This post is also available in: Italiano (Italian) Deutsch (German) 日本語 (Japanese)
What is CAD? How can it improve your workflow? Find out in this complete guide to computer-aided design—from its history to what’s next.
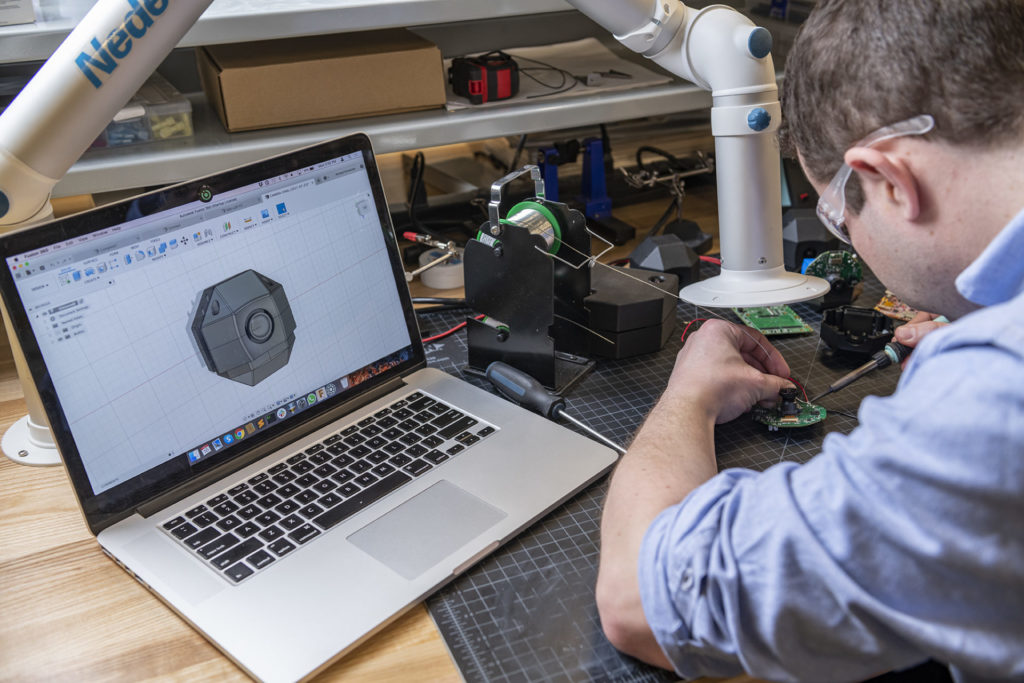
The days of drafting with pencil, paper, and protractors are winding down as most engineers, PCB designers, and architects become experts at using CAD (computer-aided design) software. CAD is software specifically to help draft documentation, visualize 2D or 3D design concepts using photorealistic renderings, simulate real-world functionality, and export CAD data to computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) software.
Elevate your design and manufacturing processes with Autodesk Fusion
Working in CAD Software
CAD centralizes product design into an automated 3D environment. Any engineering design usually starts in CAD. No matter if it’s a PCB (printed circuit board) for a gaming console or an automotive application like a custom roll cage for a Corvette, CAD is the ideal all-in-one 3d modeling environment. CAD incorporates a single-sourced library and cloud-based data management. This facilitates easy access to saved schematics, schematic symbols, 2D drawings, 2D footprints, and 3D models.
Once a CAD model is complete, the CAD file can transfer into CAM software. Autodesk Fusion integrates CAD and CAM into one friendly and accessible environment.
With 3D CAD, engineers can choose from preloaded models like doors and windows or start from scratch by utilizing fill-in parameters.
Software Advantages

CAD modeling software provide several advantages over traditional drafting techniques, such as:
- Increased accuracy for 2D drawing precise dimensions
- Automating common processes
- Access to libraries of routinely used items such as doors, windows, and manufacturing parts
- The ability to quickly adjust parts of a drawing without needing to start over
- Managing complex designs details all within one file
- Creating blocks for frequently drawn items
- Increased collaboration and visualization with colleagues through the ability to share and mark the same file
- Offline capabilities
CAD Development History at a Glance

It’s hard to imagine how many innovations and advancements were needed to arrive at present-day computer-aided design technology. CAD development can be traced back to the earliest drafting innovations like blueprinting, which employed perhaps the original “copy and paste” technical documentation process. About 120 years later, the first true origin of CAD came about when General Motors (GM) and IBM created DAC-1 a year after Ivan Sutherland invented Sketchpad.
CAD Timeline
1842: Blueprinting
Blueprinting is still widely used in various applications, but the original blueprint became obsolete primarily in the 1950s. In 1842, John Herschel—astronomer, photographer, and chemist—created the cyanotype process of blueprinting. This process occurred by drawing on semi-transparent paper over another sheet of paper and applying photosensitive potassium ferricyanide and ferric ammonium citrate mixture. The drawing was then exposed to light, turning the exposed paper blue and leaving the drawing lines white.
Blueprinting was one of the first innovations to streamline the design process and contributed significantly to the second industrial revolution. Such innovations were designed to create cheaper and easier ways to accomplish tasks.
1936-37: The Turing Machine
Since the introduction of blueprinting, there have been numerous innovations, but none more important than the creation and advancement of computers. In 1936, Alan Turing described what would later be dubbed the “Turing Machine,” which are computational machines intended to analyze the limitations of what can be computed and were designed to process real numbers.
1943: ENIAC
A collaborative effort between the US Army and the University of Pennsylvania’s Moore School of Electrical Engineering brought about the first general-purpose computer called ENIAC (Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer), designed to calculate artillery projectile ballistics.
1953: Early CNC Machines
Early Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines were considerably different from modern CNC machines. Instead of an electronic display, they utilized numerical control and a cutting tool of some variety.
1963: Sketchpad and DAC-1
A decade later, Ivan Sutherland created Sketchpad, which incorporated an innovative graphical user interface. Sketchpad allowed for more accessible human/computer interactions using icons. GM and IBM collaborated to create DAC-1 (Design Augmented by Computer), which was used for about a decade before being replaced with a newer version.
1964: First Commercial CAD Systems
Not long after Sketchpad, the earliest commercial CAD systems, like DAC-1, were made available to GM, IBM, and aerospace corporations.
1971: ADAM
Dr. Patrick J. Hanratty of Manufacturing and Consulting Services (MCS) created a system called Automated Drafting and Machining (ADAM). It’s worth noting that this 3D CAD program was introduced in the ‘70s but wasn’t incorporated into the commercial industry.
The 1980s: Desktops and 2D AutoCAD
Desktops were produced for the general public, and Autodesk’s AutoCAD was a significant advancement for the decade.
The 1990s: Solidworks Introduced
Solidworks helped usher in gradual improvements to 3D CAD.
The 2000s: Platform Availability and CAD/CAM Integration with Fusion 360
New platforms require new integration. Autodesk’s integrated, cloud CAD/CAM software, Fusion 360, is for many applications—from industrial design to PCB design. Today, Fusion 360 is spearheading the effort to make the design process quick, easy, and affordable.
The Future of 3D CAD Software
As 3D CAD software continues to develop, more advancements and tools will become available to designers. Here at Fusion, we’re always working on giving our community access to the “what’s next” of design, including:
- Generative design tools that enhance part optimization for cost, material, and different manufacturing processes.
- Comprehensive PCB design tools that support the design of tech-enabled products.
- Parametric modeling features allow you to easily make updates to dimensions and view the effects in real-time.
- A plethora of features for 3D printing/additive manufacturing (here are a few tutorials!).
- Our ongoing research in the fields of AI and machine learning.
Stay tuned as we release exciting Fusion updates each month.
Integrating CAD and CAM into product development workflows can help streamline the design process and provide high cost and time savings. With Autodesk Fusion, seamless collaboration is right at your fingertips. Try Fusion today for the ultimate integrated platform.