& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Architectural simulation uses technology to create virtual models of buildings, allowing architects, engineers, and other stakeholders to visualize and analyze designs before construction.
The architectural simulation process starts by importing a detailed design model into simulation software, where parameters such as environmental conditions, material characteristics, and operational behaviors are set. With these in place, the simulation runs various scenarios, giving insights into how the building responds to real-world conditions.
The backbone of any successful simulation is data. Detailed information about building geometry, climate data, material properties, occupancy patterns, systems performance, and more ensures that the model exhibits the performance and attributes of the physical building. This accuracy is crucial for generating realistic results, whether assessing energy efficiency, thermal comfort, or structural integrity.
Once complete, the architecture simulator provides valuable outputs, offering a glimpse into the building’s future. These outputs include vivid visualizations such as heat maps and sun path diagrams, making it easy to see how different elements come together. The simulation also provides actionable insights, comparing design options and suggesting changes that could improve performance.
Autodesk Revit, and its MEP Systems Analysis tool paired with others like Insight, provide comprehensive solutions for simulating energy performance, structural integrity, and environmental impact. InfraWorks supports larger-scale infrastructure simulations, including traffic flow and environmental assessments for better urban planning. Autodesk Forma allows architects and designers to set up geolocated projects with real-world contextual data, model complex 3D designs, and perform environmental impact analyses.
Autodesk tools like Insight and Forma integrate tightly with Revit, so users can simulate directly from BIM models without re-creating elements. That ensures more data continuity and more accuracy, preserving critical details such as materials, systems, and geometry for real-time performance analysis and informed decision making. Forma also shines in early-stage design, where architects can use site-specific data—like terrain, wind, daylight, and density—to make data-driven design choices. Autodesk platforms also enhance visualization with tools for creating renderings, 3D walk-throughs, fly-throughs, and animations, bringing designs to life while informing sustainable, efficient design solutions.
Autodesk platforms use AI to accelerate and optimize simulations. Forma, for example, uses machine learning to evaluate multiple design scenarios in real-time, providing predictive insights on factors like energy efficiency and environmental impact. These capabilities empower architects to make smarter, data-driven decisions, driving innovation, sustainability, and design excellence.
Autodesk’s cloud solutions, like BIM 360 (now part of Construction Cloud), enable real-time collaboration by providing remote access to simulation data. Teams can work simultaneously on the latest model versions, supported by powerful cloud computing that handles complex simulations faster than local hardware, enabling multi-stakeholder design review and visualization sharing, along with clash detection and review.
Architectural simulation offers advantages that enhance the design process and final outcomes, making it an invaluable tool for architects, engineers, and project stakeholders, including:
Using simulations, architects can test and refine designs in a virtual environment, reducing the likelihood of errors and design flaws in the final construction.
By evaluating energy efficiency, material impact, and environmental performance, simulations help optimize designs for sustainability, reducing a building’s carbon footprint and operational costs.
Identifying potential issues early in the design phase minimizes costly changes during construction and helps control budget overruns.
Simulations can analyze factors like lighting, acoustics, and spatial flow for designs that enhance comfort and usability for occupants.
Structural and safety simulations assess how buildings respond to stressors like wind, earthquakes, or fire so designers can address potential vulnerabilities proactively.
2D and 3D CAD tools, with enhanced insights, AI-automations, and collaboration features. Subscription includes AutoCAD on desktop, web, mobile, and seven specialized toolsets.
Plan, design, construct, and manage buildings with powerful tools for Building Information Modeling.
Computational fluid dynamics simulation and solid body motion analysis software. Available as CFD Premium and CFD Ultimate
BLDUS
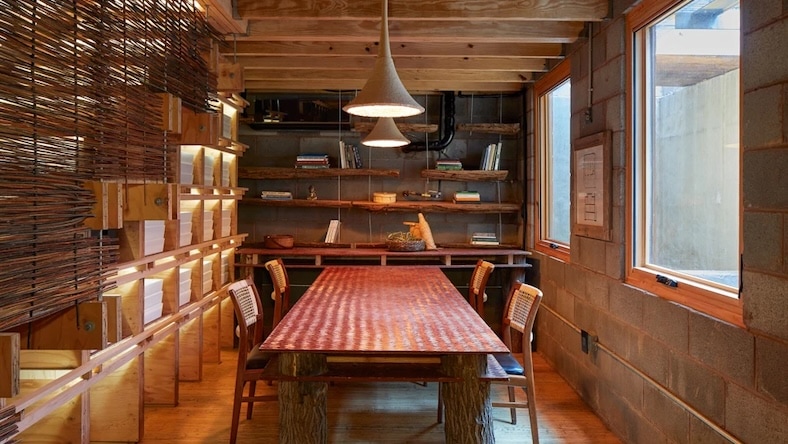
An award-winning architecture firm uses AutoCAD, Revit, and Autodesk CFD to achieve LEED Platinum certification.
Image courtesy of BLDUS ©Ty Cole/OTTO
Lake|Flato
Image courtesy of Robert G. Gomez
Baker Barrios Architects
A commercial design and architecture firm uses Forma to improve efficiency, win new work, and bring satisfied clients back to the table.
Image courtesy of Baker Barrios Architects
Follow this self-guided tutorial to use Revit and Insight to take your sustainability insights to the next level.
Learn to optimize cooling and boost energy efficiency in data centers with Autodesk CFD.
Understand the carbon impact of early design decisions with Forma’s Embodied Carbon Analysis feature.
Architectural simulation is a process that allows architects and engineers to virtually model buildings and assess their performance before construction begins. By simulating key aspects like energy efficiency, structural integrity, acoustics, and lighting, this technology helps design teams explore various scenarios, optimize for sustainability, and identify potential issues early on. With data-driven insights into how a building will interact with its environment and occupants, architectural simulation enables more informed decision making, ultimately leading to structures that are efficient and resilient and enhance the user experience.
There are various types of architectural simulations that help optimize building design and performance. Energy and environmental simulations focus on sustainability, analyzing factors such as heating, cooling, and energy efficiency. Structural simulations ensure safety by evaluating a building’s response to forces like wind and earthquakes. Daylighting, solar, and thermal simulations assess natural light, shading, and indoor temperature control to enhance comfort and reduce energy usage. Acoustic simulations manage sound quality, while people flow and safety simulations predict movement and emergency response, ensuring safety and accessibility.
Architectural simulation offers significant benefits across various project types, from large-scale commercial buildings and residential developments to healthcare facilities and educational institutions. By enabling detailed analysis of energy efficiency, structural integrity, and environmental impact, simulations help optimize comfort and sustainability in office towers, homes, and green buildings. Entertainment venues like theaters and concert halls can enhance acoustics and lighting via simulations. Meanwhile, architectural simulations can help infrastructure projects such as airports and train stations improve people flow and safety. Ultimately, architectural simulation empowers designers to create functional, resilient, and user-centered spaces, making it an invaluable tool for diverse building projects.
Architectural simulations play a crucial role in advancing sustainability by enabling data-driven optimization of building designs for energy efficiency and environmental impact. Through energy and daylighting simulations, architects can reduce energy consumption by refining heating, cooling, and lighting systems, as well as by maximizing natural light. Simulation in architecture also helps designers choose materials that enhance insulation and minimize resource use while supporting sustainable site planning through modeling of solar orientation and shading. By providing insights into sustainable design strategies, architectural simulations help create buildings that are environmentally responsible and energy efficient.
Architectural simulation is well-suited for small projects such as single-family homes and boutique offices, offering scalable solutions that optimize energy efficiency, comfort, and sustainability. While often associated with large developments, simulation tools can be adapted to the needs of smaller spaces, providing insights on material choices, space utilization, and natural lighting. These simulations help small projects meet sustainability goals, improve energy performance, and comply with local codes, often leading to significant cost savings over time.
Architectural simulations use a diverse set of data to create realistic models that predict building performance under real-world conditions. Key data includes building geometry and design details from CAD or BIM models, material properties that influence energy efficiency, and environmental factors like local climate and solar exposure. Occupancy patterns and usage data are also essential for accurately modeling heating, cooling, and ventilation needs. Performance benchmarks such as energy codes or LEED standards help guide simulations to ensure designs meet sustainability and regulatory requirements.