& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
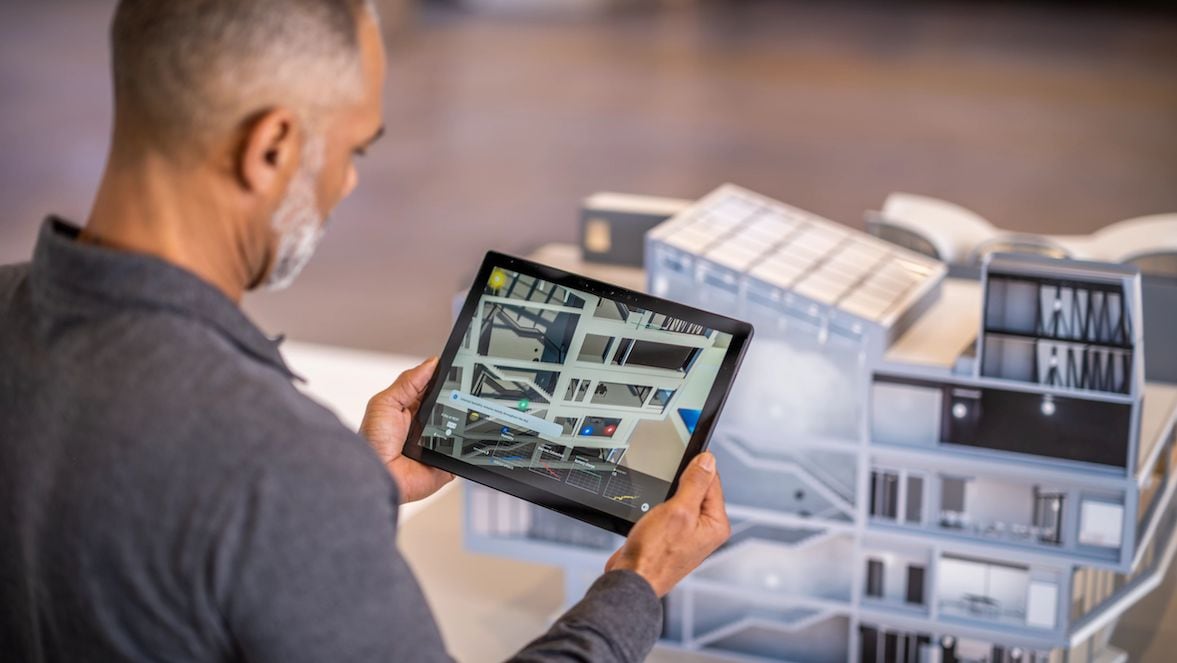
A virtual twin is a digital duplicate of a real-world object that goes beyond traditional 3D modeling. Virtual twins make it possible to run more accurate simulations and gather deep performance analytics for new layers of insight and more intelligent decision-making.
The potential for virtual twins is virtually limitless. In product and vehicle design, virtual twins allow designers to simulate how machines will work and how people will interact with them. In health care, they can simulate the workings of the human body and how a particular medicine or treatment might affect it. In infrastructure management, such as water systems, virtual twins help planners look ahead and predict the operation of various assets.
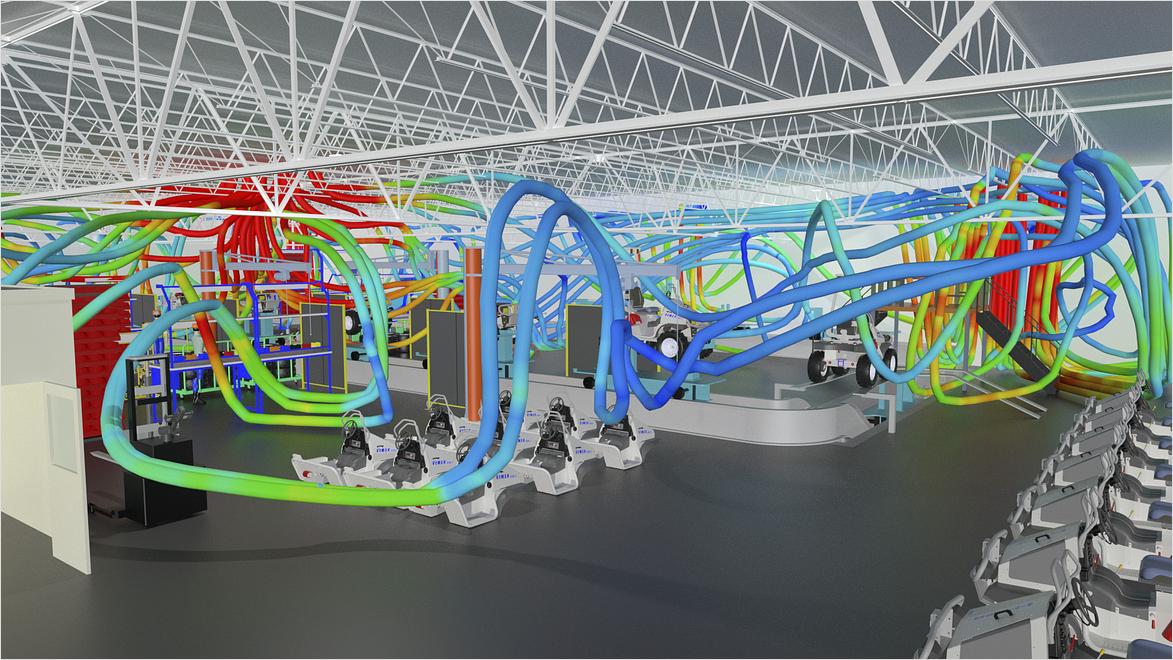
What are virtual twins good for? Unlike traditional 3D models, virtual twins provide performance feedback for dynamic, ongoing improvements. This level of detail can help makers lower costs by fine-tuning processes, equipment, and workflows for increased speed and efficiency. Virtual twins adapt to live data, so you can refine even post-prototype designs, reducing the time from concept to market. This increased efficiency from virtual twin insights makes your operations faster, more affordable, and safer. Industries such as medicine and transport have already embraced this technology, and now factories can use the same caliber of data-driven decision-making.
Though virtual twins and digital twins have many similarities, there are some crucial differences.
Virtual twins are designed to be simulations of objects and systems, allowing scenarios to be tested before real-world implementation takes place. Digital twins, on the other hand, are intended to directly mirror physical assets in place, using live data.
In considering virtual twins vs. digital twins, virtual twins rely purely on simulation and virtual modeling, while digital twins incorporate data from Internet of Things (IoT) devices and other real-time data sources.
Key benefits of a digital twin include enhancing operational efficiency and limiting downtime. In contrast, a virtual twin allows you to test products and technologies without real-world risk, reducing time to market.
Virtual twin technology revolutionizes every step from design to execution, dramatically simplifying processes and setting new standards in many industries.
Virtual twins let you test your design changes and see their impacts before committing to costly physical prototypes or production adjustments. Get real-time data and insights to optimize efficiency, minimize errors, and make smarter decisions—ultimately saving time and money.
No more delays going back to the drawing board after each prototype. Evaluating your work in a complete environment simulation with a virtual twin lets you test as many live runs as necessary to find the optimum design.
Whether it’s designing a robot/human collaboration space or practicing putting a stent in a patient’s artery, you can perfect the technique by practicing on a virtual twin as many times as necessary.
Design, test, tweak, and test again endlessly with virtual twins, finding and eliminating every choke point digitally before you begin the physical process.
When deployed across a single platform, every vested project participant can add or interrogate virtual twin data that impacts their work, showing a more complete picture for everyone.
Virtual twins can enhance the resilience of a business in a number of ways. They make it possible to identify potential operational failures before they happen, preventing downtime and avoiding bad outcomes or publicity. Virtual twins can also be used to wargame worst-case scenarios so the business is ready if things don’t go according to plan and can prepare contingencies in advance.
As computing power increases and is bolstered by increasingly complex artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms, the sky’s the limit for virtual twins. Greater processing power and complexity will create more realistic simulations, eventually reaching parity with the real world. The increase of data flowing from IoT devices will provide extensive data for virtual twins to work with. From urban planning that uses extensive and realistic virtual twins of entire cities to more accurate virtual twins of patients in health care, use cases are growing across many sectors.
Powerful BIM and CAD tools for designers, engineers, and contractors, including Revit, AutoCAD, Civil 3D, Forma Site Design, and more
Get Inventor + AutoCAD + Autodesk Fusion + more—Professional-grade tools for product development and manufacturing planning.
ARCADIS
Image courtesy of Arcadis
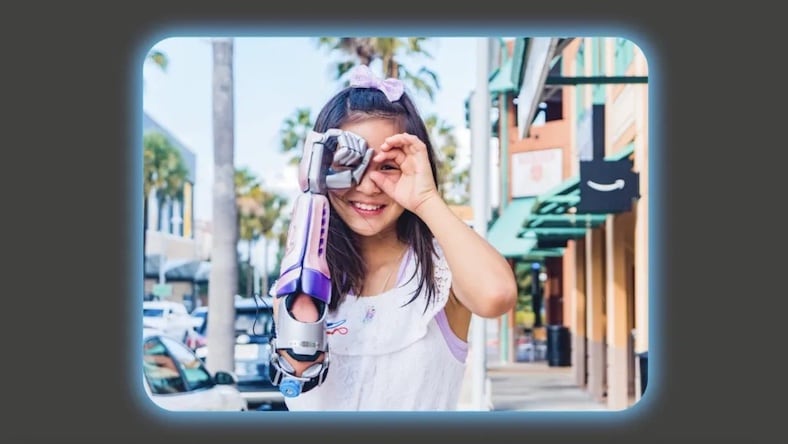
LIMBITLESS SOLUTIONS
Bionic arm maker Limitless is a University of Central Florida nonprofit using Autodesk Fusion to make 3D printed prosthetic arms for kids—and creating virtual twins of prosthetics to make them a perfect fit for the user.
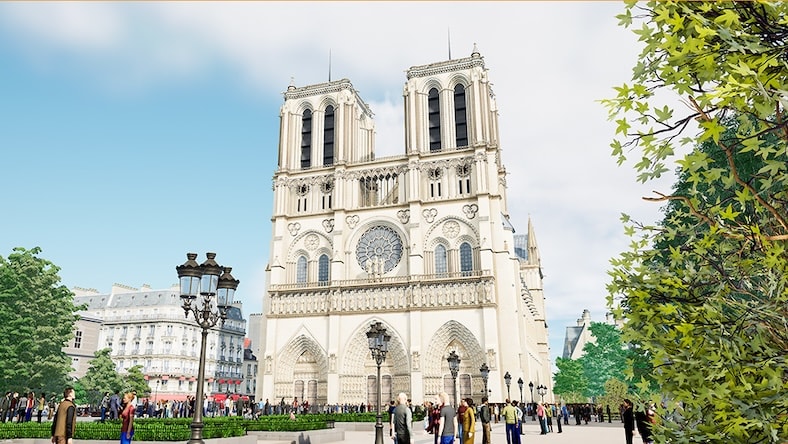
NOTRE-DAME DE PARIS
See how virtual twin technology helped historians and engineers reimagine the surrounding grounds after the devastating fire at Paris’ Notre-Dame Cathedral in 2019.
Learn how collecting data from across the project and connected domains (like the local environment) is putting tomorrow's manufacturing capability in your hands today.
Watch and learn how to better design a factory operation in these examples of virtual twins at work, from collecting information to deploying and connecting your model.
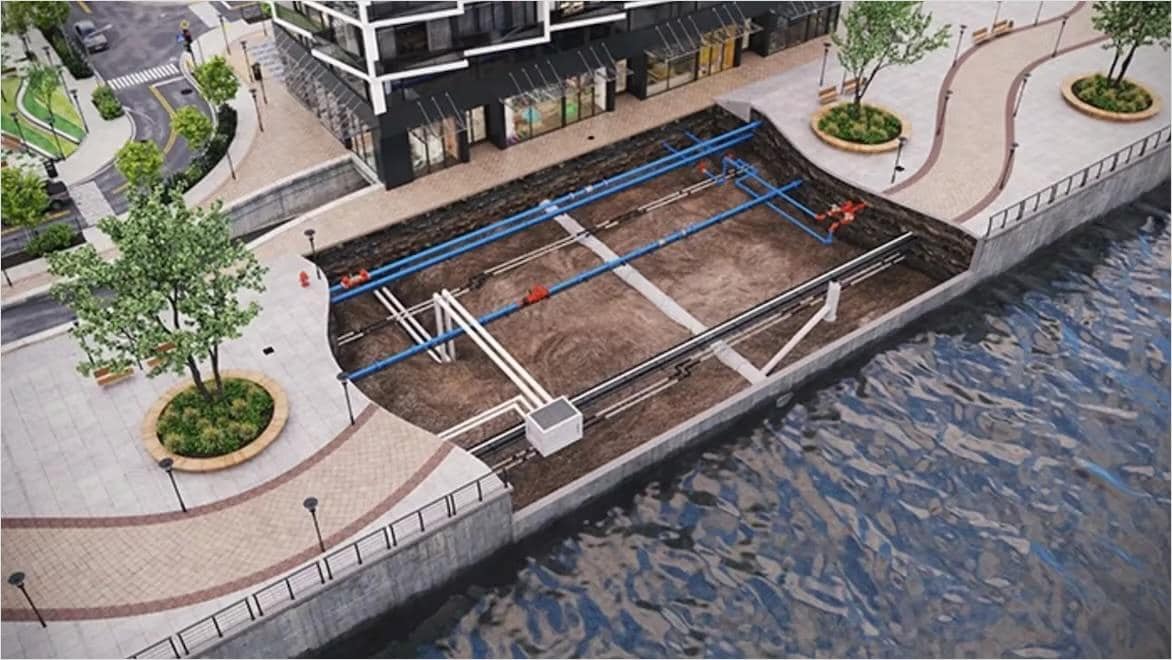
Read how Scottish water authorities used virtual twin modeling to regulate water use in centuries-old water systems.
Discover how a Swedish architecture firm is using advanced technology to catalog building materials to maximize their reuse potential.
A digital twin is a digital representation of a project (process, system, object, etc.) created directly from the 3D design model. It can be quite static in its natural state.
The meaning of a virtual twin goes deeper, introducing data beyond shapes, sizes, and dimensions. Temporal data about how a space or thing behaves over time reveals how it’s being used. Meanwhile, connecting the model to data from the wider environment situates it in a more realistic modeling framework to reveal even richer performance measurements.
A virtual twin is created using specialized software, providing a model that can run simulations. Real-world data is added to ensure that the simulation very closely models the physical counterpart it’s representing.
Virtual twins can help to make companies more efficient by maximizing resource use and minimizing waste. They can, for example, help optimize the energy consumption of a product or system, avoiding the waste caused by solutions that fail in the real world with insufficient testing.
Virtual twins make it possible to carry out extensive testing without needing to build successive prototypes. This helps reduce time to market and can uncover or prevent potential issues before production, saving time.