& Construction

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D
& Manufacturing

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD

Integrated BIM tools, including Revit, AutoCAD, and Civil 3D

Professional CAD/CAM tools built on Inventor and AutoCAD
Choose a template in Civil 3D, set up the coordinate system, set the project units, and define the surface.
Type:
Tutorial
Length:
6 min.
Tutorial resources
These downloadable resources will be used to complete this tutorial:
Transcript
00:04
When you are importing and exporting surface data between Civil 3D and InfoDrainage,
00:08
it is very important to set up the coordinate system properly.
00:11
Often, when users run into problems with model objects and surfaces not lining up,
00:17
it is because the coordinate system has not been configured correctly.
00:20
The project units and the template also must be correct to ensure a smooth data exchange.
00:27
In Civil 3D, the first step is to choose the template.
00:30
Click Start > New > Browse Templates, and for this exercise, select Metric templates.
00:38
Be aware that this example is located in the United Kingdom, specifically, in Great Britian.
00:44
Next, set up the UK grid coordinate system.
00:47
In the Toolspace, click the Settings tab, then right-click the current drawing
00:52
and select Edit Drawing Settings.
00:55
In the Drawing Settings dialog, you must set the categories and coordinate system according to your local standards.
01:02
For this example, under Drawing units, select Meters.
01:07
Under Angular Units, select Degrees.
01:11
Ensure that the Imperial to Metric conversion drop-down shows as International Foot,
01:17
and that the Scale is set at 1:1000.
01:20
In the Zone group, expand the Categories drop-down and select Great Britain.
01:25
Also, the Available coordinate systems, Selected coordinate system code,
01:30
and Description should all be set to OSGB 1936 British National Grid.
01:37
Next, you need to set up the surface data that is used to define, among other attributes,
01:42
manhole cover levels and pond perimeter levels.
01:45
On the ribbon, Insert tab, Import panel, click LandXML.
01:52
Browse to and select the file Road1.xml from the dataset.
01:56
Click Open.
01:58
In the Import LandXML dialog, in the tree view,
02:02
expand the Surfaces node and the Surface description node,
02:06
and ensure that the SourceData node is deselected.
02:09
Click OK.
02:11
If any information boxes appear, close them.
02:15
The surface model appears in the drawing window.
02:19
In the Toolspace, click the Prospector tab.
02:22
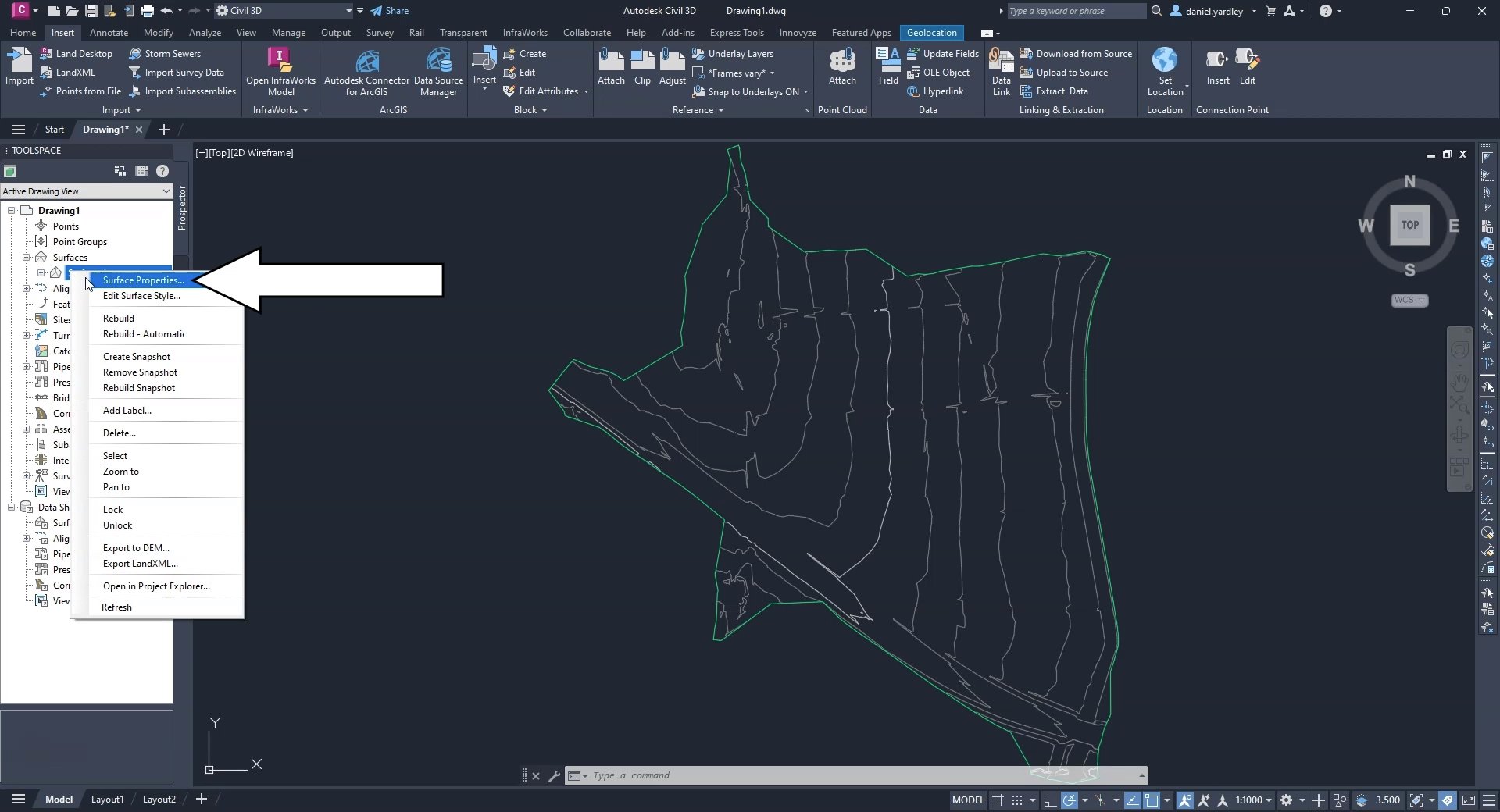
Expand Surfaces, and then right-click Surface1 and select Surface Properties.
02:29
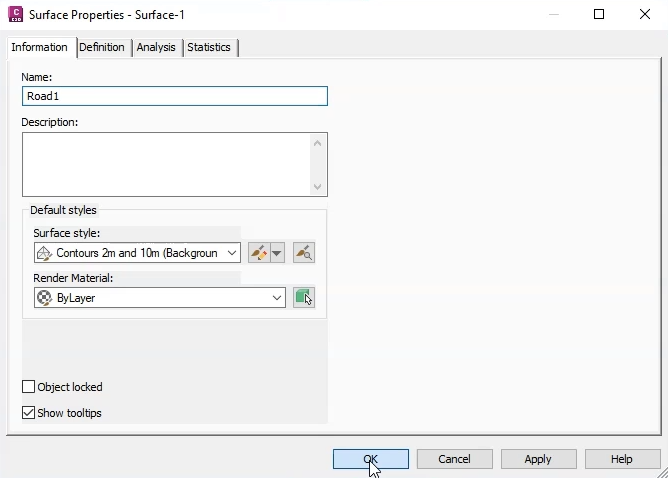
In the Surface Properties dialog for this surface,
02:32
you can edit the surface properties to change the name of the surface.
02:36
Rename it “Road1” to match the surface data.
02:40
Optionally, you can add a description or edit its default styles,
02:44
but for this exercise, leave them as-is and click OK.
02:48
The template, coordinate system, and surface file are now all configured.
02:53
Again, for your local projects, you would configure these settings to match your local standards.
Video transcript
00:04
When you are importing and exporting surface data between Civil 3D and InfoDrainage,
00:08
it is very important to set up the coordinate system properly.
00:11
Often, when users run into problems with model objects and surfaces not lining up,
00:17
it is because the coordinate system has not been configured correctly.
00:20
The project units and the template also must be correct to ensure a smooth data exchange.
00:27
In Civil 3D, the first step is to choose the template.
00:30
Click Start > New > Browse Templates, and for this exercise, select Metric templates.
00:38
Be aware that this example is located in the United Kingdom, specifically, in Great Britian.
00:44
Next, set up the UK grid coordinate system.
00:47
In the Toolspace, click the Settings tab, then right-click the current drawing
00:52
and select Edit Drawing Settings.
00:55
In the Drawing Settings dialog, you must set the categories and coordinate system according to your local standards.
01:02
For this example, under Drawing units, select Meters.
01:07
Under Angular Units, select Degrees.
01:11
Ensure that the Imperial to Metric conversion drop-down shows as International Foot,
01:17
and that the Scale is set at 1:1000.
01:20
In the Zone group, expand the Categories drop-down and select Great Britain.
01:25
Also, the Available coordinate systems, Selected coordinate system code,
01:30
and Description should all be set to OSGB 1936 British National Grid.
01:37
Next, you need to set up the surface data that is used to define, among other attributes,
01:42
manhole cover levels and pond perimeter levels.
01:45
On the ribbon, Insert tab, Import panel, click LandXML.
01:52
Browse to and select the file Road1.xml from the dataset.
01:56
Click Open.
01:58
In the Import LandXML dialog, in the tree view,
02:02
expand the Surfaces node and the Surface description node,
02:06
and ensure that the SourceData node is deselected.
02:09
Click OK.
02:11
If any information boxes appear, close them.
02:15
The surface model appears in the drawing window.
02:19
In the Toolspace, click the Prospector tab.
02:22
Expand Surfaces, and then right-click Surface1 and select Surface Properties.
02:29
In the Surface Properties dialog for this surface,
02:32
you can edit the surface properties to change the name of the surface.
02:36
Rename it “Road1” to match the surface data.
02:40
Optionally, you can add a description or edit its default styles,
02:44
but for this exercise, leave them as-is and click OK.
02:48
The template, coordinate system, and surface file are now all configured.
02:53
Again, for your local projects, you would configure these settings to match your local standards.
When importing and exporting surface data between Civil 3D and InfoDrainage, it is very important to set up the coordinate system properly, to prevent problems with model objects and surfaces not lining up. The project units and the template also must be correct to ensure a smooth data exchange.
First, choose the template:
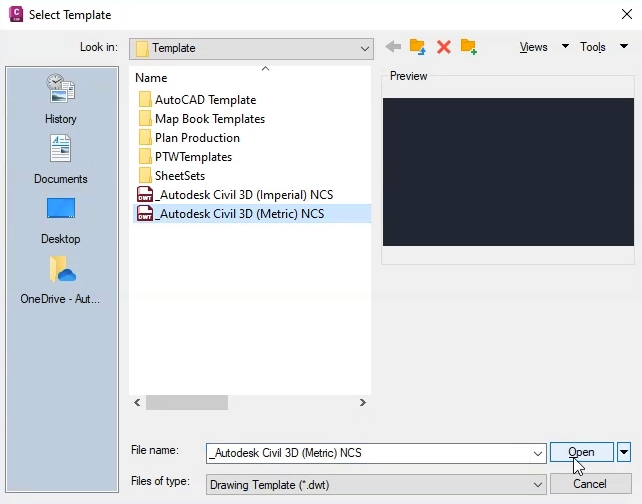
Next, set the categories and coordinate system according to your local standards. This example is located in the United Kingdom—specifically, Great Britian—so the settings used here are for the UK grid coordinate system:
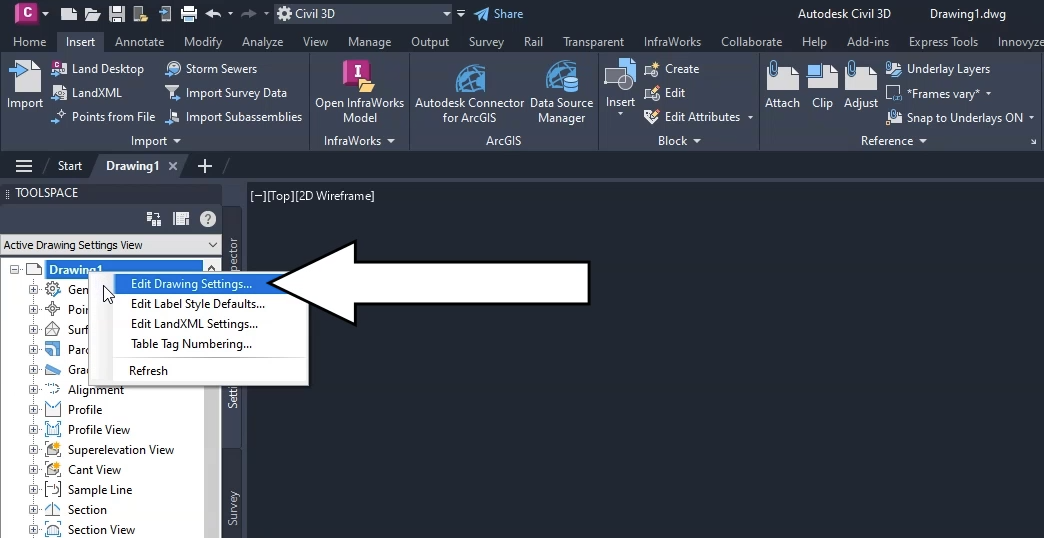
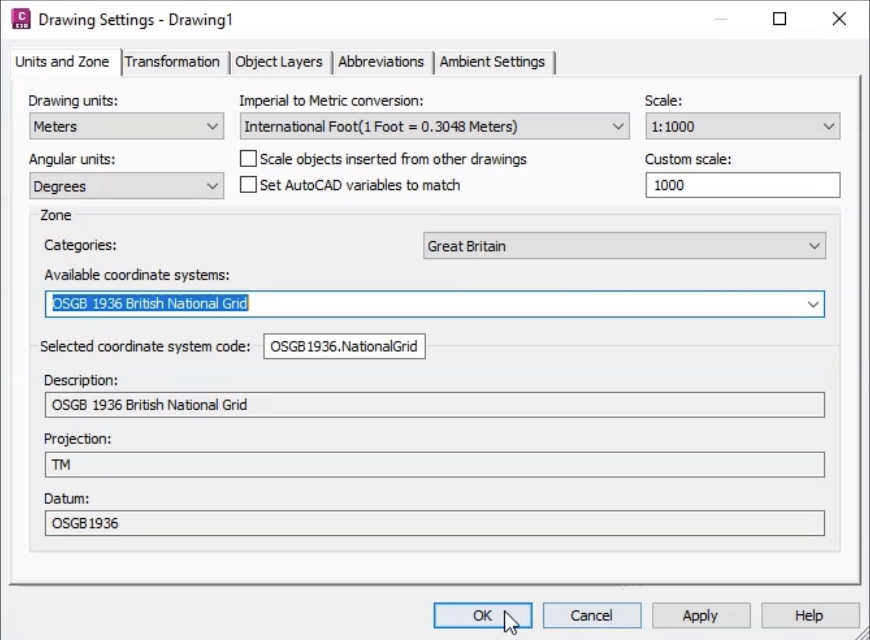
Next, set up the surface data used to define manhole cover levels and pond perimeter levels.
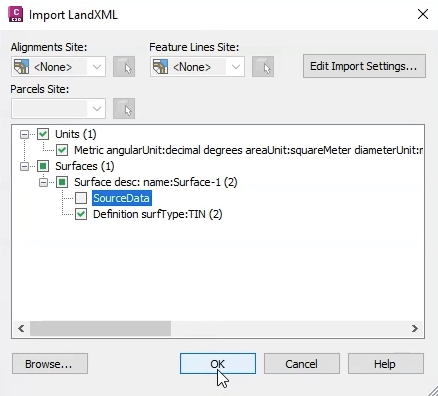
The surface model appears in the drawing window.
You could also add a description or edit the default styles, but for this exercise, leave them as-is.
The template, coordinate system, and surface file are now all configured.
IMPORTANT: For your local projects, you would configure these settings to match your local standards.
Industry:
Role:
How to buy
Privacy | Do not sell or share my personal information | Cookie preferences | Report noncompliance | Terms of use | Legal | © 2025 Autodesk Inc. All rights reserved
Sign in for the best experience
Save your progress
Get access to courses
Receive personalized recommendations
May we collect and use your data?
Learn more about the Third Party Services we use and our Privacy Statement.May we collect and use your data to tailor your experience?
Explore the benefits of a customized experience by managing your privacy settings for this site or visit our Privacy Statement to learn more about your options.