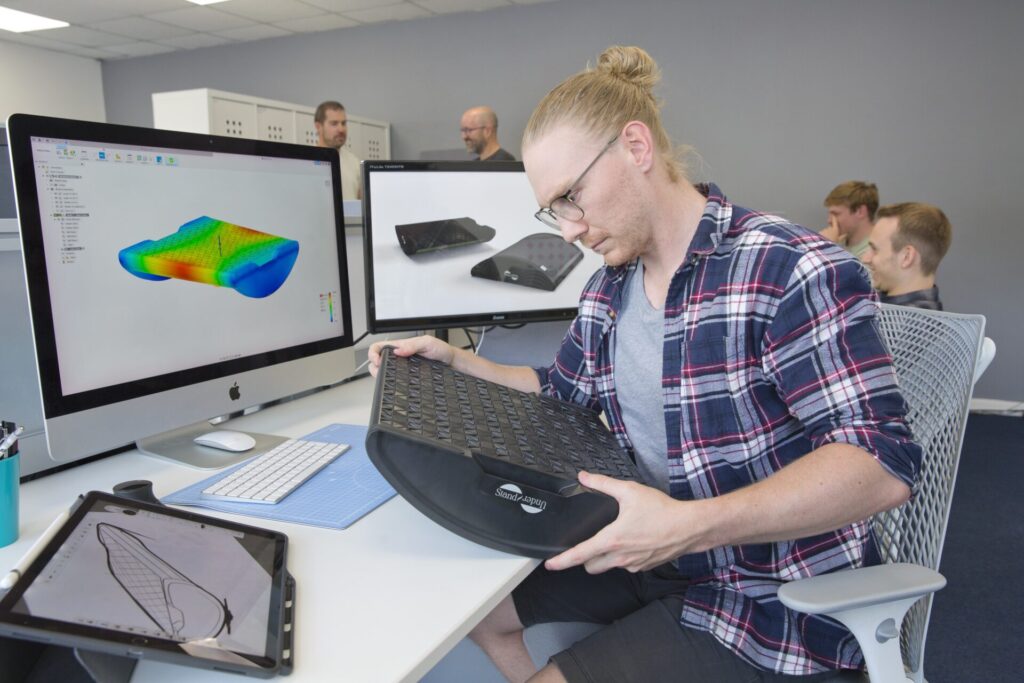

Testing is not a one-time activity but an ongoing process throughout the product development cycle. Once manufacturing begins, additional testing is performed to ensure the produced units meet the required quality standards.
Testing at this stage often includes sampling, statistical process control, and quality assurance protocols to identify manufacturing defects, performance issues, or deviations from specifications. Feedback from this testing phase is essential for continuous improvement and maintaining product consistency.
The reality is that many of these stages (and the tools you need to complete them) overlap and intertwine as you bring your idea from concept to reality. Autodesk Fusion offers an integrated CAD, CAM, CAE, and PCB platform that enables teams to do it all with one tool. Ready to streamline your product development process with Fusion?