Step-by-step:
InfoWater Pro offers a variety of data exchange tools to address most challenges related to data formats. One of these tools is the GIS Gateway. It provides a powerful way to manage data exchange settings to allow you to quickly load and save data between InfoWater Pro and GIS data sources. The data exchange settings are set up once and can be re-used in the future.
- To create a GIS exchange cluster, first, start a new ArcGIS Pro Blank Template Map project.

- In the Create a New Project dialog box, name the new project; in this case, “Training_Model”.
- In the New Project Location dialog box, browse to and select the folder where you want to save the project, such as “Training” in this example, and click OK.
- From the ArcGIS Pro toolbar, Layer panel, click Add Data.
- In the Add Data dialog box, double-click the .gdb sample file.
- Select the Watermains feature class.
- Click OK.

- On the ribbon, InfoWater Pro tab, Project panel, click Initialize to establish the links between the ArcGIS Pro Document file and the InfoWater Pro database tables.
- In the Create New InfoWater Project dialog box, for the spatial reference, make sure that Same as active map is selected.
- Click OK.
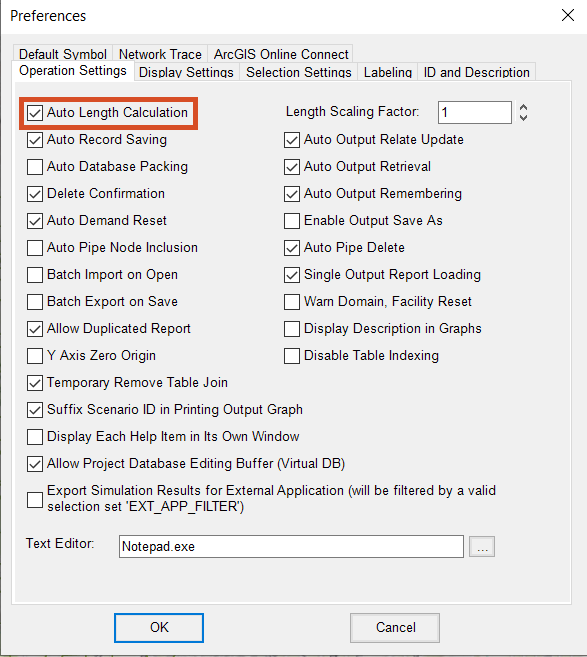
- In the InfoWater Pro ribbon, Project panel, click Preferences.
- In the Preferences dialog box, Operation Settings tab, select Auto Length Calculation.
You can now access the GIS Gateway, which stores information in exchange clusters. Exchange clusters are sets of data-exchange parameters that control how data is loaded from GIS data to InfoWater Pro. Each cluster is unique to a data source and element type. For example, if you want to import two shapefiles for pipes and one shapefile for tanks, you need to create three exchange clusters.
- On the ribbon, InfoWater Pro tab, in the Exchange panel, click GIS Gateway.
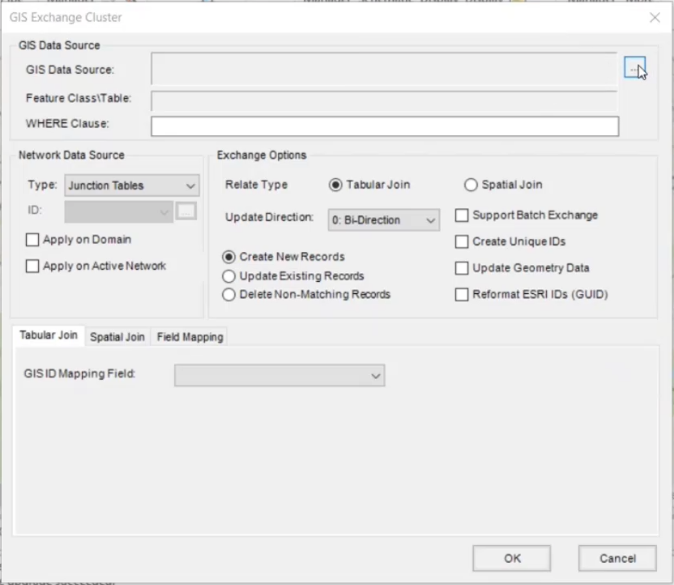
- In the GIS Gateway dialog box, under GIS Exchange Cluster, click Add to create a new cluster for a single data source that you want to bring into InfoWater Pro.
- In the Identification popup, add the cluster ID, using the naming convention of ID, with no spaces, a comma, and then your description, which can have spaces. For example, “PIPES, New Pipe Import”.
- Click OK.
- In the GIS Exchange Cluster dialog box, next to GIS Data Source, click More (…) to open the file browser.
- In the Open dialog box, locate the .gdb sample file.
- Select the Watermains feature class.
- Click OK.
In the GIS Data Source group, the Feature Class\Table field is automatically filled in with the specific feature class or table within the selected database.
- Expand the Type drop-down and select the InfoWater Pro database tables to be used by the GIS Exchange Cluster, such as Pipe Tables.
- Click the Tabular Join tab.
- Use the GIS ID Mapping Field to denote which field in the GIS layer is to be matched with the respective ID field in the selected InfoWater Pro data table. For this example, select FAC_ID.
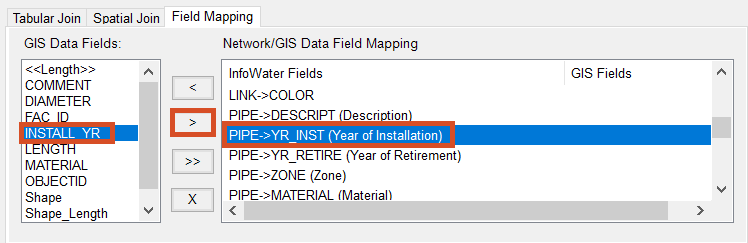
- Click the Field Mapping tab.
In the Field Mapping tab, you map corresponding fields to each other prior to performing the GIS Exchange. This ensures that the GIS data you are importing is associated to the proper InfoWater Pro field in the table.
- Under GIS Data Fields, select INSTALL_YR.
- Under Network/GIS Data Field Mapping, select PIPE->YR_INST.
- Click the arrow (>) icon.
- Repeat steps 25 – 27 to map COMMENT to PIPE->DESCRIPT.
- Click the double arrow (>>) icon to auto-map the remaining GIS fields.
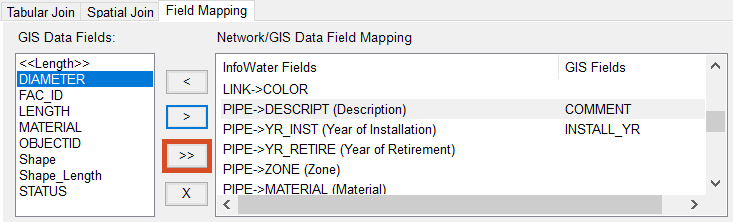
All fields in the GIS with the same name and data type are automatically mapped.
Use the WHERE Clause field to create a script to query the specific items to import. If you leave this field blank, then everything in the data source is imported.
- Enter a WHERE Clause of STATUS = 1. This clause restricts the import to only pipes that are existing in the system, as identified using the field STATUS.
- Click OK.
- Back in the GIS Gateway, click Load.
- In the Load Data from GIS Layer or Table dialog box, select the exchange cluster to load (in this case, PIPES, New Pipe Import).
- Click Load.
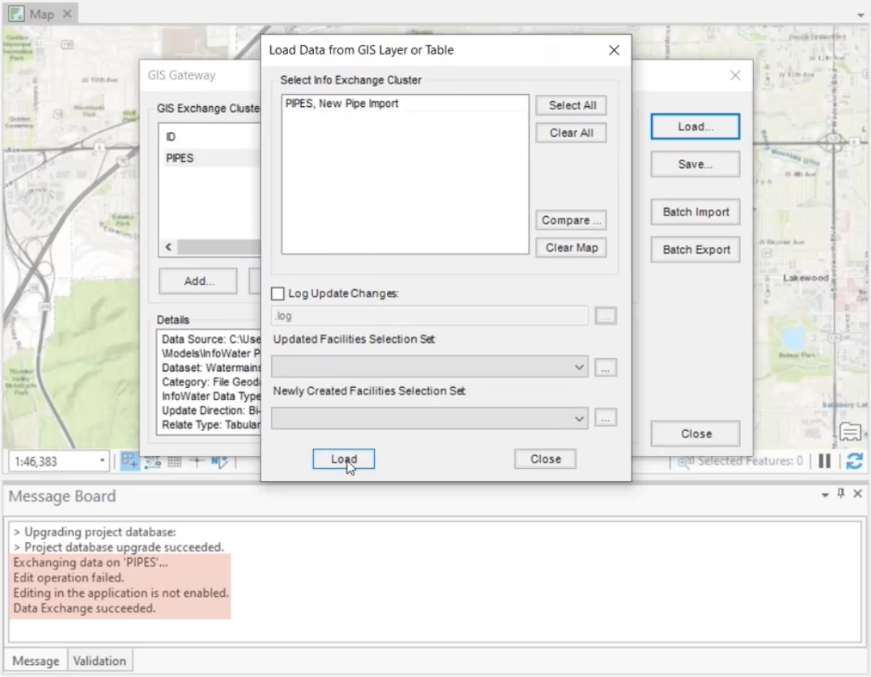
The GIS data sources are loaded, based on the selections, settings, and filters that you entered.
- Close the GIS Gateway.
- On the InfoWater Pro ribbon, Edit panel, use the Select tool to select some of the pipes you just added to the model.
Follow these same steps to use the GIS Gateway to import other GIS data sources from the same geodatabase file, such as valves and tanks.









