& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
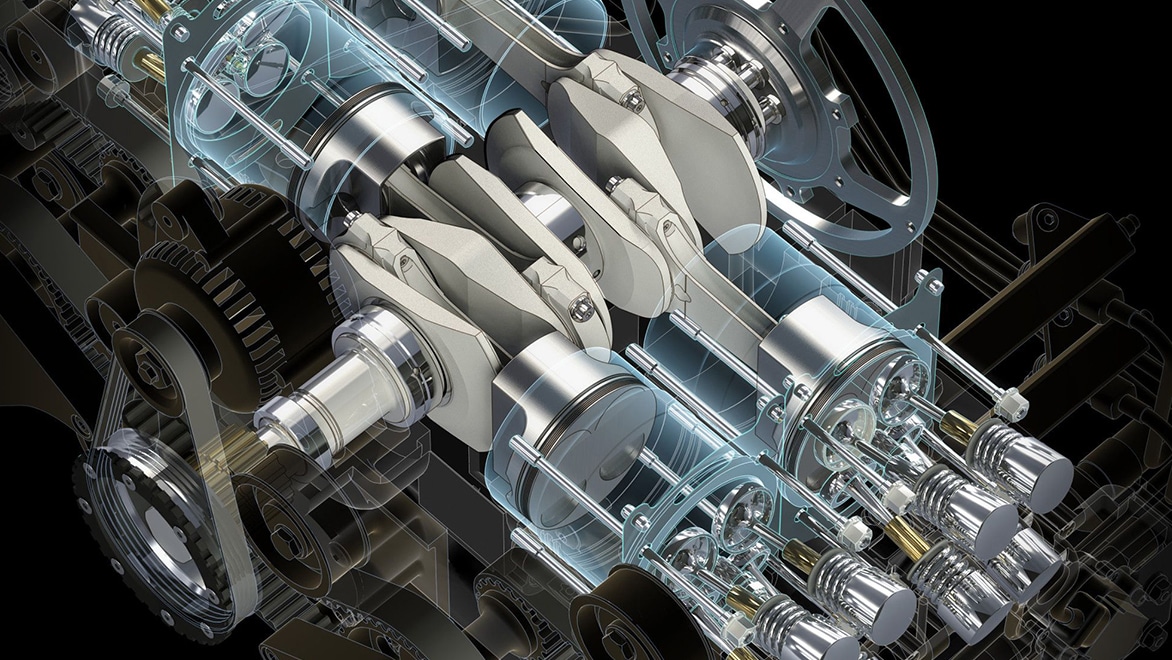
Engineers and designers use mechanical engineering design software to model (US site), validate and communicate ideas before production. Additional tools are available and sometimes integrated in 3D engineering software for manufacturing products on a CNC machine or 3D printer. Mechanical engineering design software is employed across many industries, including industrial machine, automotive and consumer product design.
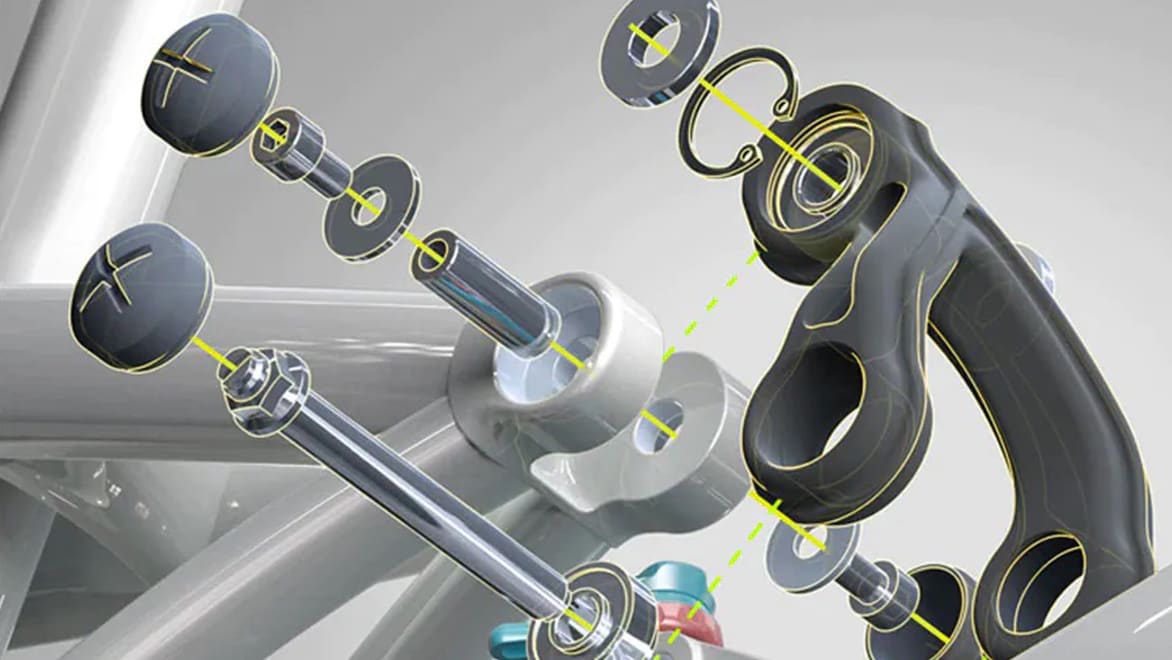
All machines, whether used by consumers or industry, rely on myriad different parts, components and interworking systems, and these need to be designed carefully to ensure that they work as intended and without errors. This is the role of mechanical design engineers. They must consider how each individual part and component will work alongside each other, and within the wider environment. Mechanical engineering software like Autodesk Fusion gives them the tools and data they need to plan, test and implement their designs. Mechanical drawing software can also be used to refine already existing designs and find ways to make them better.
Software for mechanical engineering is at its most effective when it’s at your fingertips whenever you need it. Autodesk Fusion gives you that versatility by offering fully integrated CAD, CAE, CAM and PCB mechanical design capabilities wholly within the cloud. This means that you can take your CAD mechanical engineering work on the road, work from multiple offices seamlessly or collaborate with colleagues across the planet easily and without obstacles.
CAD engineering software is commonly used by mechanical design engineers. The models created by CAD software such as Autodesk Fusion and AutoCAD are often used as inputs for other mechanical engineering design tools.
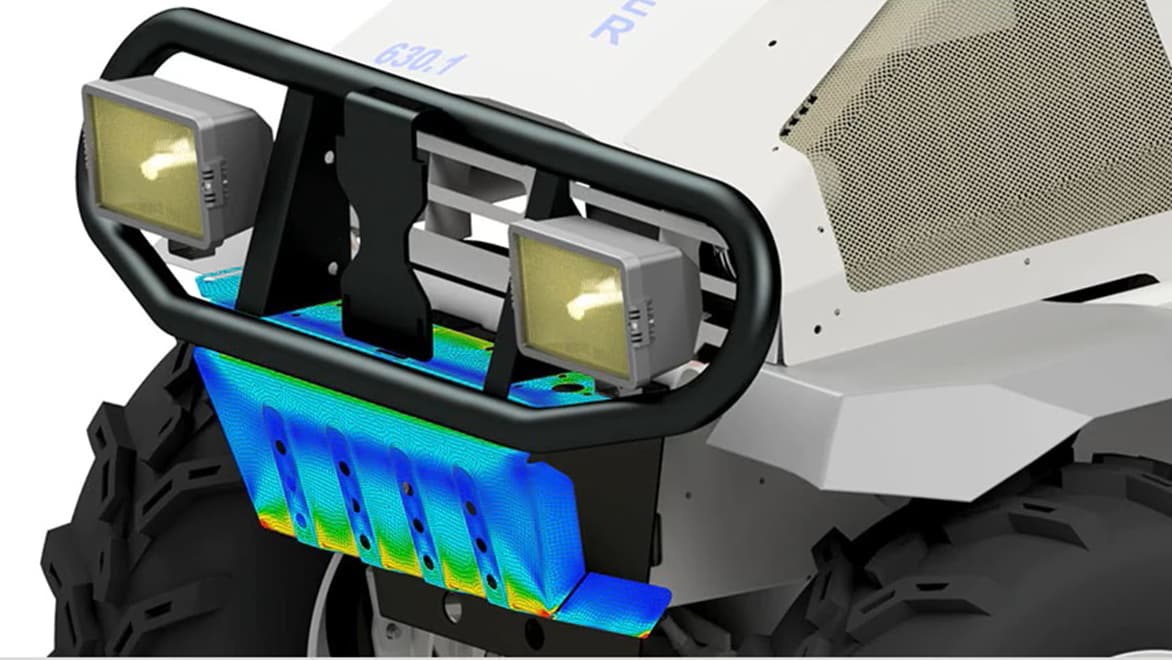
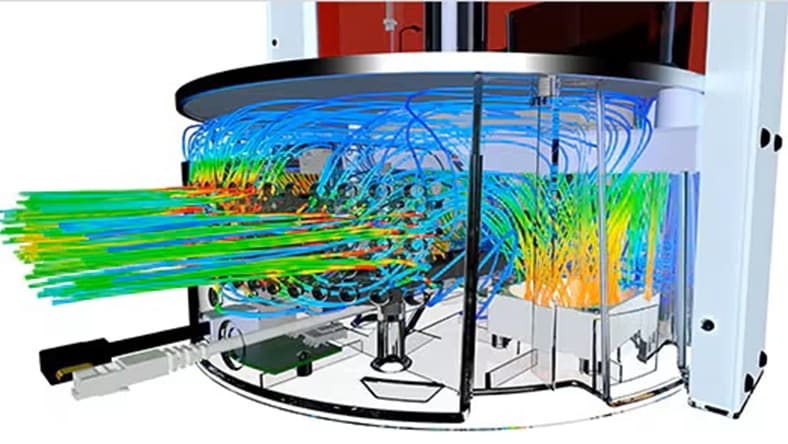
CAE covers a broad range of analyses. CAE software allows you to perform complex tasks such as finite element analysis (FEA) and computational fluid dynamics (CFD) virtually before creating physical prototypes.
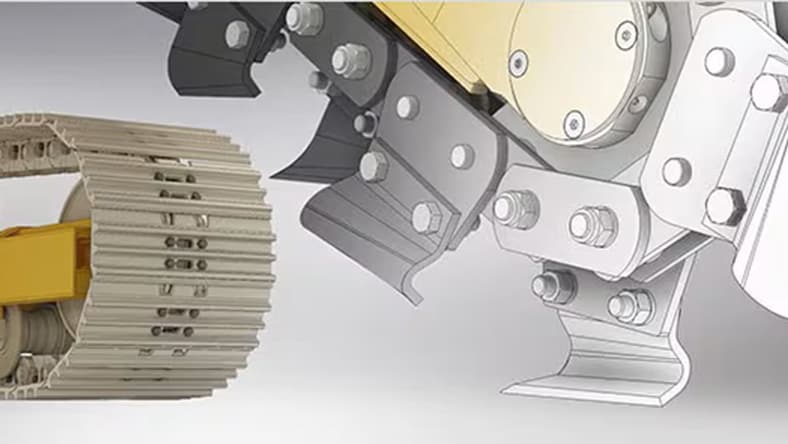
CAM refers to the use of mechanical engineering software to help automate the manufacturing process. CAM is typically used to create toolpaths for 2.5-axis to 5-axis CNC milling, turning and mill-turn (US site).
Get Inventor + AutoCAD + Autodesk Fusion + more – Professional-grade tools for product development and manufacturing planning
Powerful product design and engineering tools for 3D mechanical design, simulation, visualisation and documentation.
2D and 3D CAD tools, with enhanced insights, AI-automations and collaboration features. Subscription includes AutoCAD on desktop, web, mobile and seven specialized toolsets.
Integrated 2.5- to 5-axis CAD/CAM programming solution for Inventor and SOLIDWORKS – available as Inventor CAM and HSMWorks
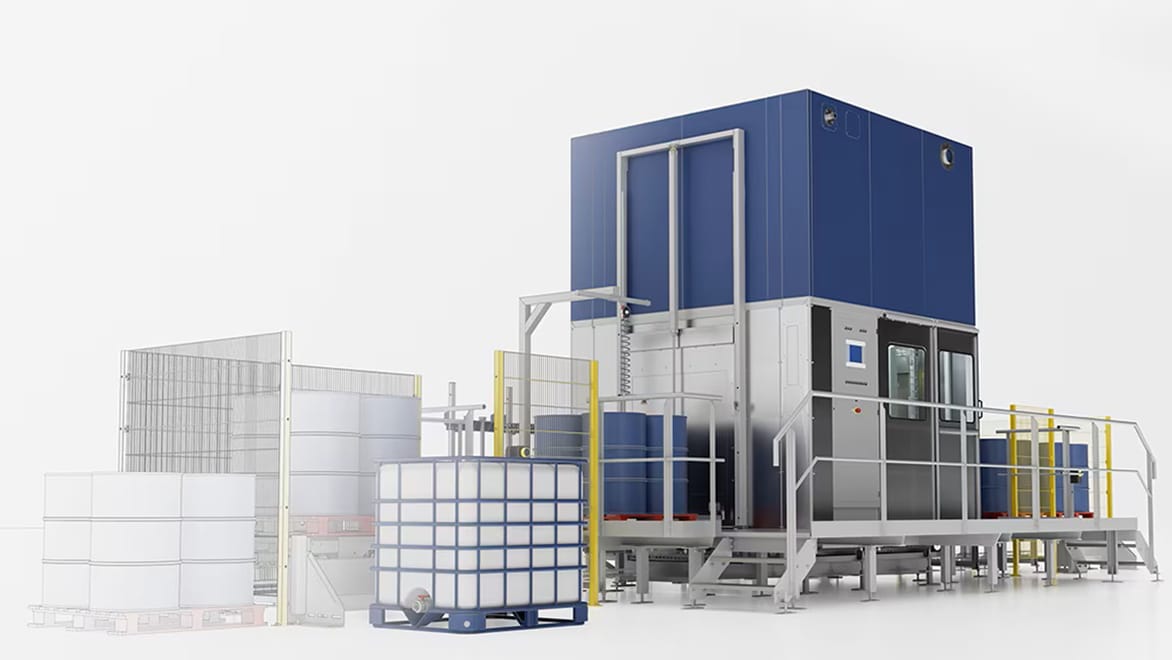
Swissomation uses Autodesk Fusion’s mechanical engineering capabilities for 3D modelling, CAM and live review for collaboration with customers from any location on any device.
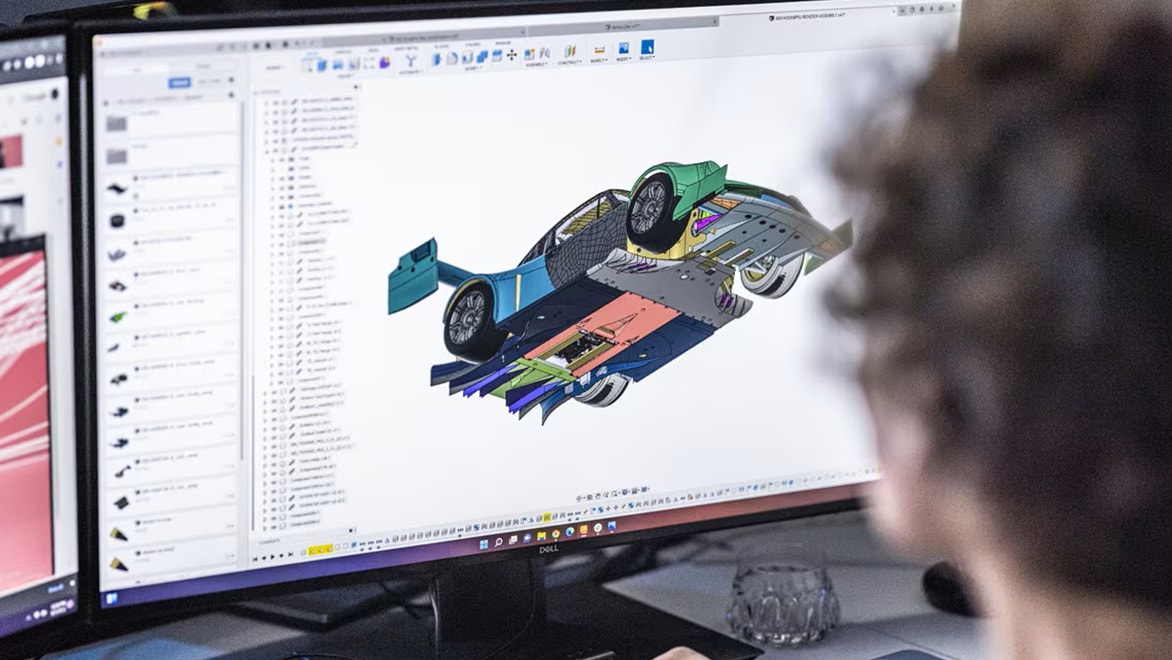
KMP is a fast-paced team of mechanical engineers using Autodesk Fusion to design and make specialised components for their high-performance race cars.
Mechanical design can take a long time if you have to start from scratch every time. Fortunately, AutoCAD comes complete with a mechanical toolset that features more than 700,000 intelligent parts and features to get you started or to enhance your designs. This means you can rapidly create AutoCAD mechanical drawings with standard components in no time at all. You can also easily import models from elsewhere to bolster the tools at your disposal for your mechanical designs.
Even the smallest changes in a mechanical design model can mean a substantial amount of work. Fortunately, our Autodesk Fusion mechanical engineering software employs parametric modelling to save you time and help you uncover the best designs. Parametric modelling allows you to tweak a single feature or measurement, and have that change carried out in a relational way across the whole model. Particularly useful for experimenting with prototypes or fine-tuning optimisations, it’s mechanical engineering design done smart.
Design and make anything with Inventor, featuring integrated mechanical design tools for advanced simulation and 5-axis CAM. Collection also includes access to Autodesk Fusion for mechanical engineers, helping you get on the path to the future of making things with our cloud-based product innovation platform.
Whether you’re just getting to know Inventor or are a seasoned user of 3D CAD engineering software, check out these tutorials to see how you can put Inventor to work for you.
Experience the power of cloud-based 3D CAD engineering software. Learn 3D modelling and 3D printing with beginner and advanced tutorials.
As technology, manufacturing, and workplace collaboration take new shape, adapt with new engineering skills to stay at the top of your game.
The Internet of Things (IoT) (US site) is radically transforming industries. Learn the essentials of IoT and the advanced mechanical design skills engineers will need to design smart products.
Learn more about free Autodesk software access for students (US site), educators (US site) and administrators (US site) from qualifying educational institutions.
Explore Autodesk partner WorldSkills and how competitors leveraged Inventor to develop their entries for the mechanical engineering design competition.
You can use AutoCAD for a wide range of steps in the engineering process. You can design in 3D to fully visualise your products, plans and prototypes including machines, consumer goods and tools. When it comes to manufacturing, you can generate AutoCAD mechanical drawings from your 3D engineering designs to guide the process. It can also be used to analyse the performance of existing products, so you can improve on them and create new models.
You can choose from a number of different 3D engineering software subscription plans. Each product can be bought on a Standard, Premium or Enterprise plan. Standard is ideal for individuals and small teams, and includes full use of the software, product usage reporting, single sign-on and 8x5 live support. If your team is medium or large, then Premium is ideal, featuring directory sync, coaching for users and 24x7 live support. And for extra-large teams, the Enterprise plan gives you the ability to add your own metadata to your 3D engineering software, control download access and gives you a managed success plan.
Yes, both AutoCAD and Autodesk Fusion allow you do design using wireframe models, enabling you to modify your designs more easily using iterative design processes. Changes can be made and tested quickly without the need for time-consuming rendering operations.
Thanks to Autodesk's 3D mechanical engineering design software, you can create more accurate and precise models in less time. There are also substantial reduced physical costs as realistic 3D models negate the need for endless physical prototypes, and engineers are freer to innovate and test new designs with even limited resources.